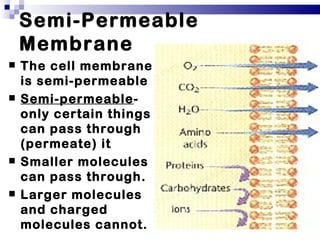
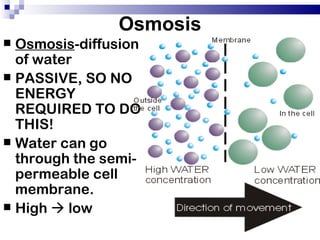
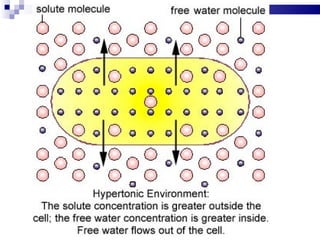
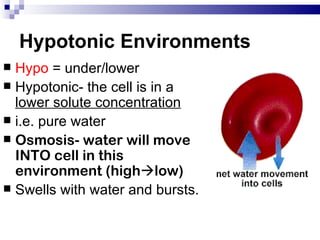
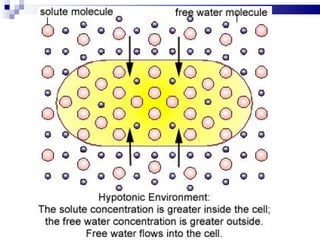
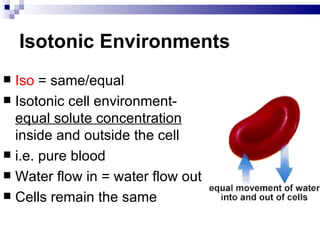
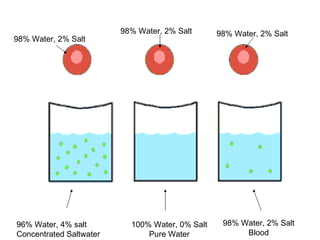
The cell membrane is semi-permeable, allowing smaller molecules to pass through via passive transport like diffusion and osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentration without energy, while osmosis is the diffusion of water through the semi-permeable membrane. In a hypotonic environment with a lower solute concentration outside the cell, osmosis causes water to enter the cell, potentially bursting it. In a hypertonic environment with a higher external solute concentration, osmosis causes water to exit the cell, potentially causing it to shrivel. An isotonic environment has equal internal and external solute concentrations, allowing the cell to remain stable.