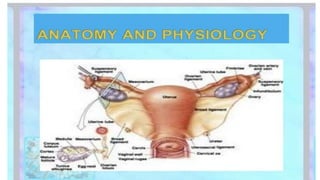
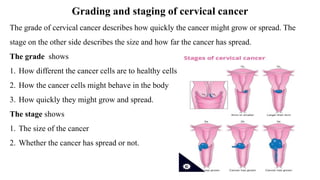
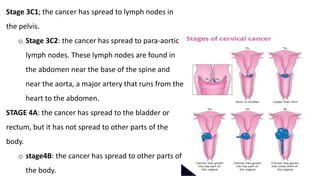
Cervical cancer develops slowly over time and is usually caused by HPV infection. It begins in the cervix and can spread to other nearby tissues and organs. Early stage cancers are often asymptomatic while later stages may cause abnormal bleeding or discharge. Diagnosis involves pap smears, biopsies, and imaging tests. Treatment depends on the stage but may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination. Adopting safe sex practices, getting the HPV vaccine, and undergoing regular pap smears can help prevent cervical cancer.