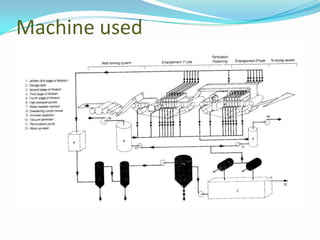
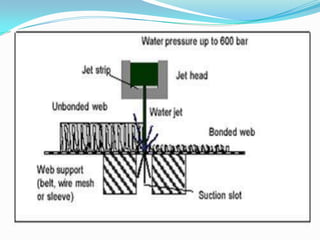
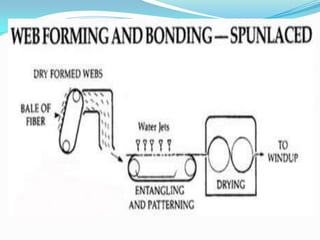
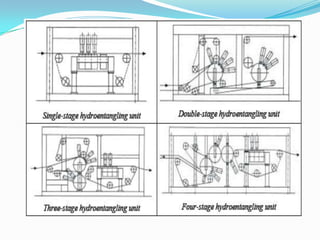
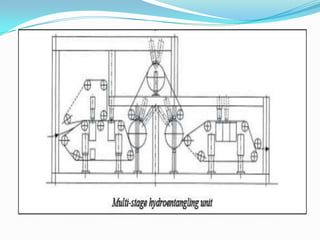
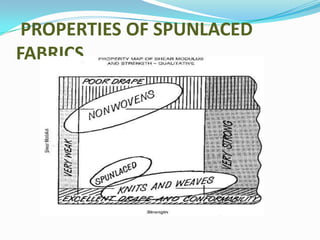
Spunlacing, also known as hydroentanglement, is a process for bonding nonwoven fabrics using high-pressure water jets. Precursor webs made of fibers like cellulose are passed through multiple rows of water jets that entangle the fibers. This produces a bonded nonwoven fabric with properties like softness and absorbency. Key aspects of the process include forming the precursor web, passing it through water entanglement units with fine jet nozzles, and drying the saturated fabric. The process produces fabrics widely used in applications such as wipes, towels, and medical and protective clothing due to its strength and lack of binders.