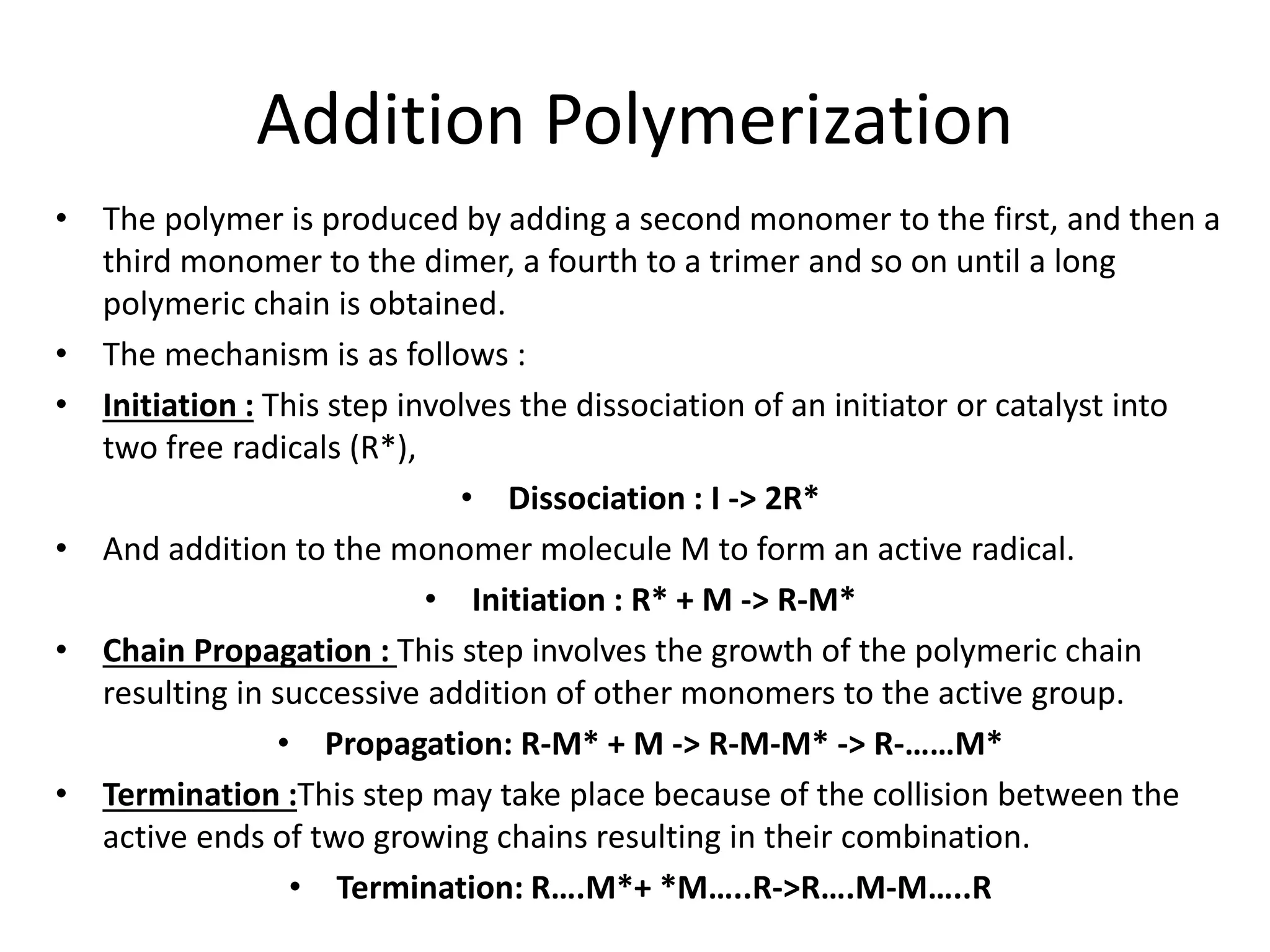
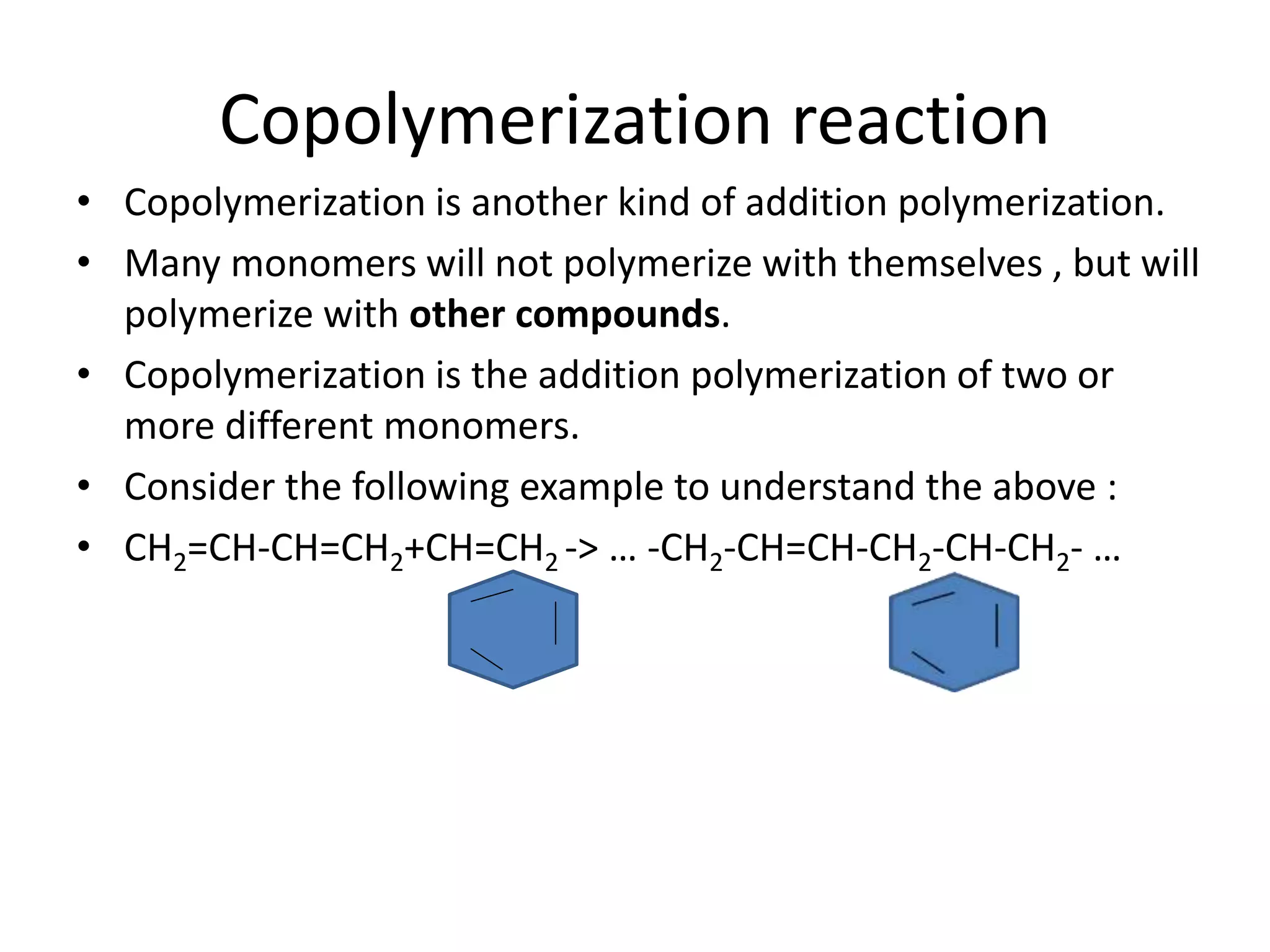
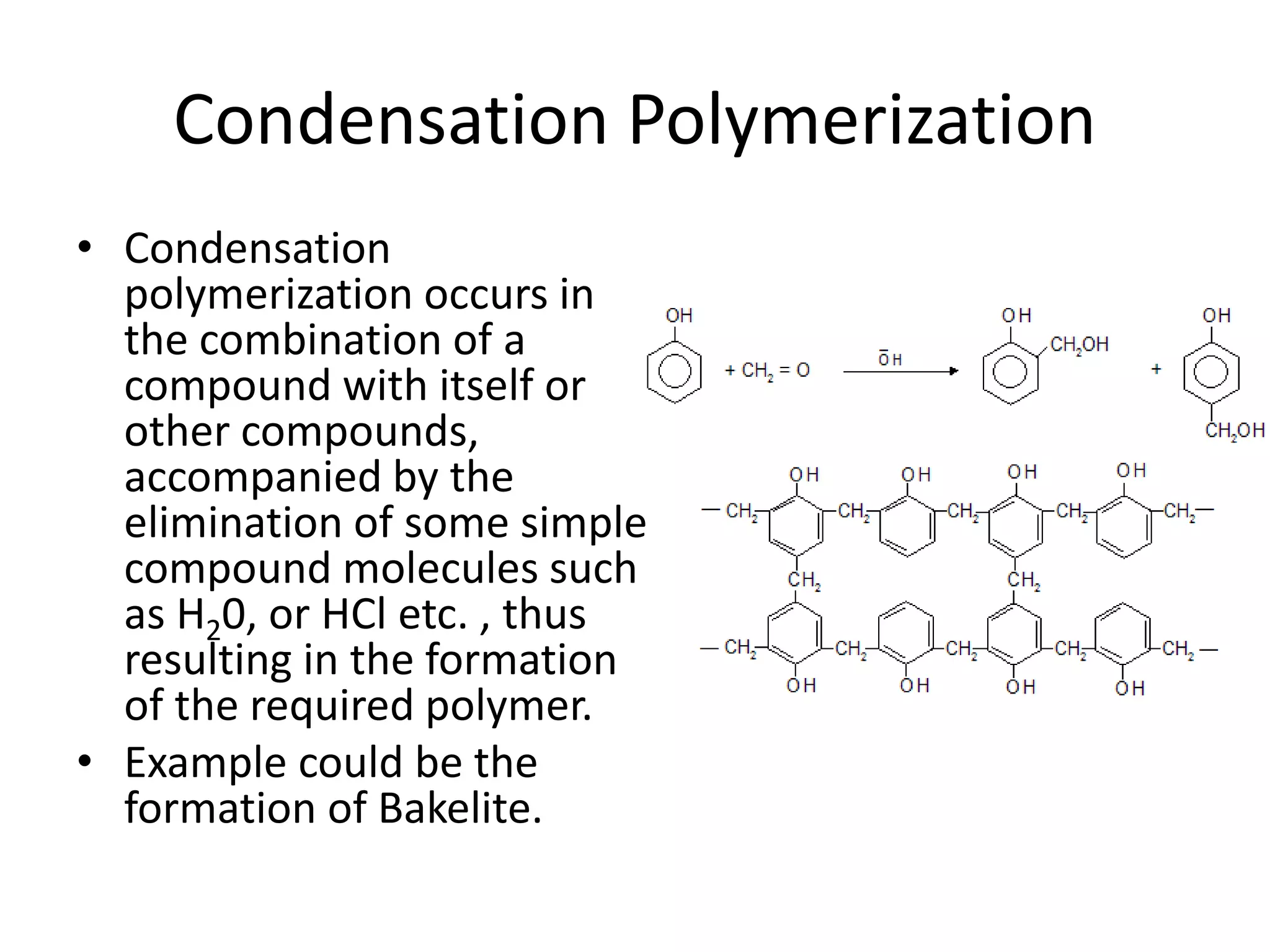
