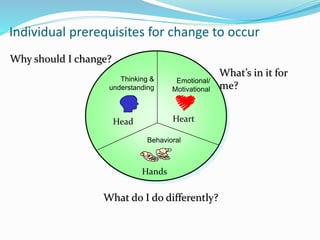
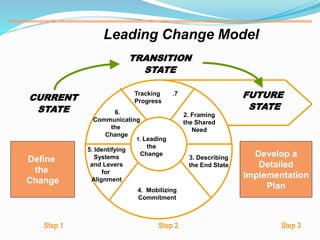
This document discusses change management and leadership. It defines change management as a structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from their current state to a desired future state. It also discusses various change models, including Kotter's 8-step change model, and identifies common obstacles to and factors affecting change, such as resistance, communication, and organizational culture. The key difference identified between change management and leadership is that the former focuses on controlling change through incremental steps while the latter takes a more collaborative approach through inspiring vision.