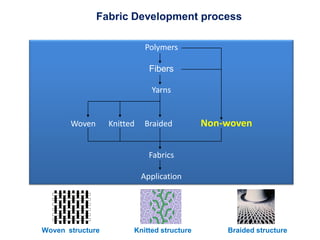
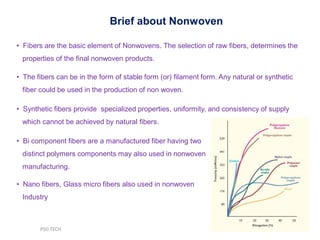
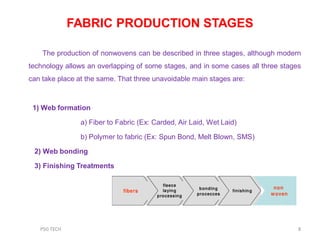
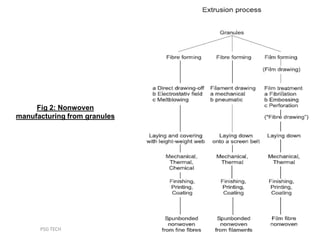
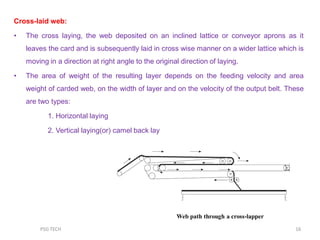
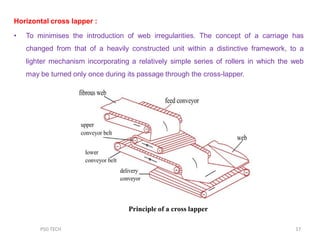
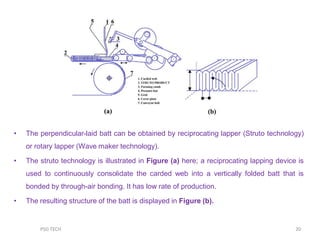
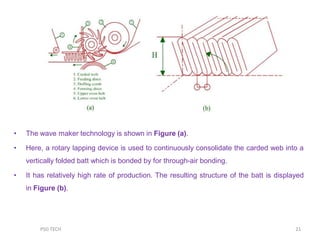
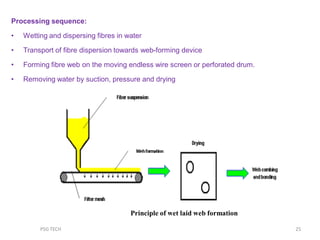
This document discusses nonwoven web formation. It describes how fibers are opened, individualized, and formed into a continuous web. The key stages of nonwoven production are web formation, bonding the web, and finishing treatments. Common web formation methods include carding, air laying, and wet laying. Carding individualizes fibers and forms them into a parallel web. Cross-lapping and vertical lapping are used to build thickness. Web formation determines the properties of the final nonwoven fabric.