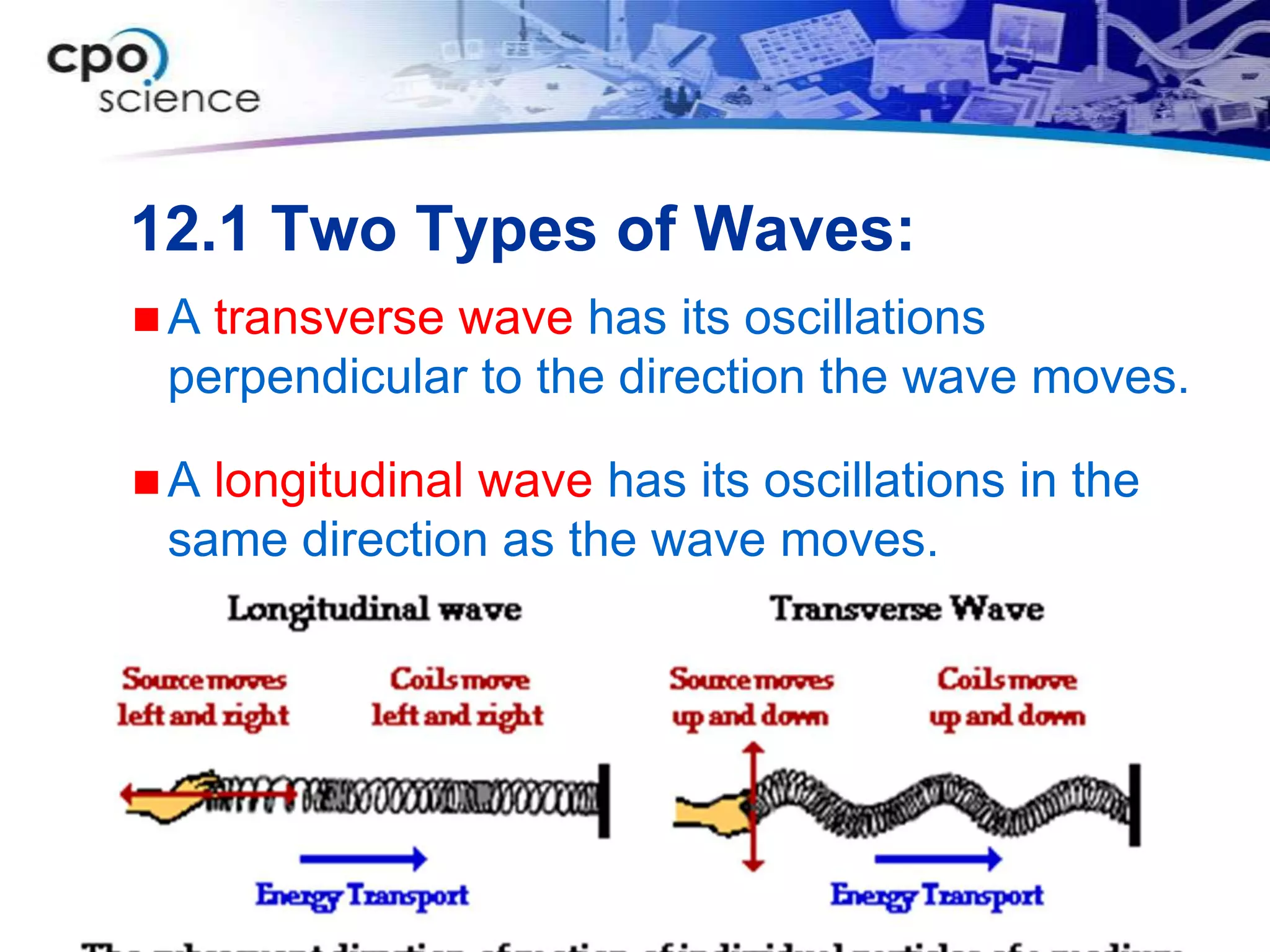
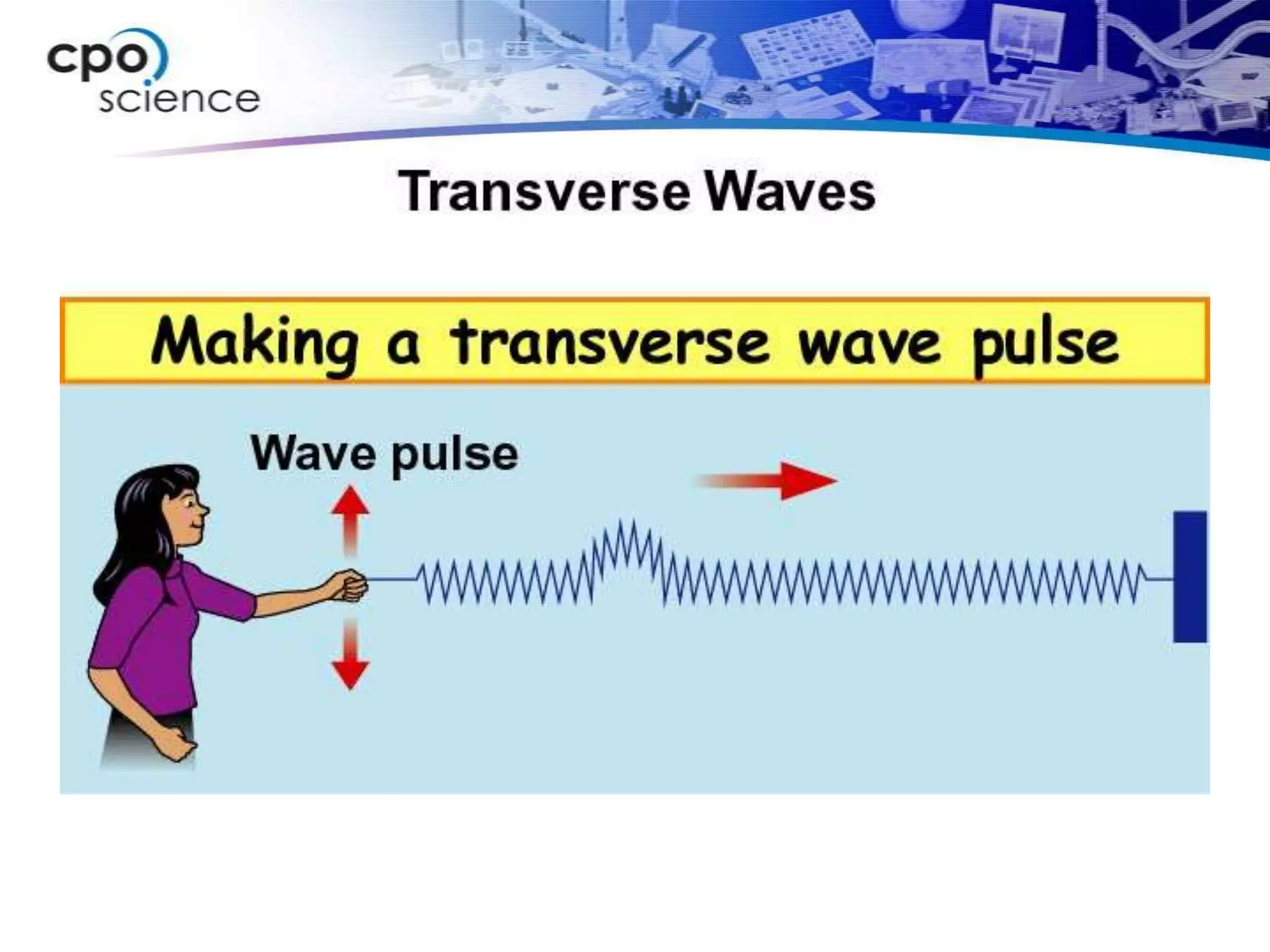
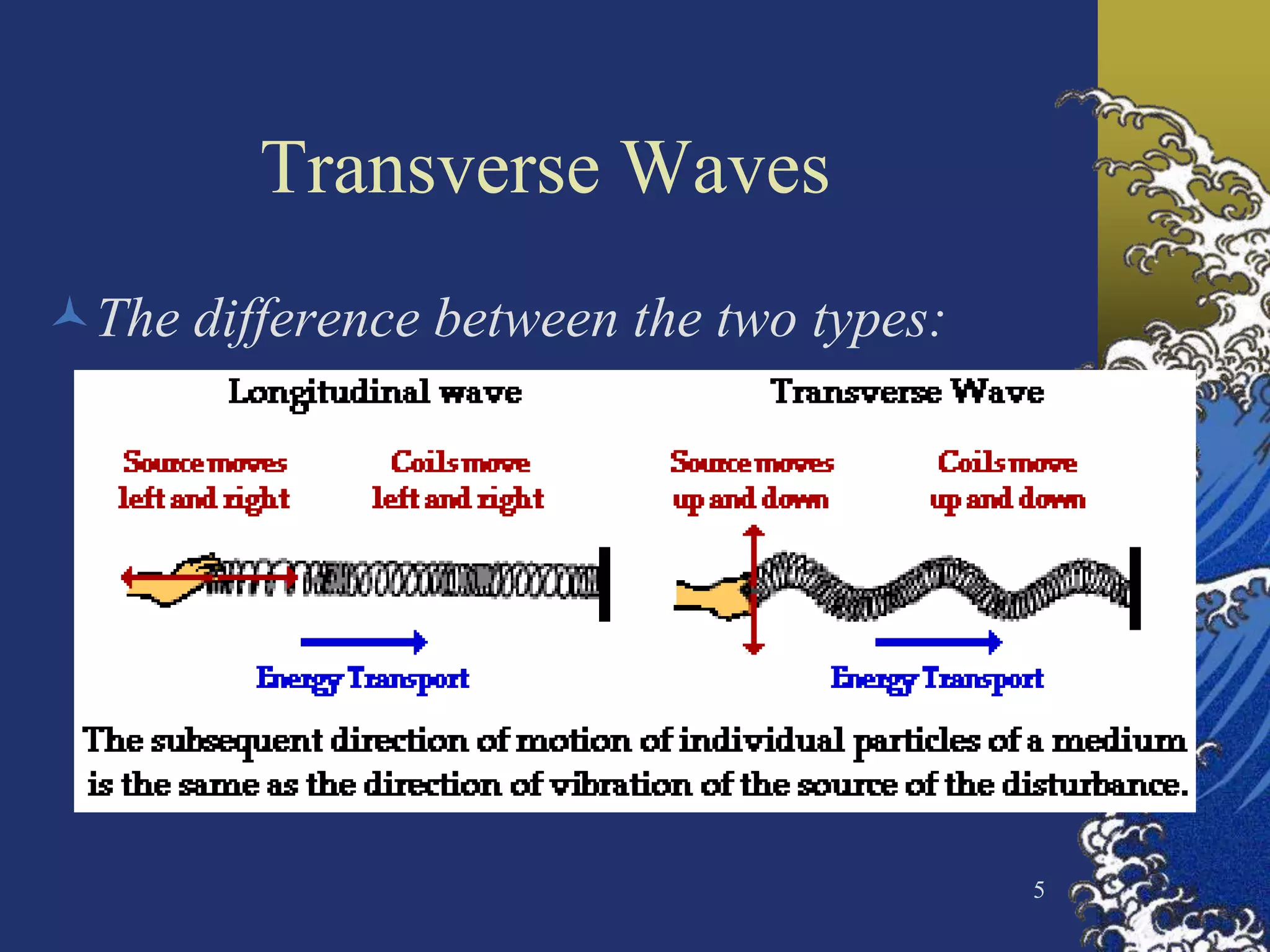
