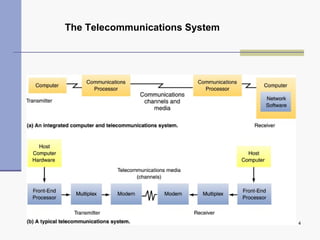
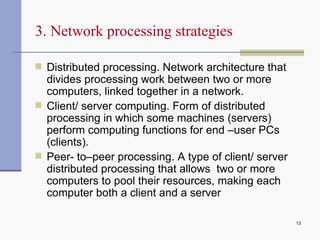
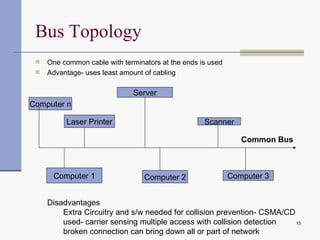
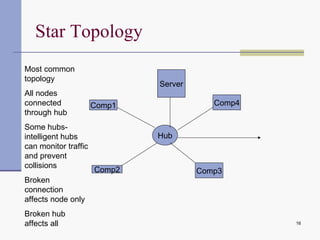
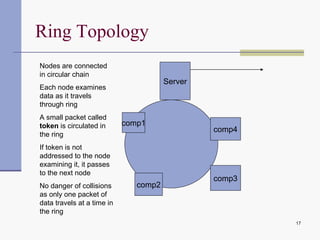
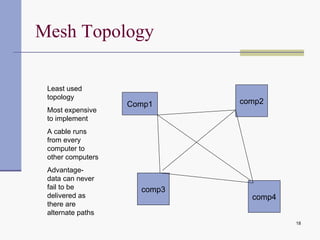
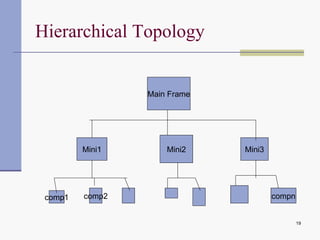
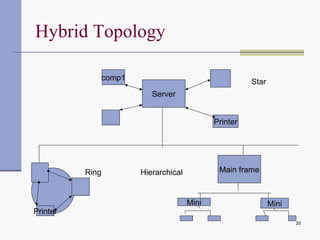
Computer networks allow computers to communicate and share resources. They can be used for simultaneous access to shared data and devices, personal communications like email and messaging, video and audio conferencing, and easier backups. Networks connect computers through hardware, software, and communication media. They transmit information electronically between locations using technologies like cables, wireless transmission, and networking protocols. Common network topologies include bus, star, ring, and mesh configurations.