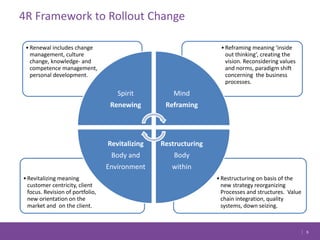
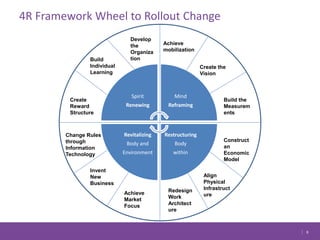
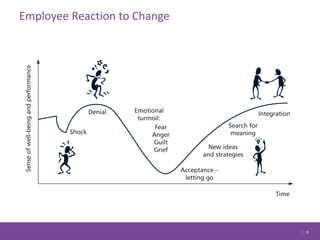
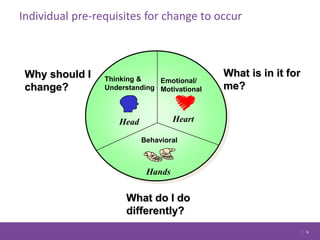
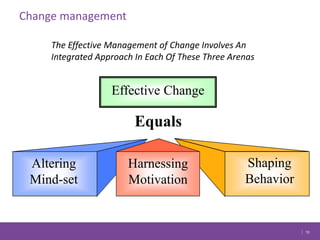
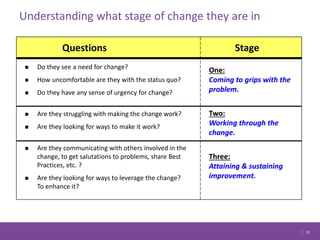
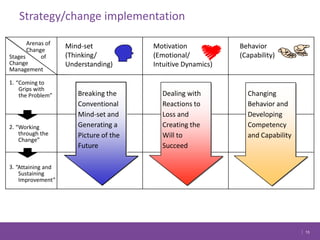
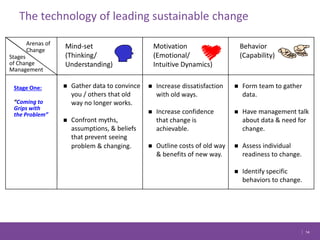
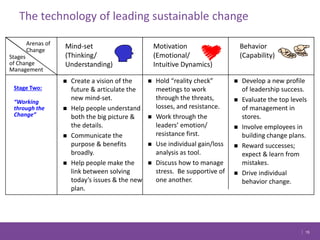
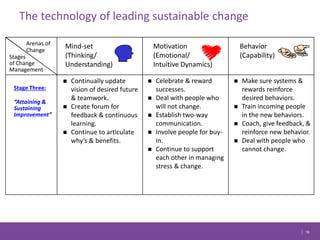
The document discusses managing change in organizations. It defines change management as the process of managing people through change to achieve business goals. It explains that change is important for organizations to keep pace with technology, customer demands, and business processes. The document outlines a 4R framework for rolling out change, including restructuring, revitalizing, reframing, and renewal. It also discusses the three stages of change management: coming to grips with the problem, working through the change, and attaining and sustaining improvement.