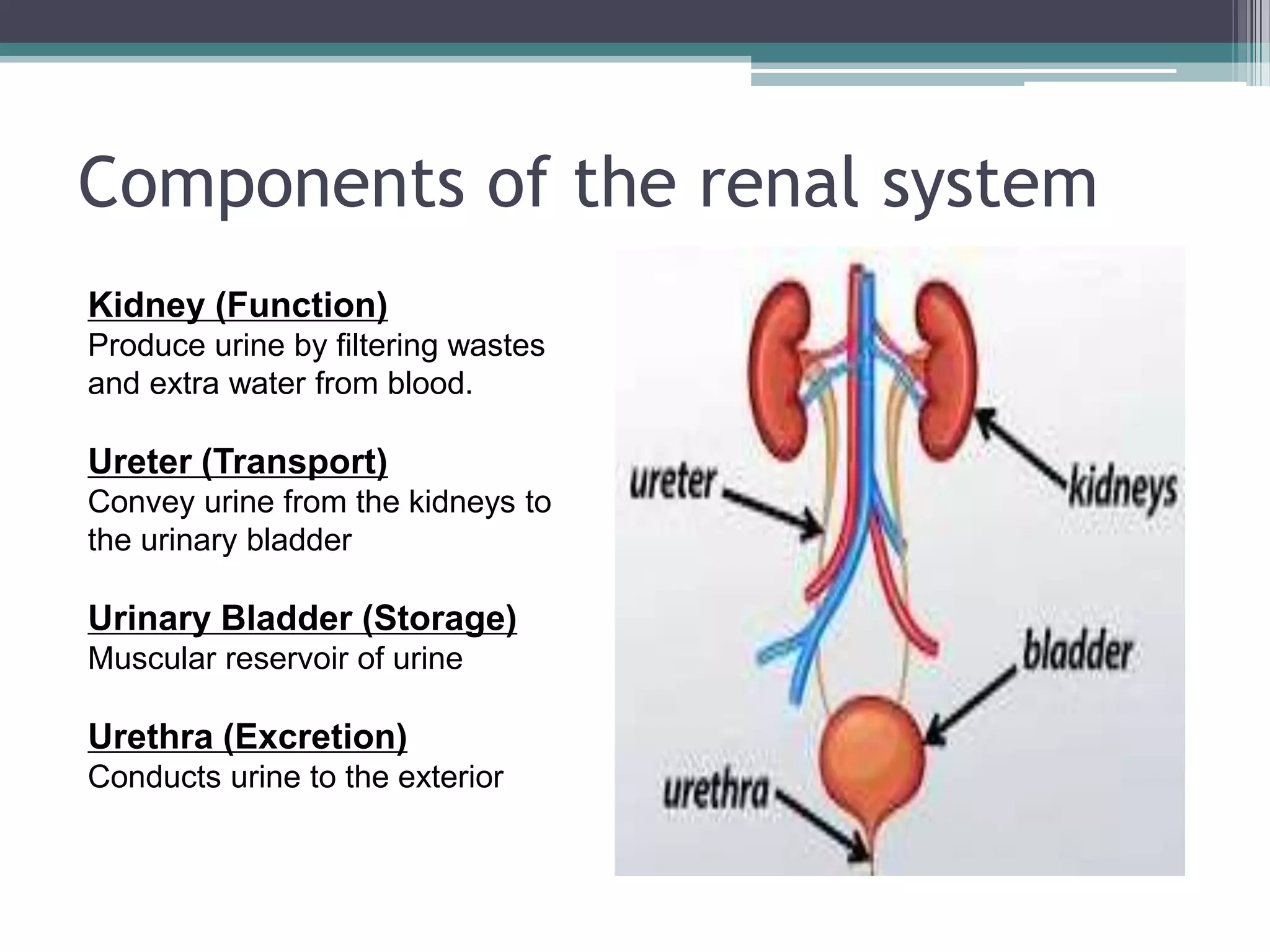
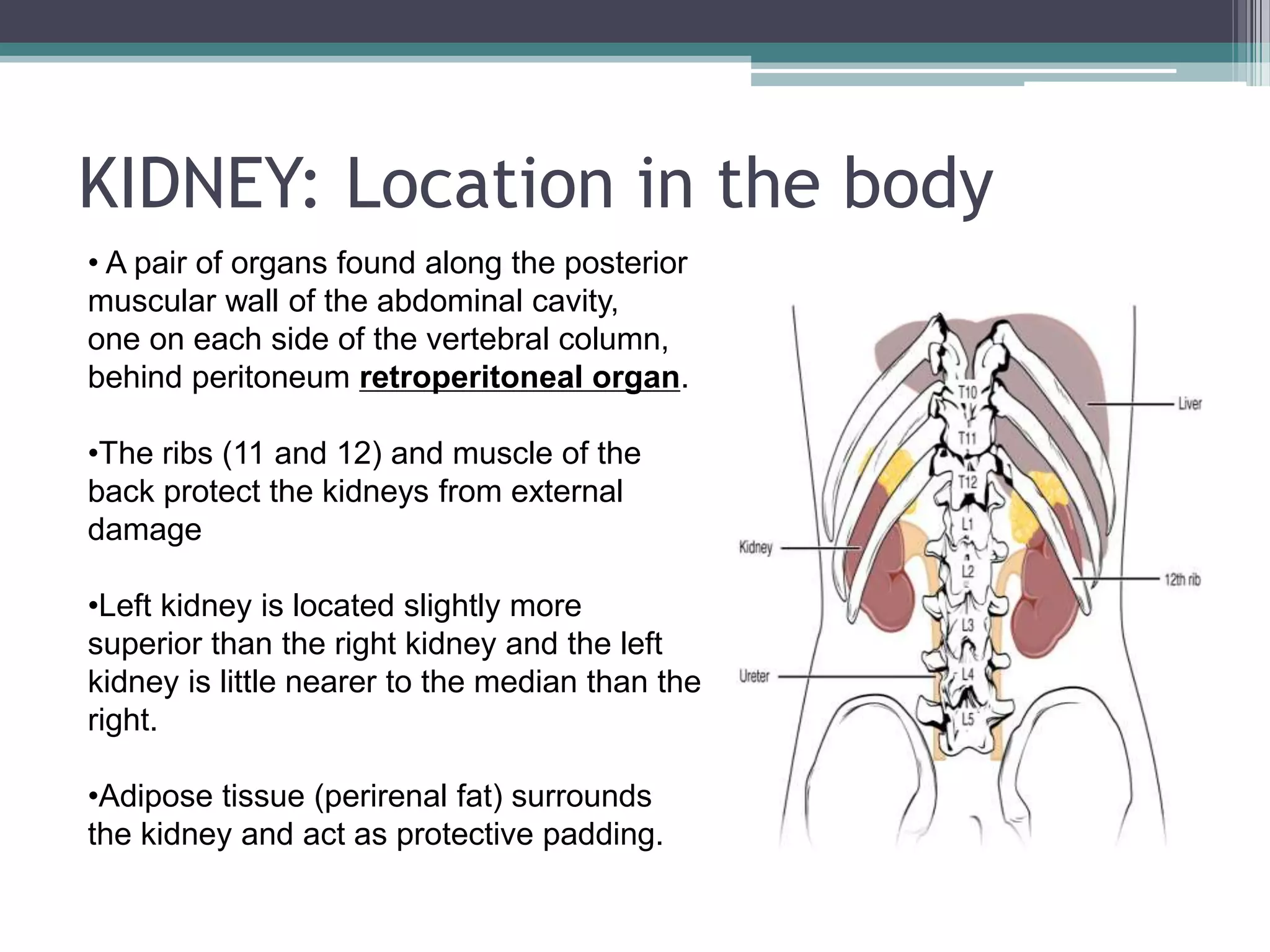
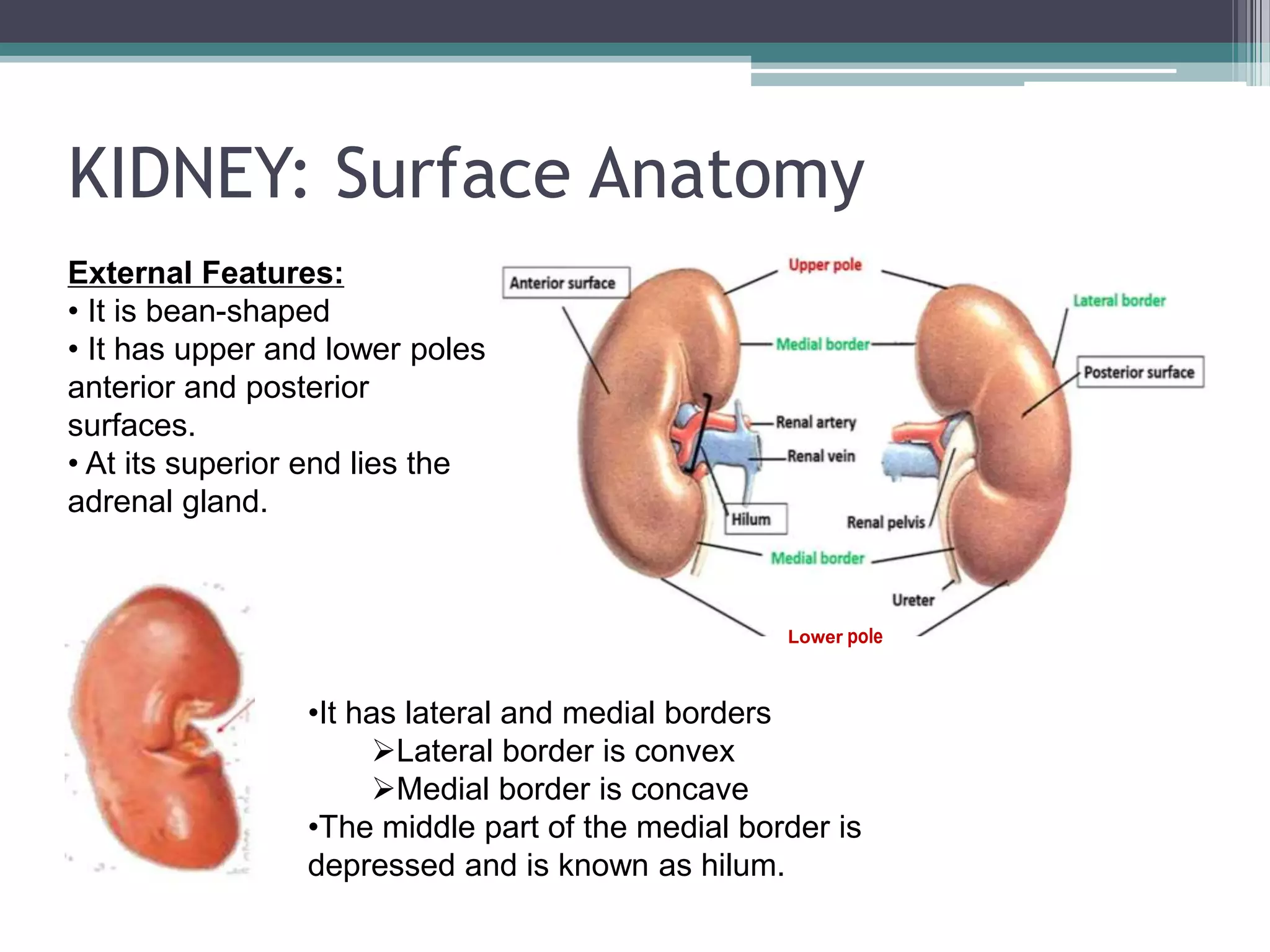