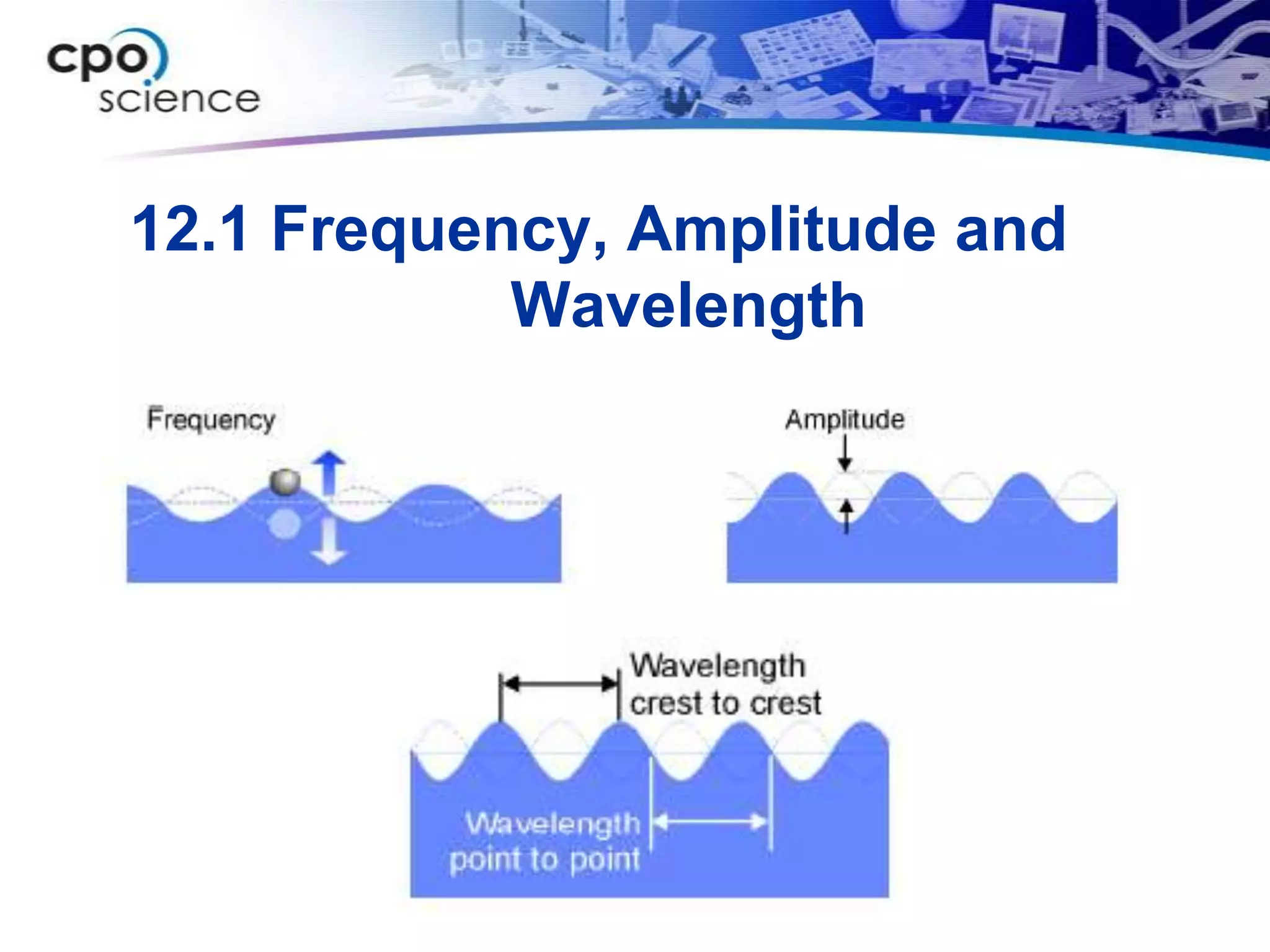
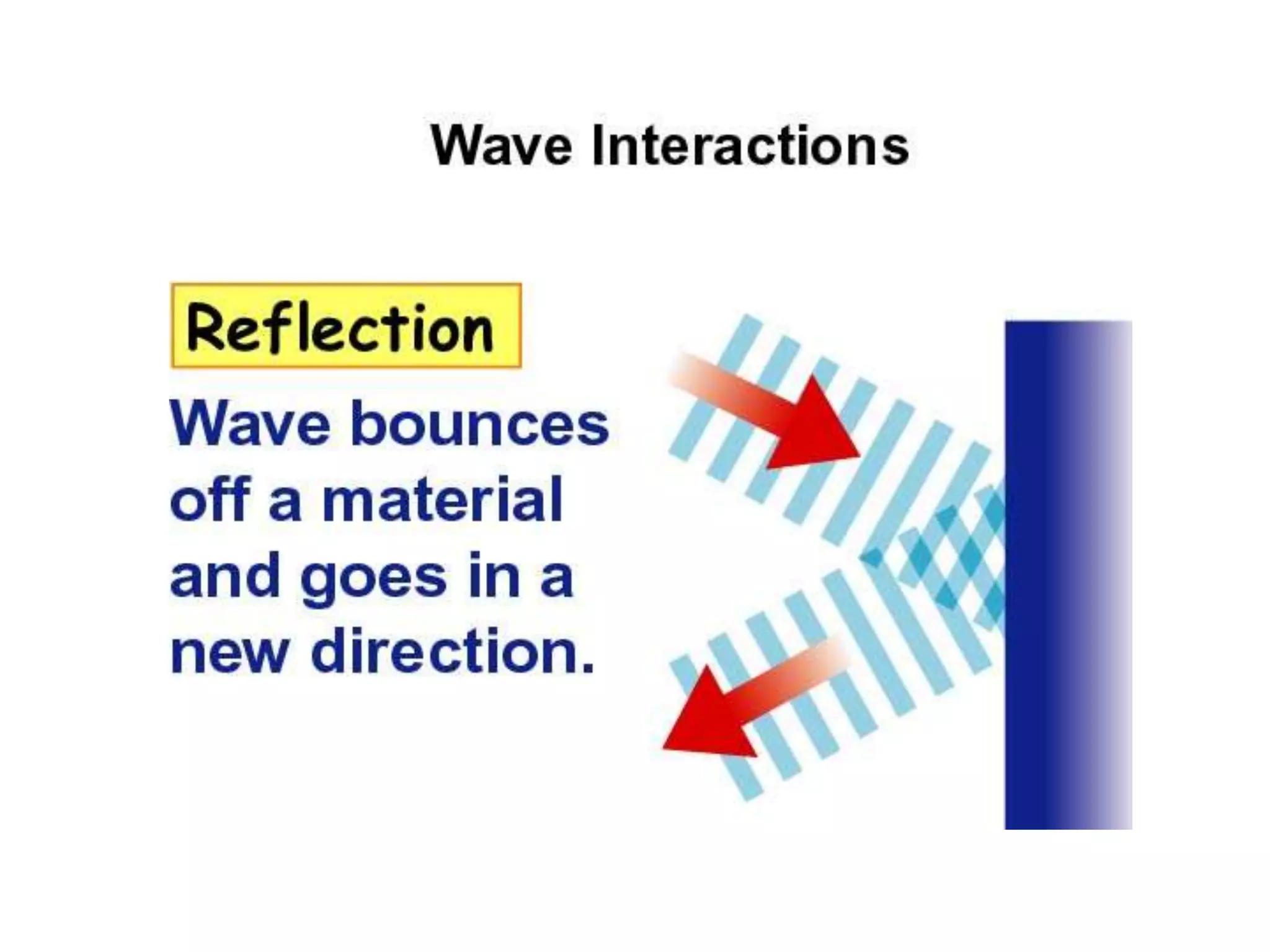
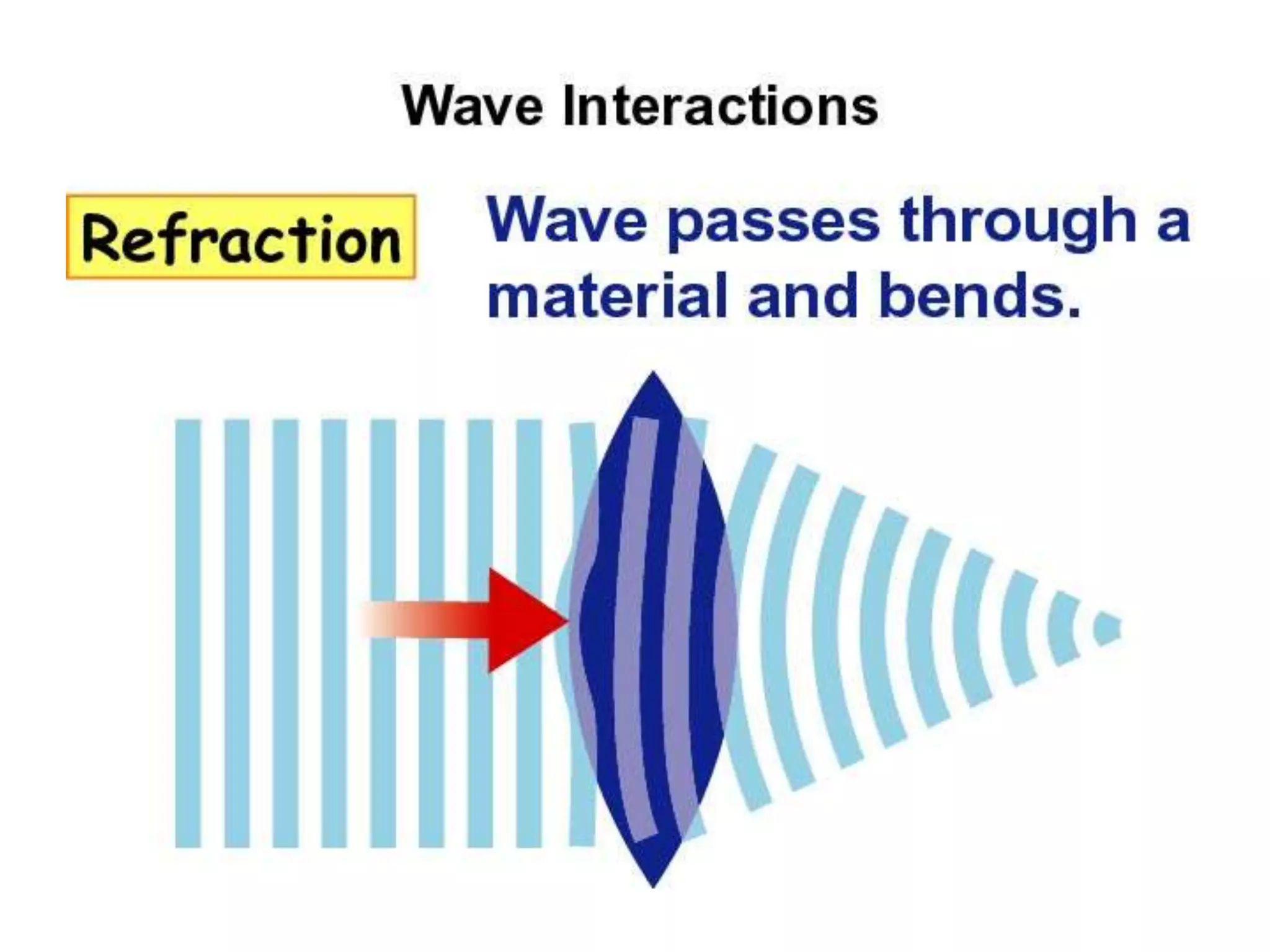
