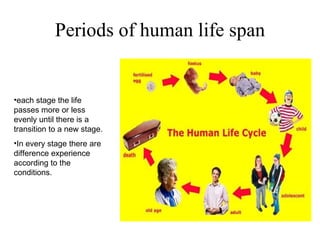
The document discusses human nature and human behavior across different stages of life. It defines human nature as the set of characteristics common to all humans, including ways of thinking, feeling and acting. It then outlines several reasons for studying human nature, such as to understand why people behave differently and how to motivate people. The document also discusses the primary and secondary dimensions that shape individual differences, and how understanding human nature can help organizations adapt to individuals. Finally, it outlines the different stages of human life from infancy to later adulthood.