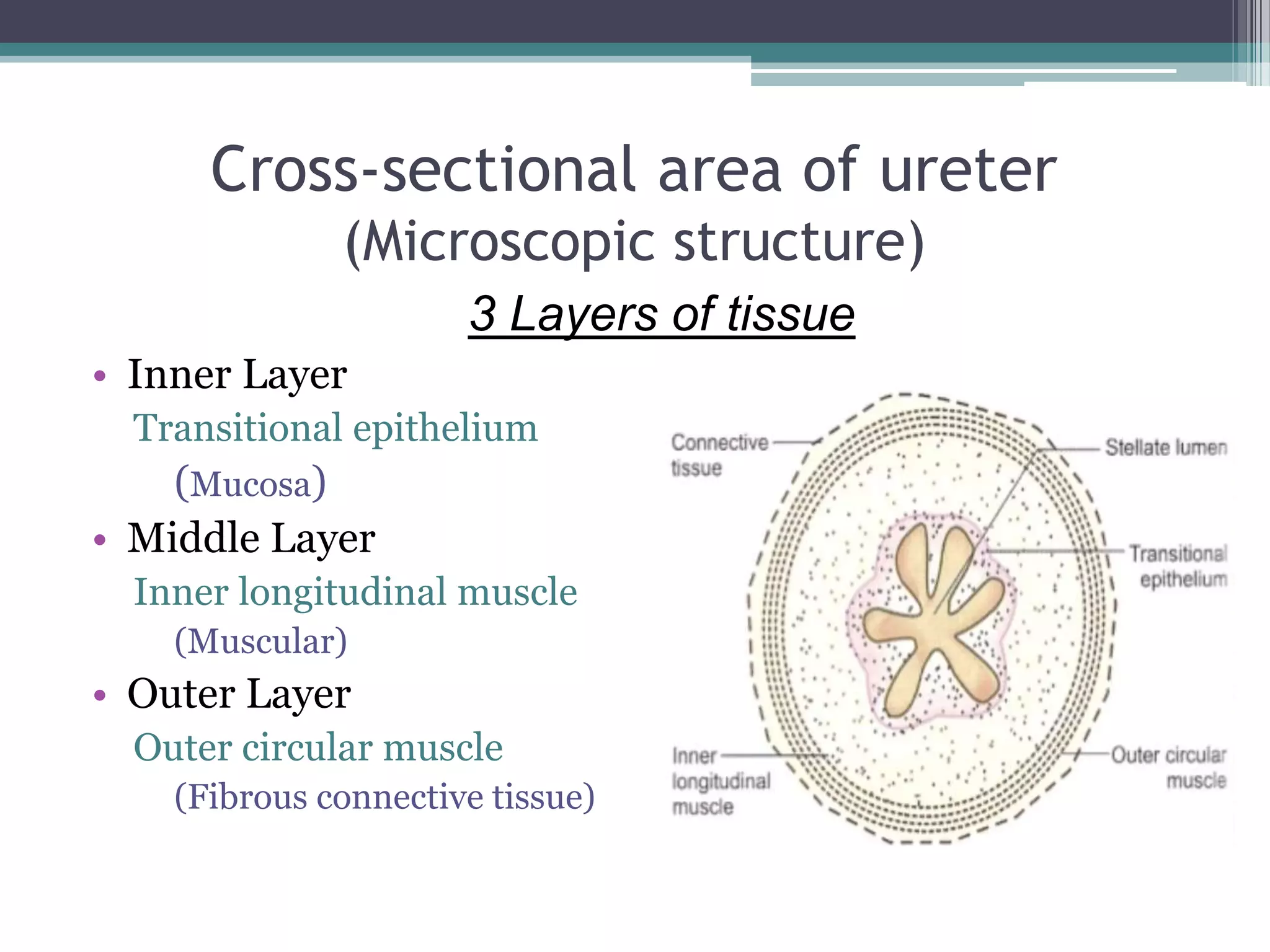
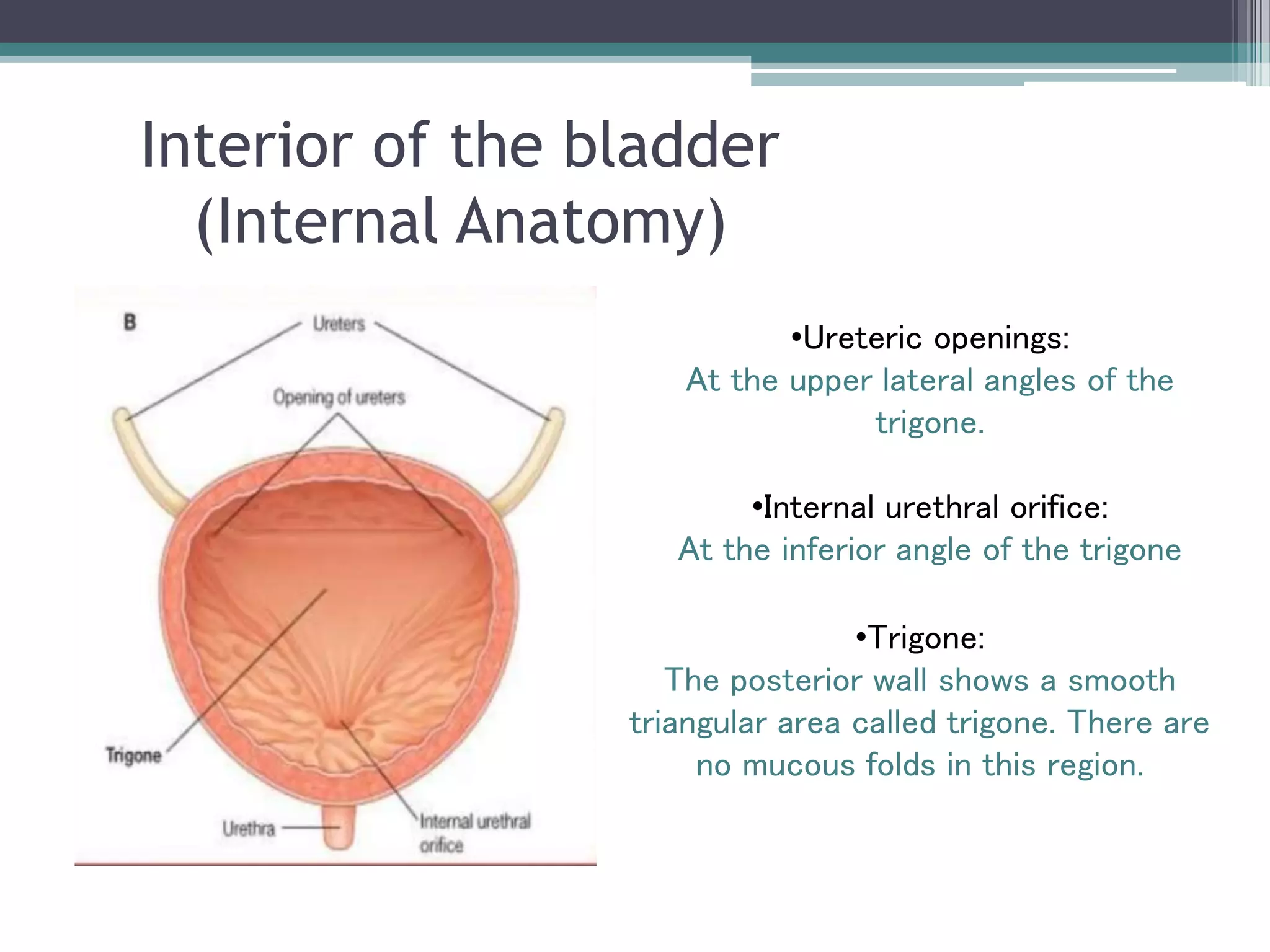