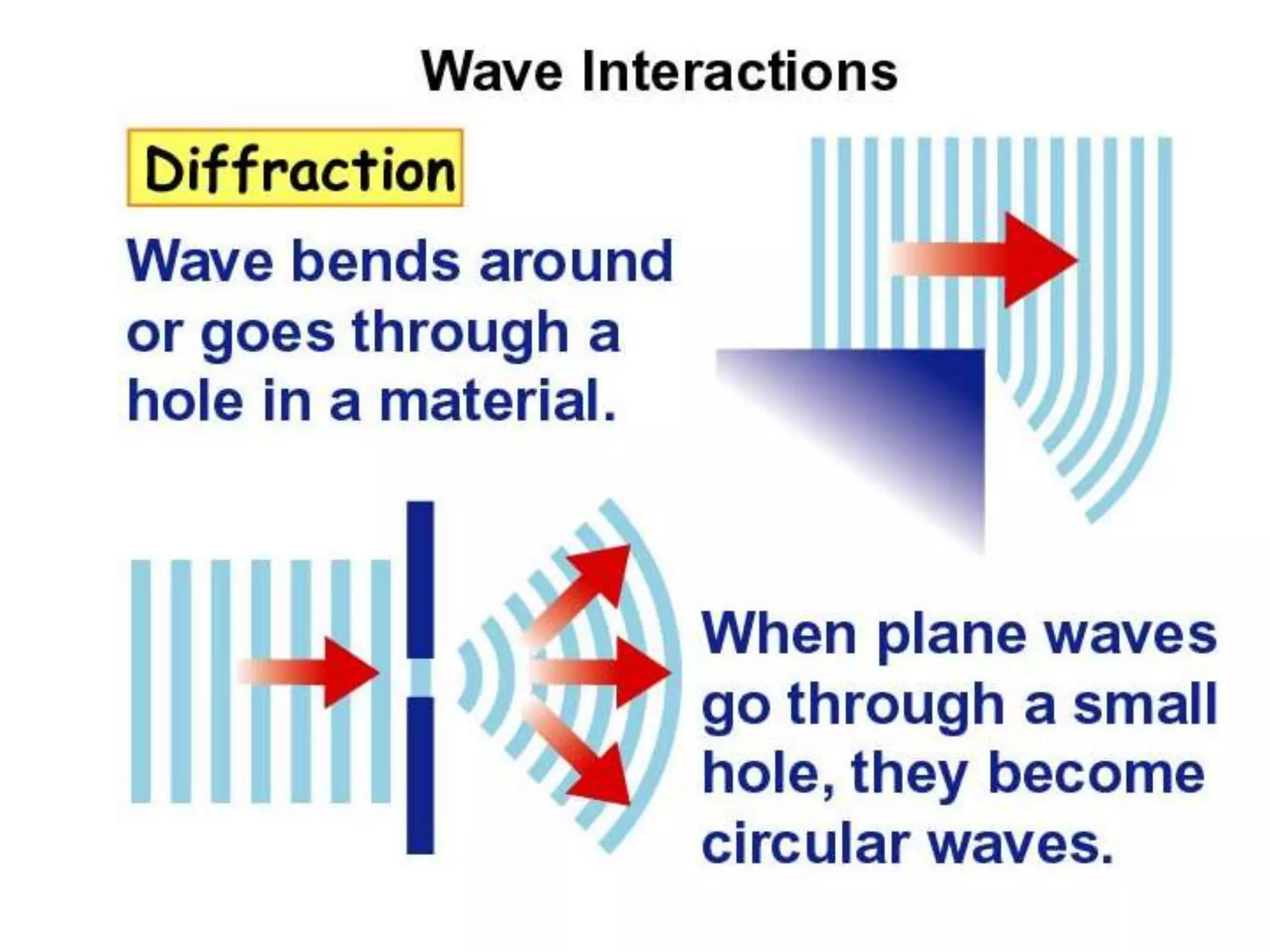
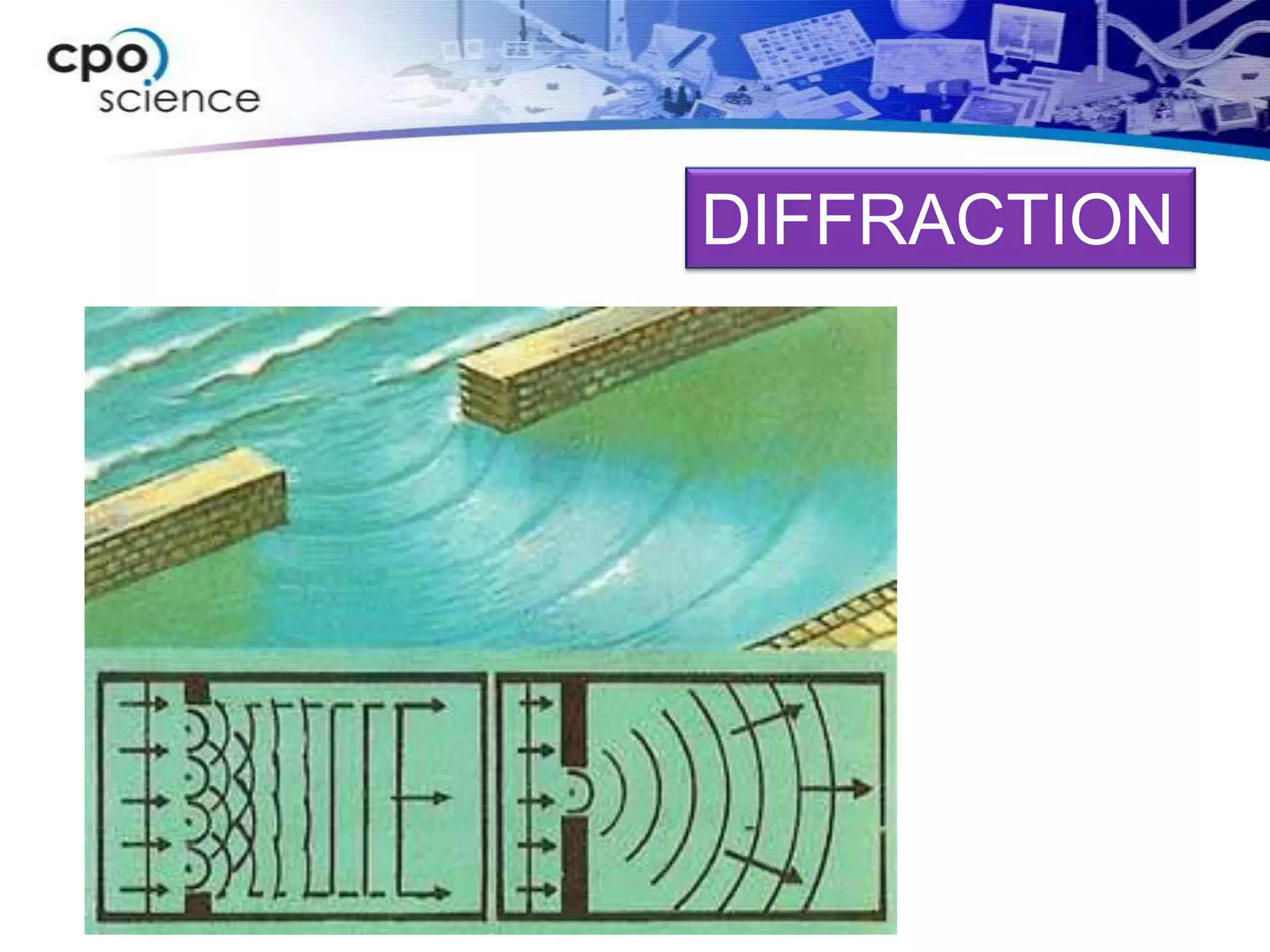
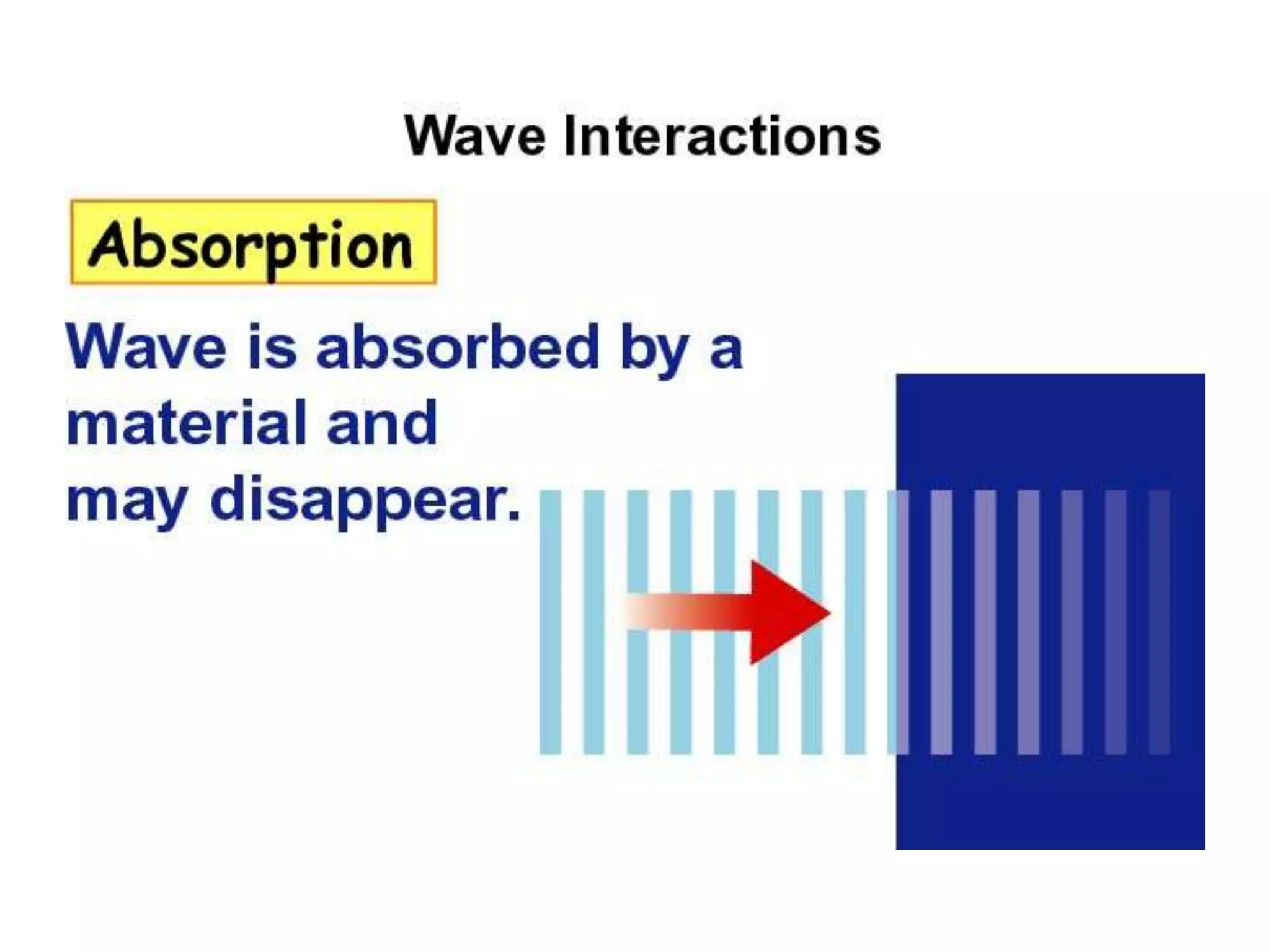