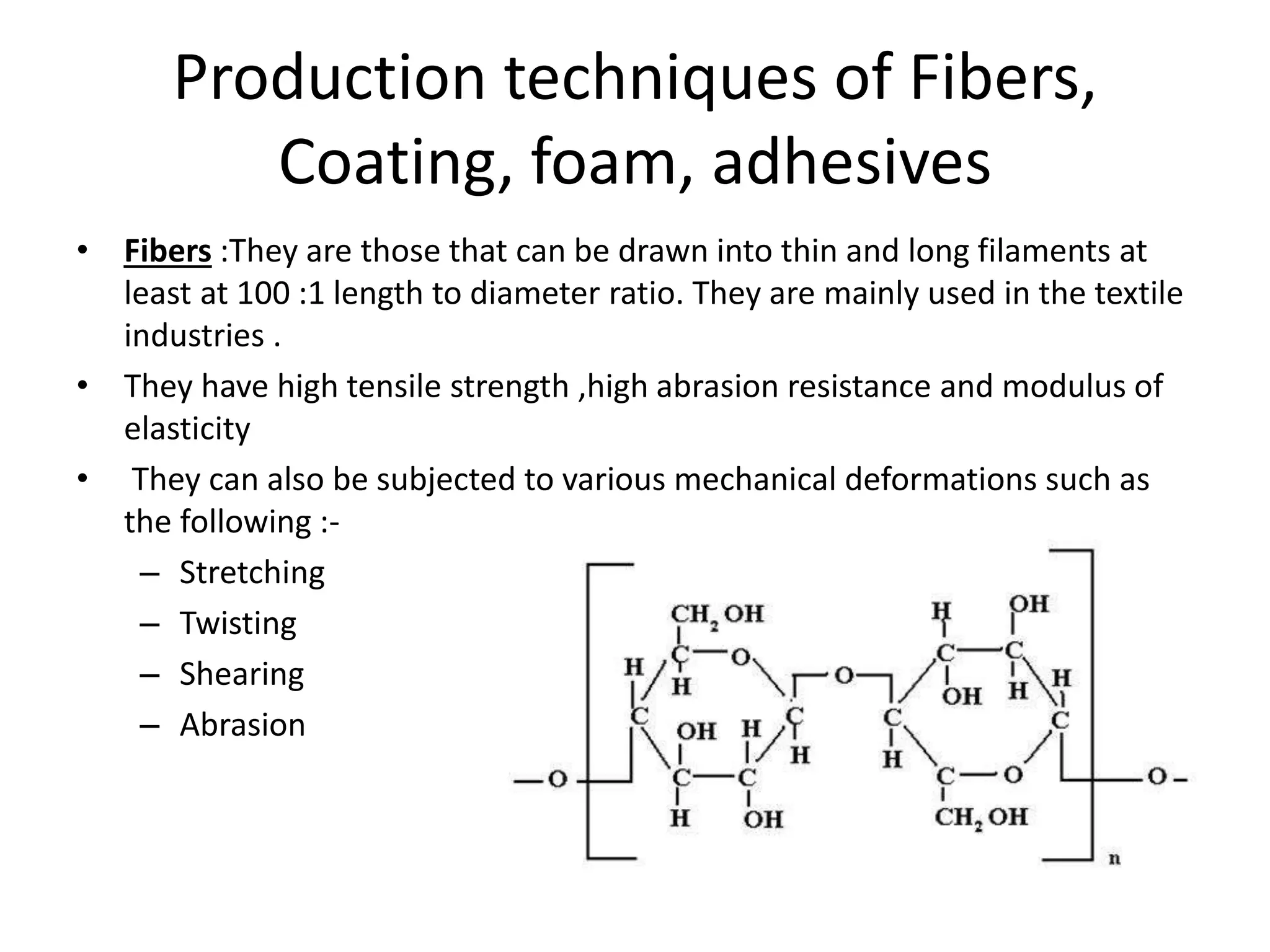
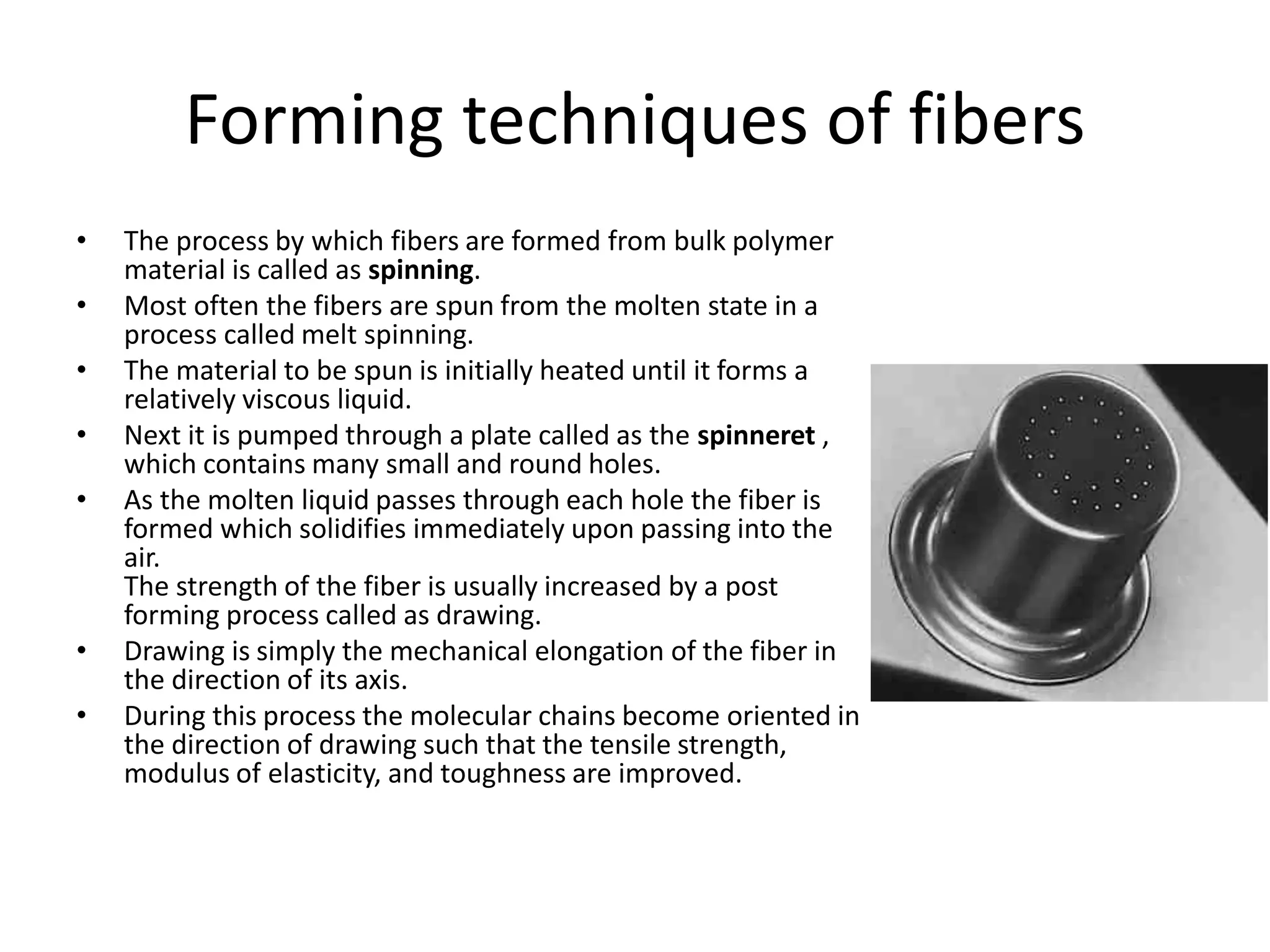
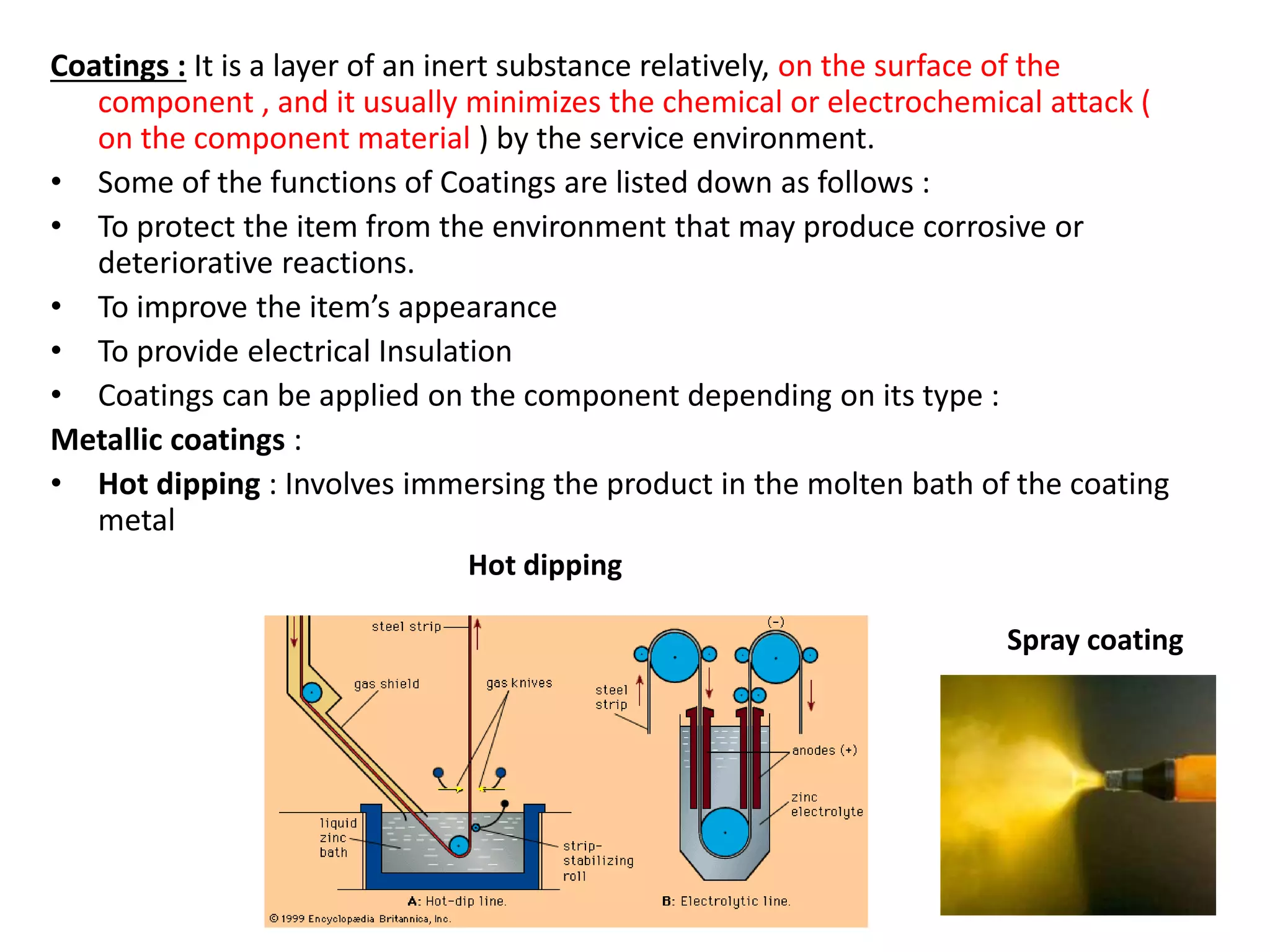