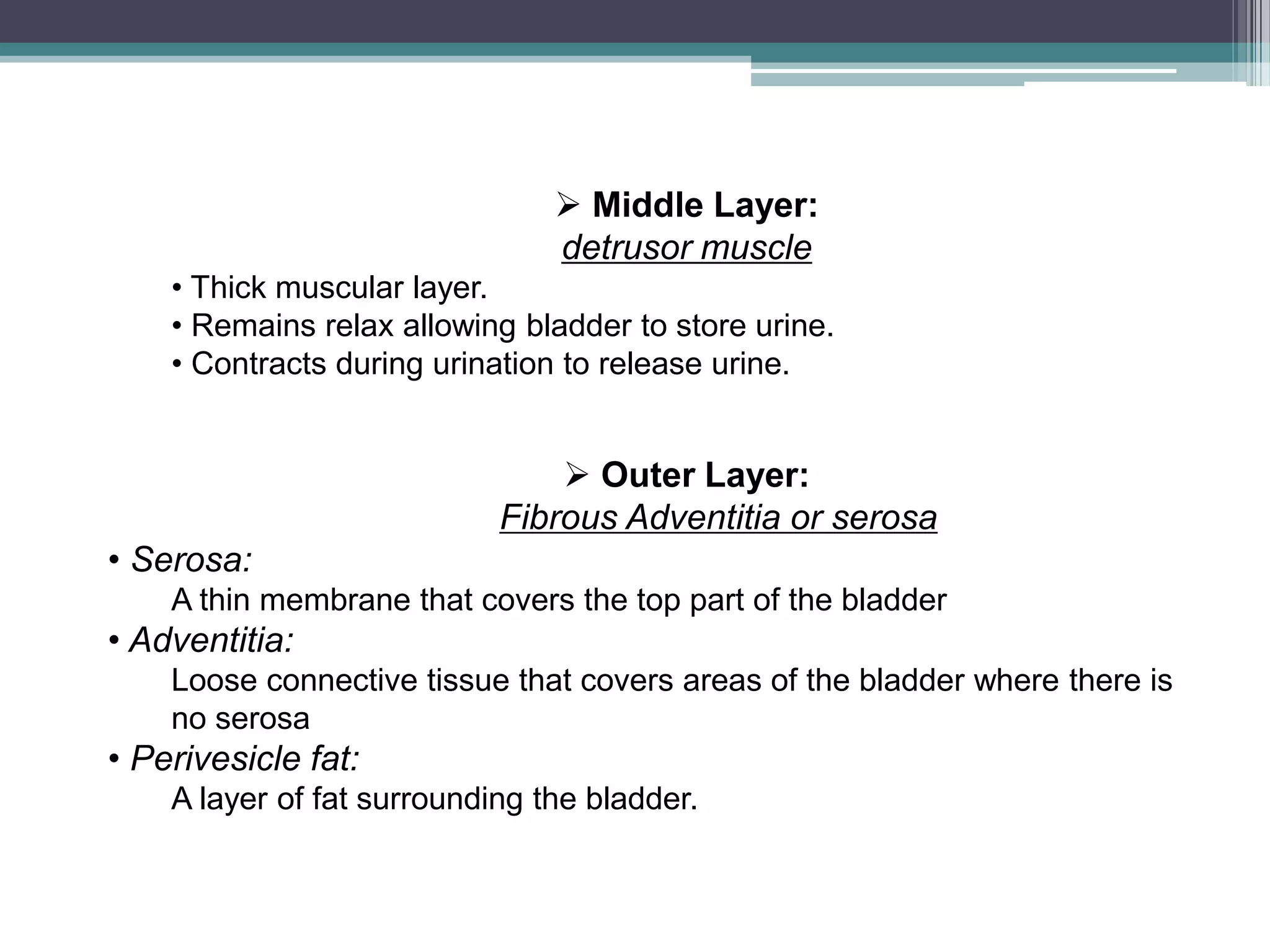
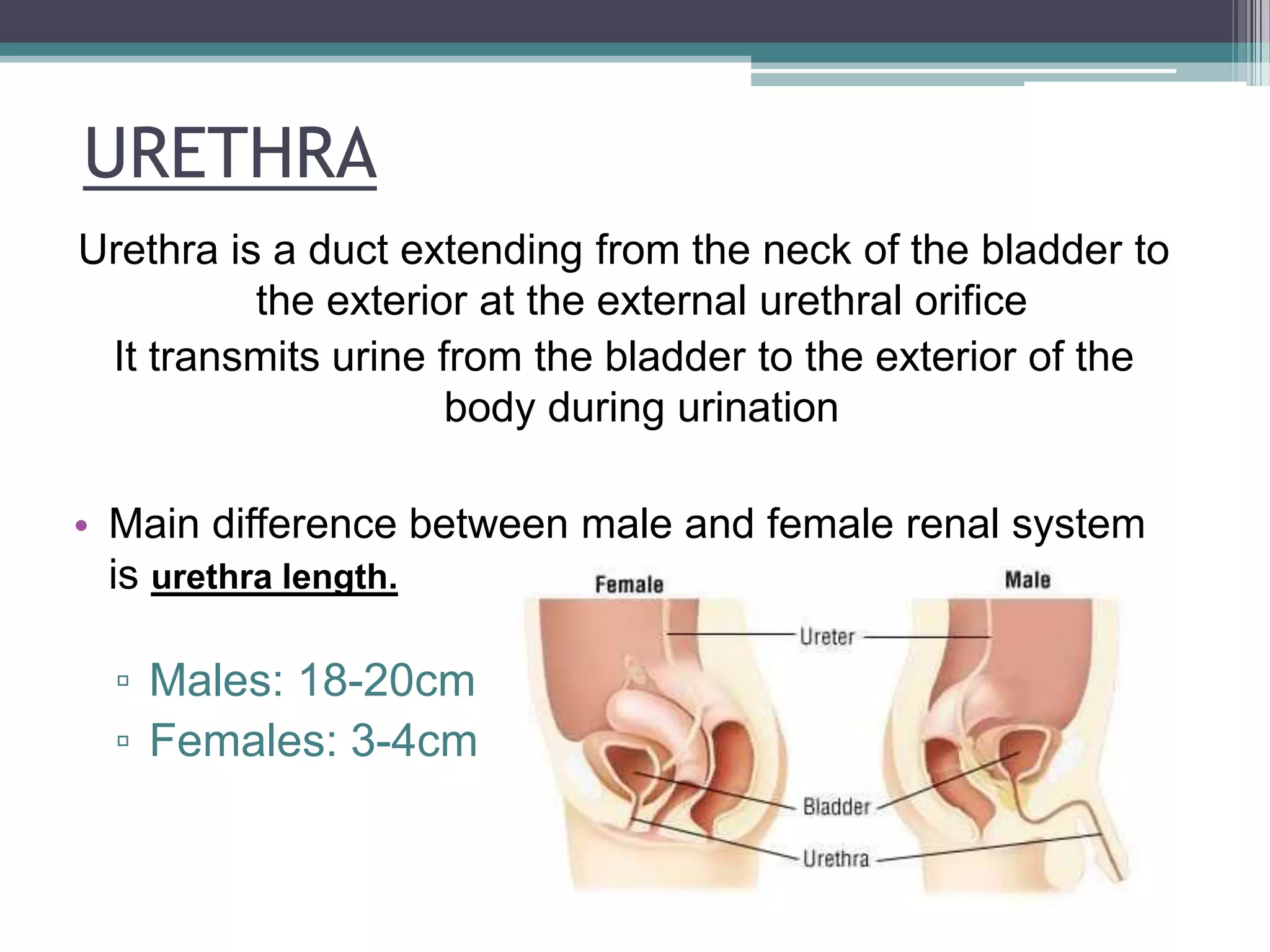
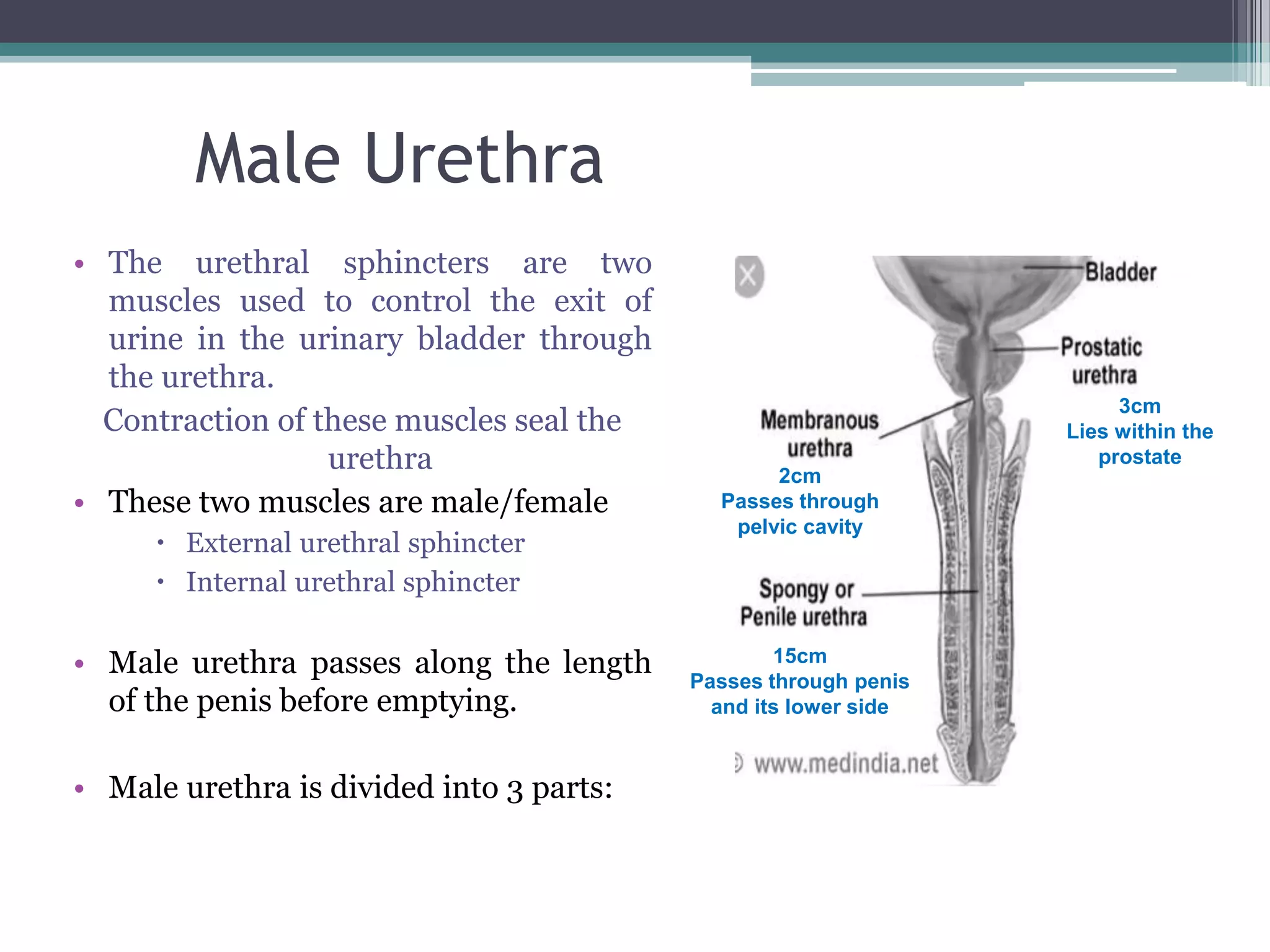
