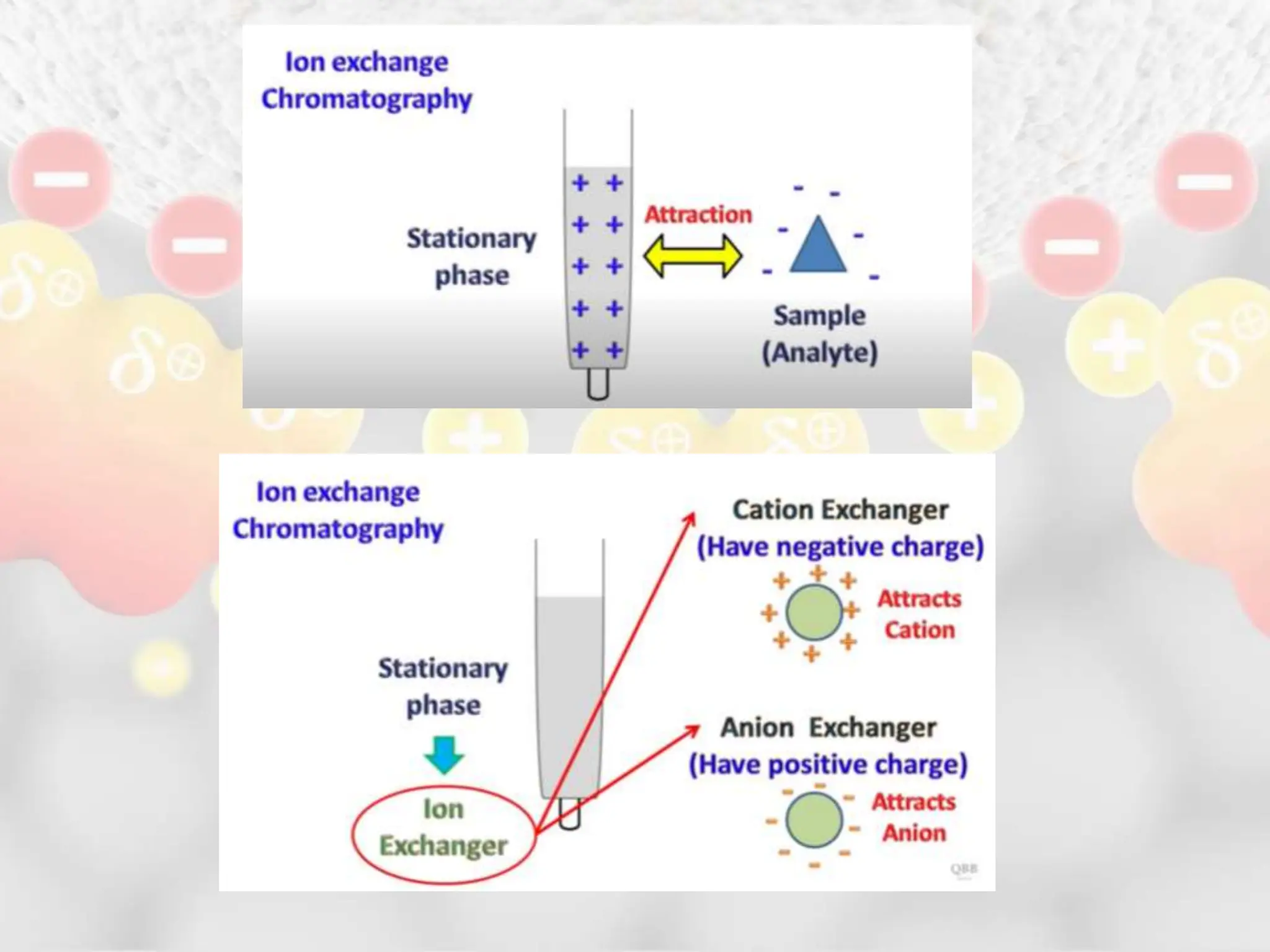
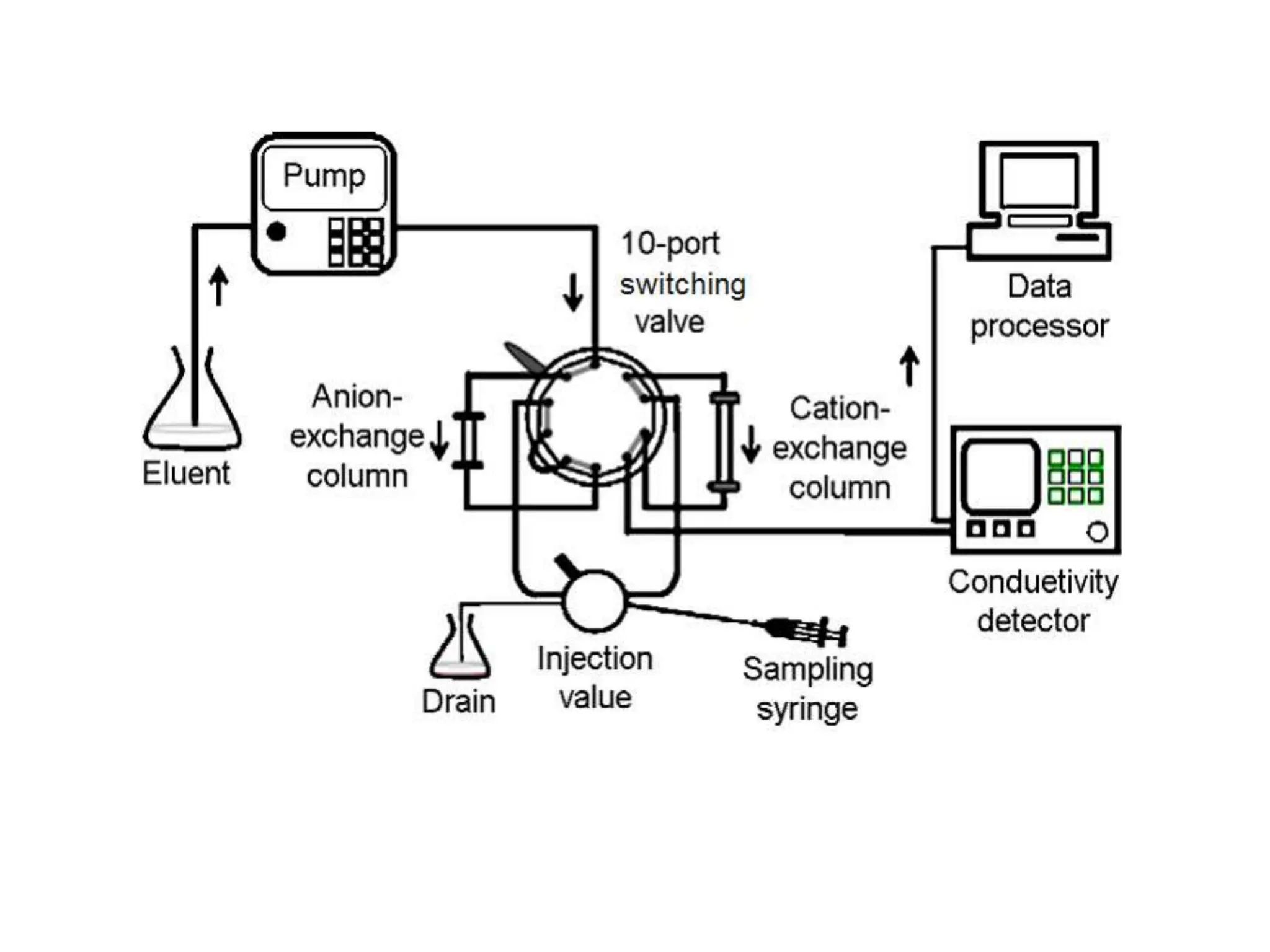
Ion exchange chromatography is a process that separates charged ions using an ion exchange resin. The resin exchanges ions from a sample solution for ions on the resin surface according to their relative affinities. There are two main types of resins - cation exchange resins that attract positively charged ions and anion exchange resins that attract negatively charged ions. The separation occurs through reversible ion exchange between the ions in the sample and resin as the sample passes through a column packed with the resin. Ion exchange chromatography has applications in water softening, enzyme extraction, and purification and separation of ions, sugars, amino acids and proteins.