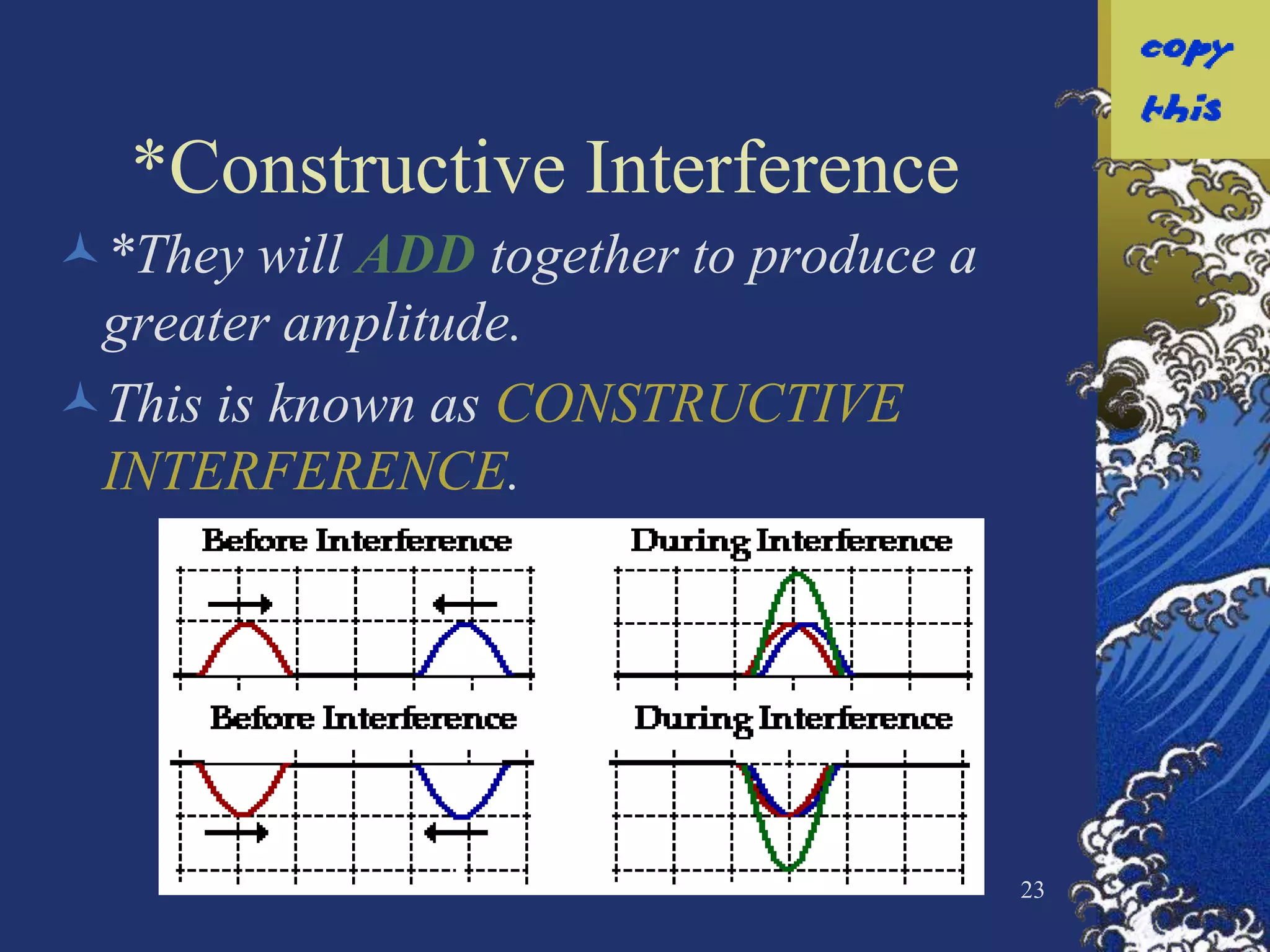
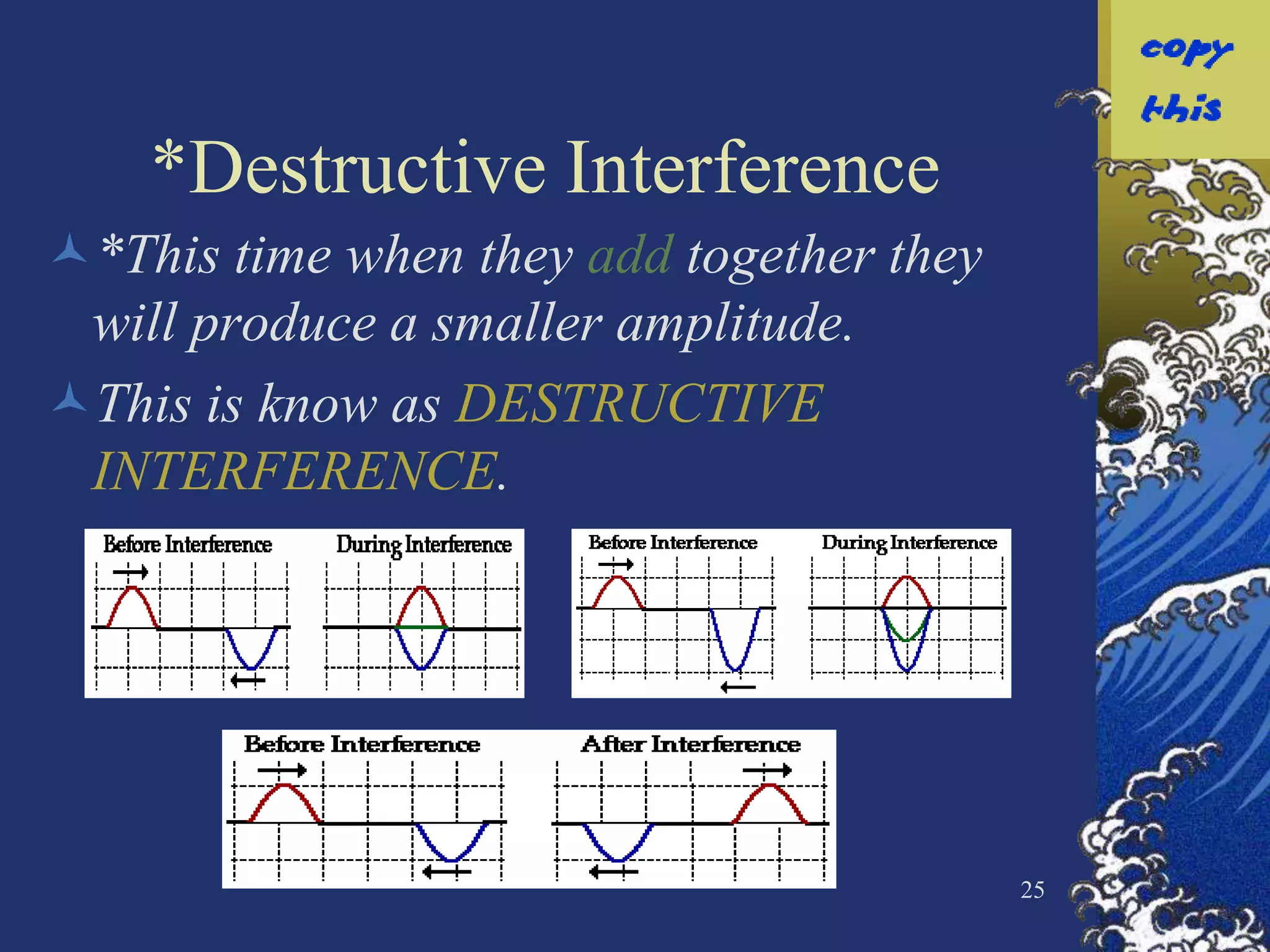
The document discusses two types of waves - transverse waves where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of motion and longitudinal waves where the oscillations are parallel. It covers wave characteristics like frequency, amplitude and wavelength and how waves interact with objects through reflection, refraction, diffraction and absorption as well as interference when two waves meet. Key concepts are explained and examples are provided to illustrate wave behavior and interactions.