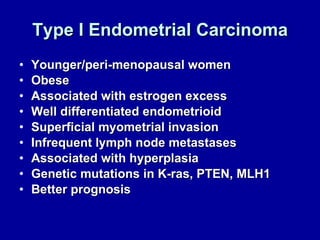
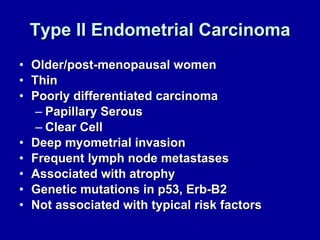
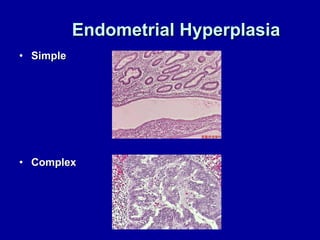
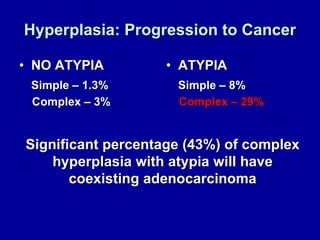
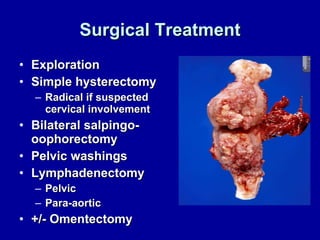
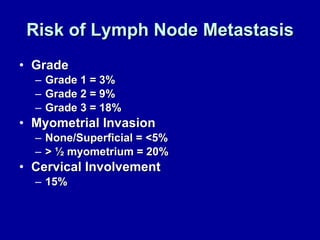
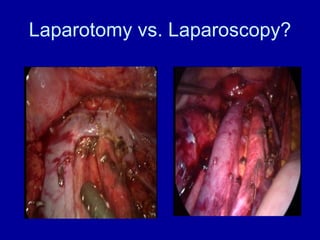
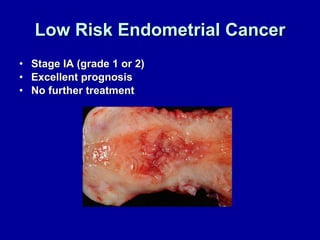
Uterine cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women in the US. There are two main types: Type I is more common in younger women, associated with obesity and estrogen excess. Type II occurs in older women and has worse prognosis. Risk factors include obesity, estrogen exposure, and certain genetic syndromes. Diagnosis involves endometrial biopsy and imaging. Treatment consists of surgery including hysterectomy, with radiation and chemotherapy sometimes used adjuvantly depending on stage and risk factors. Prognosis depends on stage, grade, depth of invasion and other factors.