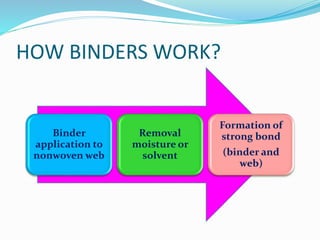
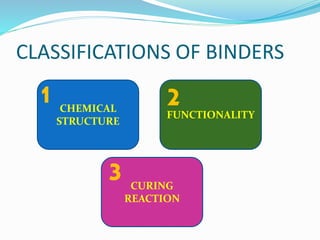
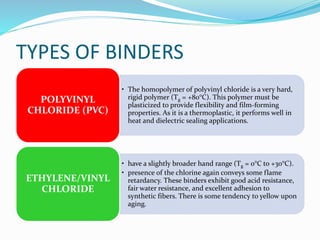
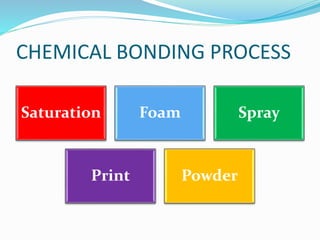
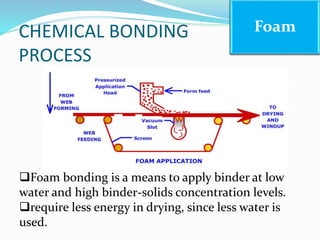
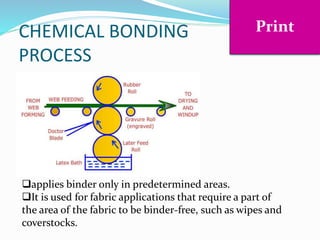
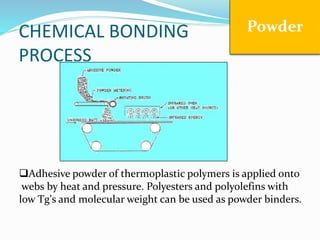
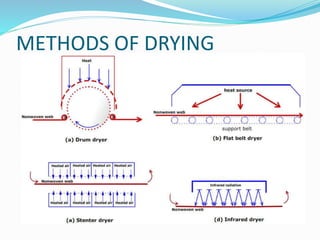
Chemical bonding involves applying a liquid binder to a nonwoven web to improve its characteristics such as strength and durability. Binders work by being applied to the web and then forming strong bonds between the binder and fibers as the moisture or solvent is removed. There are various types of binders classified based on their chemical structure and functionality, including acrylics, styrenated acrylics, and vinyl acetates. Common chemical bonding processes involve saturating, foaming, spraying, printing, or applying binder powders to nonwoven webs. The bonded webs find applications in products like wipes, medical fabrics, and apparel.