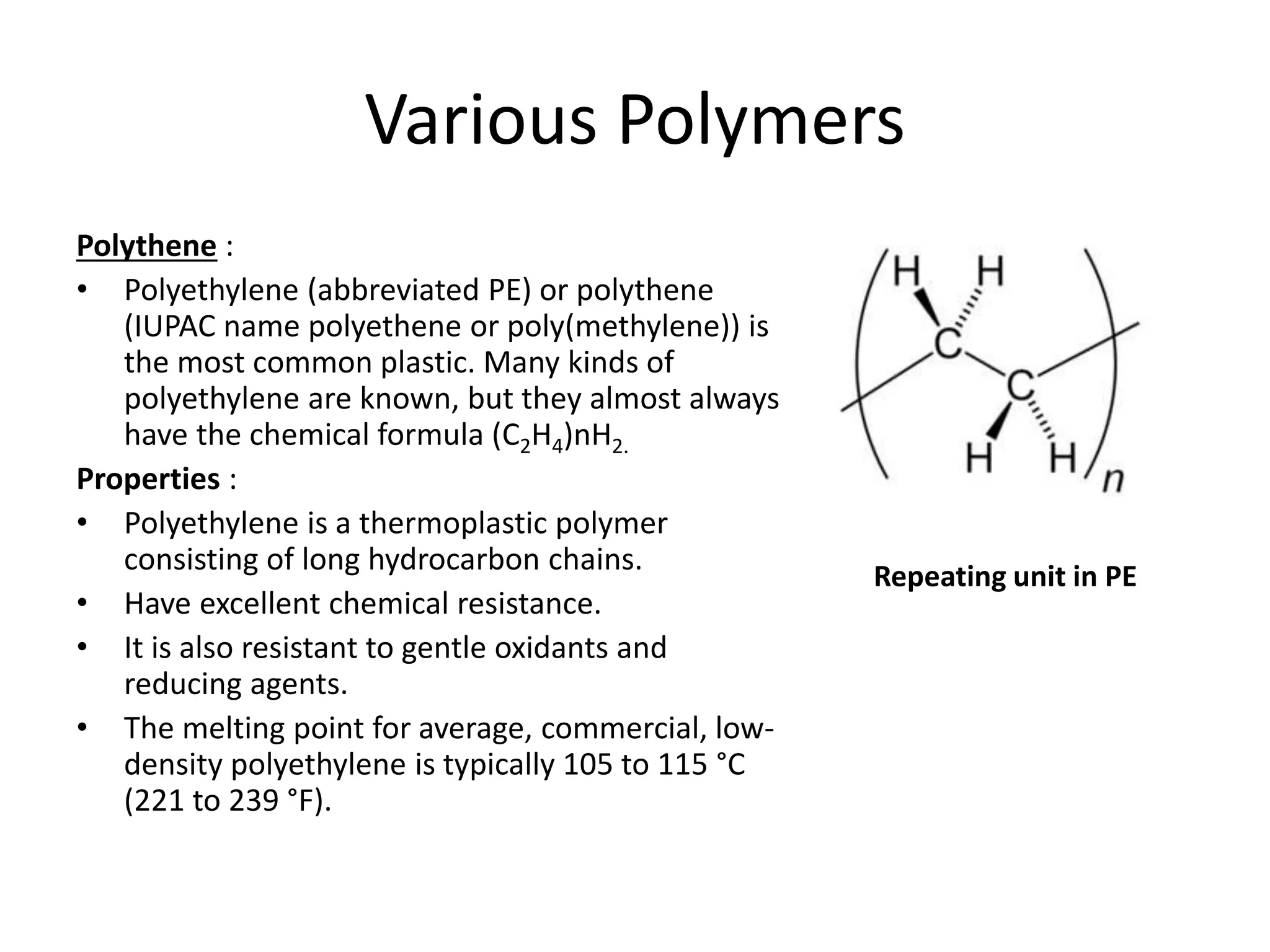
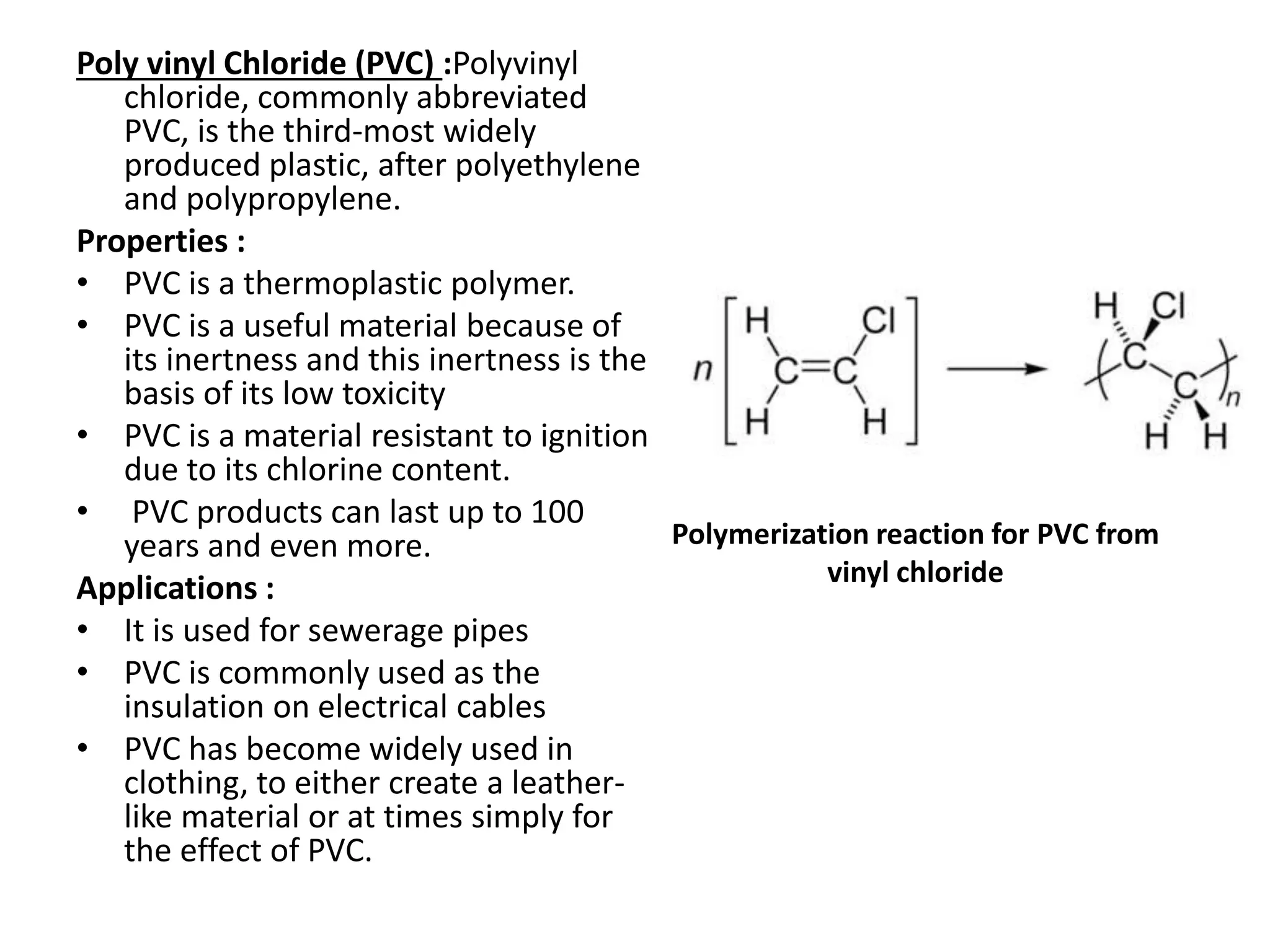
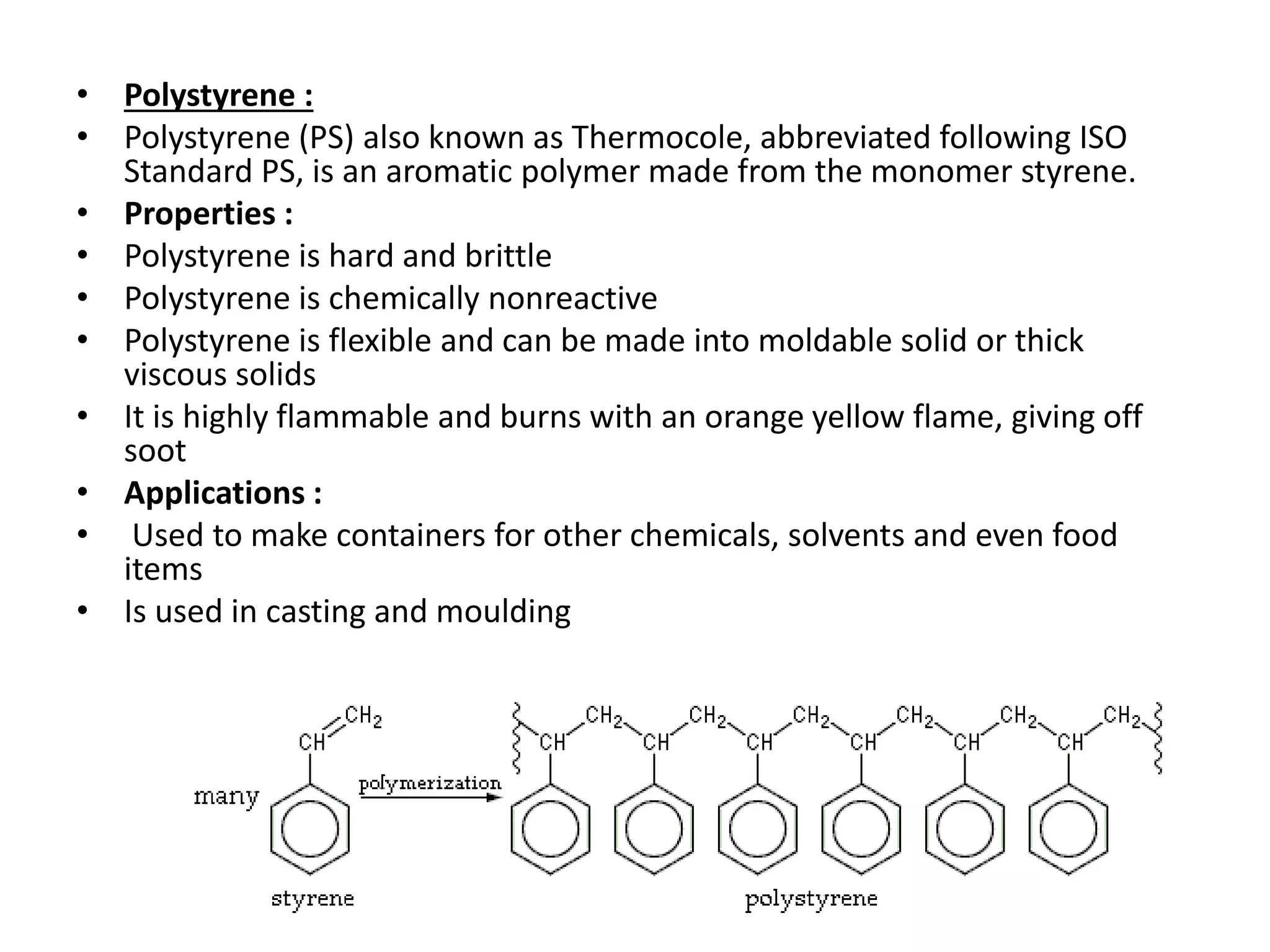
