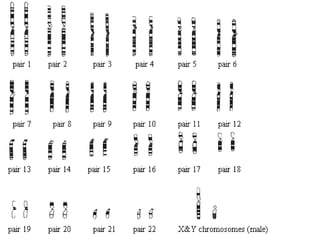
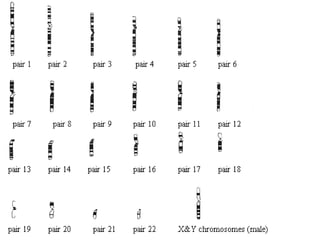
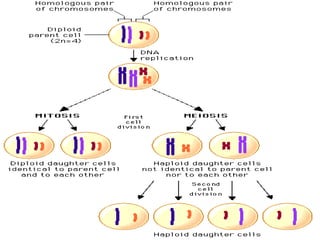
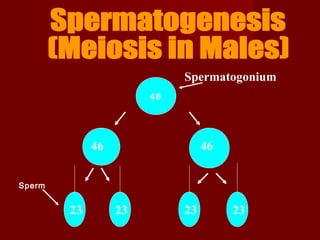
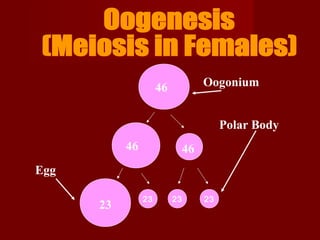
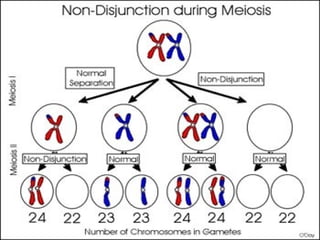
Human cells contain either 46 chromosomes (somatic cells) or 23 chromosomes (gamete cells). Somatic cells are formed through mitosis and contain homologous chromosome pairs, while gamete cells are formed through meiosis which reduces the number of chromosomes by half. Meiosis involves the production of haploid gametes through nuclear division from a parent cell containing 46 chromosomes.