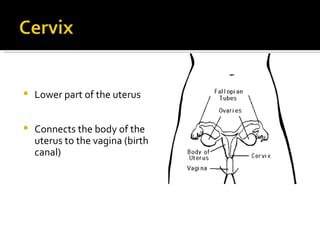
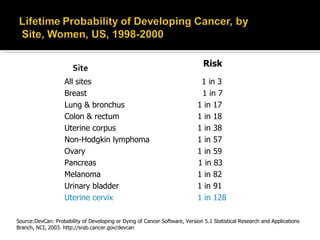
Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. It begins as pre-cancerous changes to cervical cells and can progress to cancer. About 10,520 new cases are diagnosed in the US each year, with risks highest for those who are sexually active at a young age or have HPV. Screening via Pap tests can detect cell abnormalities early when treatment is most effective. Treatment options depend on cancer stage and may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or vaccines.