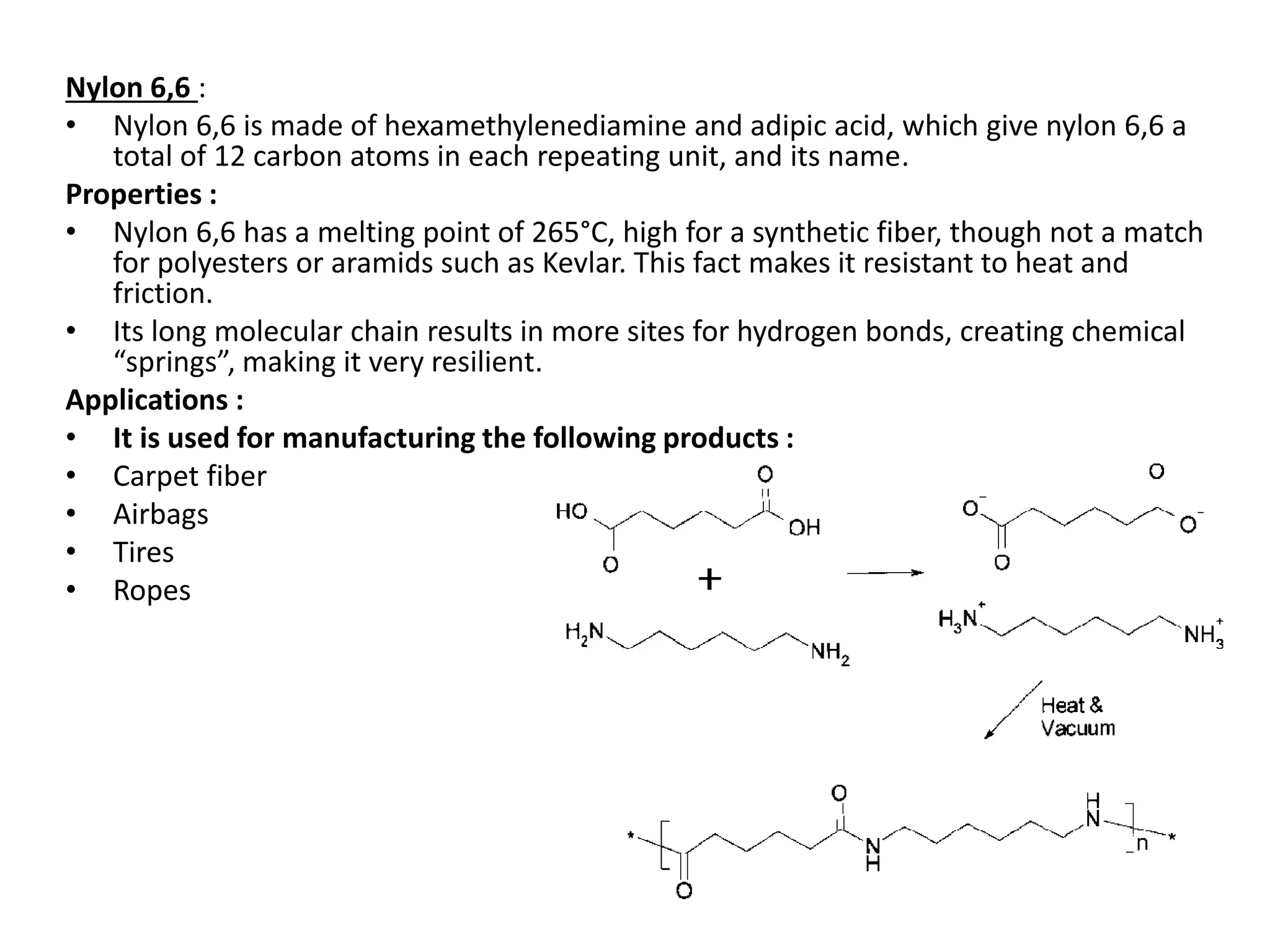
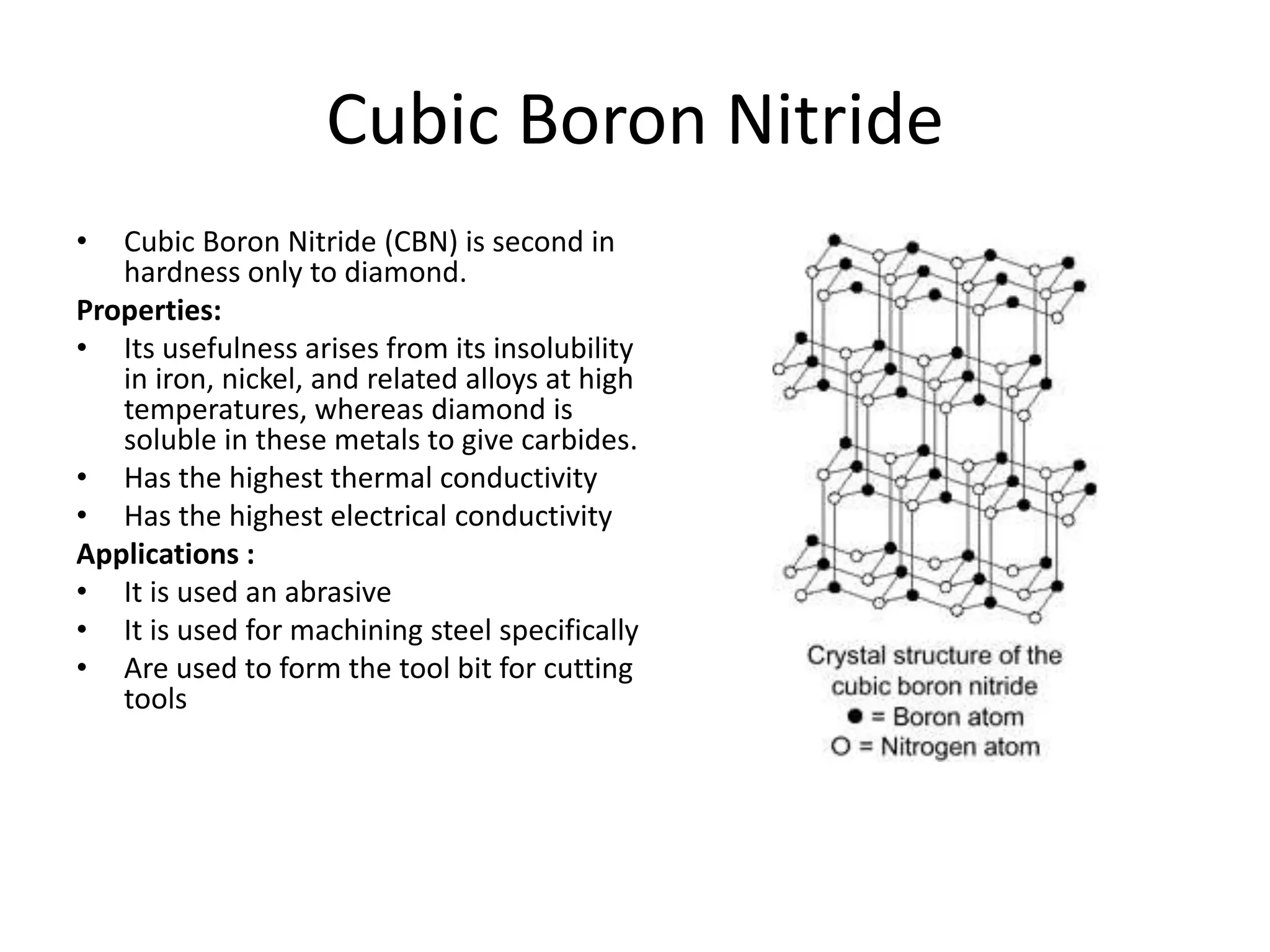
Polymeric materials are formed by joining many small monomer units together through chemical reactions. They have properties like low density, good corrosion resistance, and mouldability. There are three main types of polymerization reactions: addition, copolymerization, and condensation. Polymeric materials can be formed into fibers, coatings, foams, and used as adhesives through various production techniques. Common polymers include polyethene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, nylon 6,6, and teflon.