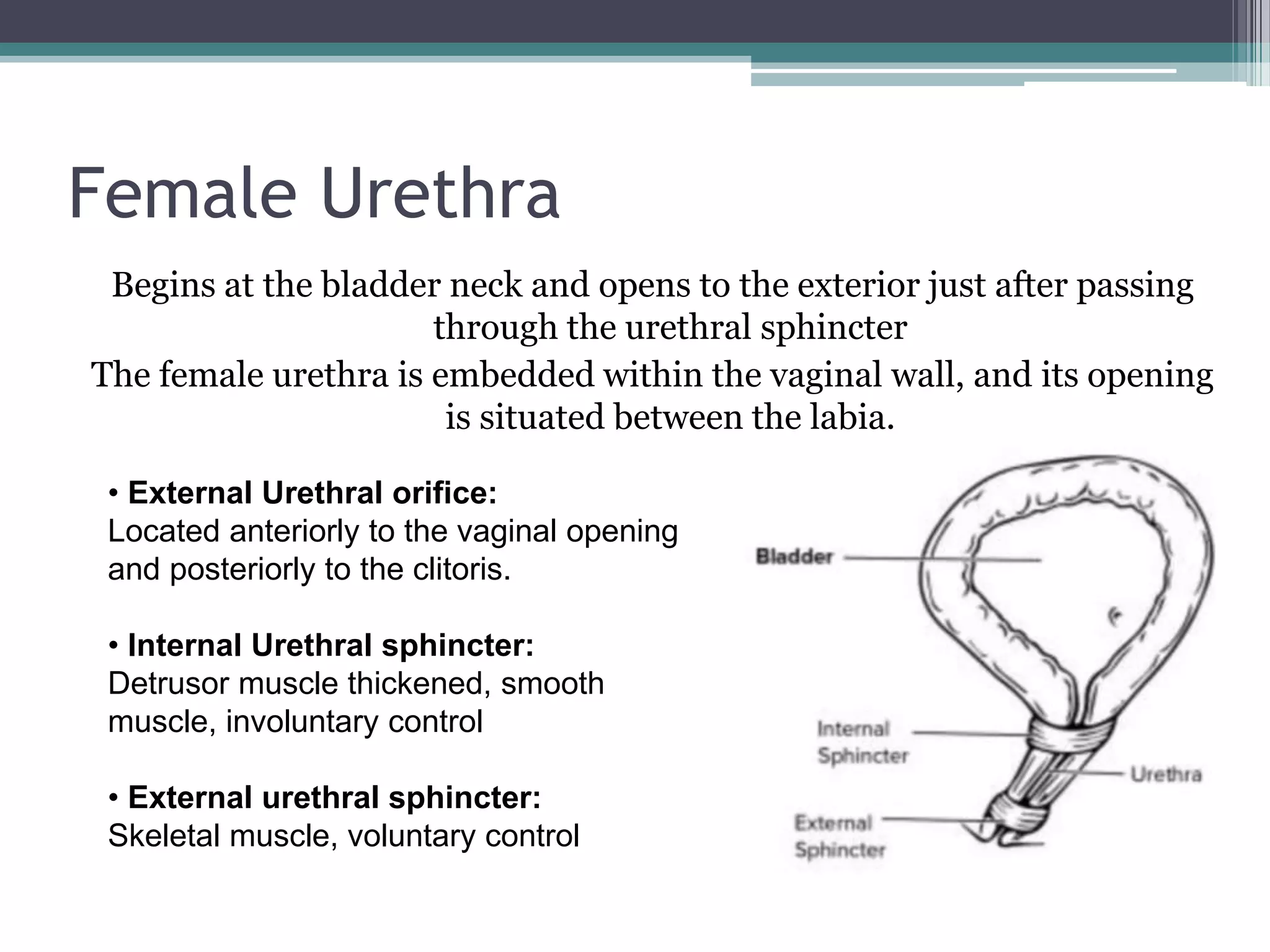
The renal system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The ureters then transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder, where it is stored. When full, the bladder empties through the urethra, which exits the body. The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the abdominal cavity that contain millions of nephrons to filter blood. The ureters are muscular tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that expands as it fills with urine before emptying through the urethra.