Polysiloxanes, also known as silicones, are synthesized via ring-opening polymerization of cyclosiloxanes. They can be prepared through cationic polymerization using initiators like Lewis acids, or anionic polymerization using bases. Cationic polymerization may proceed by acidolysis/condensation or generation of an active propagating center. Anionic polymerization yields higher molecular weight polymers through chain propagation and termination with end-capping. Copolymers and crosslinked polysiloxanes can also be synthesized. Hybrid polymers combining polysiloxane segments with other backbones can be prepared through step-growth condensation polymerization.





![This relatively complicated reaction has been replaced by the so-called
“Direct Process” or “Rochow Process, which starts from elemental silicon. It
is illustrated by the reaction
(4)
But the process also yields RSiCl3 and R3SiCl, which can be removed by
distillation. Compounds of formula R2SiCl2 are extremely important,
because they provide access to the preparation of a wide variety of
substances having both organic and inorganic character.Their hydrolysis
gives dihydroxy structures which condense to give the basic [-SiR2O-] repeat
unit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-6-320.jpg)
![ The polysiloxanes were also prepared by condensation reactions. In
fact, Friedel and Crafts reported the condensation of Si(C2H5)2(OR)2,
where R=alkyl, with water producing [(C2H5)2SiO]n and the alcohol in
1866:
At present, polysiloxane polymers are usually prepared by ring-opening
polymerizations of small cyclic oligomers that have been prepared by
hydrolysis (a condensation reaction) of the appropriate
dihalodialkylsilane. But even today some special siloxanes use
condensation reactions for the polymerization step.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-7-320.jpg)

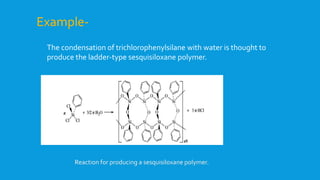
![The Cyclotrisiloxane [{Si(CH=CH2)2{SiMe2}O3] Can Be Prepared
ByThe Condensation Of Divinyldichlorosilane With
Tetramethyldisiloxane-1,3-diol .
Example-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-10-320.jpg)
![The compound [{SiPh2}{SiMe2}2O3] can be prepared by
the condensation of Me2SiCl2 with tetraphenyldisiloxane-
1,3-diol .
Example-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-11-320.jpg)

![Cyclosiloxanes, [R2SiO]n, (n = 3,4) can be polymerized by ROP
methods to the corresponding linear polymer [R2SiO]n (R = alkyl,
aryl).Two different types of initiators are used for this reaction-
(1) Cationic initiators
(2) Anionic initiators.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-13-320.jpg)

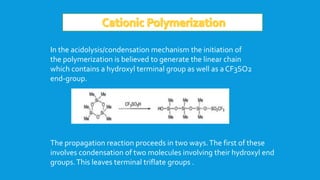
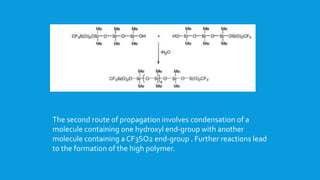
![This type of polymerization reaction can also be used to generate short
chain linear siloxanes.Thus, carrying out the acid-catalyzed ROP of
[Me2SiO]4 in the presence of the disiloxane Me3Si-O-SiMe3 allows the
formation of (predominantly) Me3SiO(SiMe2O)4Me3Si.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-17-320.jpg)
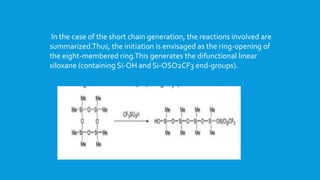

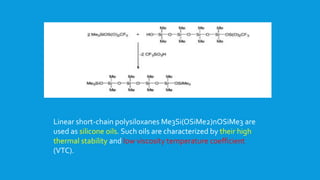
![The second mechanism of cationic polymerization involves the
generation of an active propagation center.This could be an oxonium
ion (oxygen centered cation) or a siliconium ion (silicon-centered
cation).This type of ion has been detected in small molecule
experiments.Thus, the reaction of Me3SiH and Me3Si0SiMe3 with
[Ph3C]+[B(C6F5)4]~ leads to the formation of [(Me3Si)3O]+ which has
been detected by NMR spectroscopic methods.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-21-320.jpg)
![Another example of an oxonium ion generation involves the reaction
of Me3SiH with [Me2Si0]3 with [Ph3C]+[B(C6F5)4]~ to generate the
cyclotrisiloxane-centered oxonium ion.
Generation of a cyclotrisiloxane-based oxonium ion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-22-320.jpg)

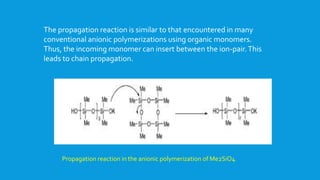
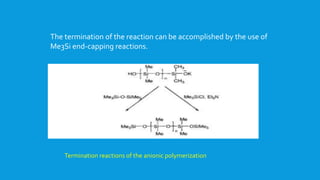
![The anionic polymerization is initiated by the reaction of the base
with a cyclosiloxane such as [Me2Si0]4 to generate the open-chain
compound with a Si-O"K+end-group .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-24-320.jpg)
![Copolymers of the type [(SiR2O)n(SiR'2O)m] can be prepared by the
polymerization of mixtures of cyclosiloxanes.Thus, for example, heating a
mixture of [Me2SiO]4 and [Ph2SiO]4 in the presence of KOH as the catalyst
affords the random copolymer [{Me2SiO}n{Ph2SiO}m]
Copolymerization of a mixture of [Me2SiO]4 and [Ph2SiO]4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-27-320.jpg)

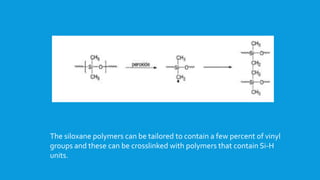

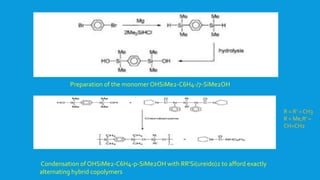
![Another example for the synthesis of hybrid polymers…
Block copolymers containing polysiloxane segments and
polyphosphazene segments have been synthesized by the reaction of
hydride-terminated polysiloxane H-[Si(Me2)-O]n-SiMe2H with the
telechelic polyphosphazene containing an amino end-group.
Poly(phosphazene-siloxane) block copolymers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-32-320.jpg)
![[Ronald_D._Archer]_Inorganic_and_Organo
metallic
Mark J., Allcock H.,West R. Inorganic
Polymers
[Vadapalli_Chandrasekhar]_Inorganic_and_
organometallic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polysiloxanes1-150426224351-conversion-gate01/85/Polysiloxanes-1-33-320.jpg)
