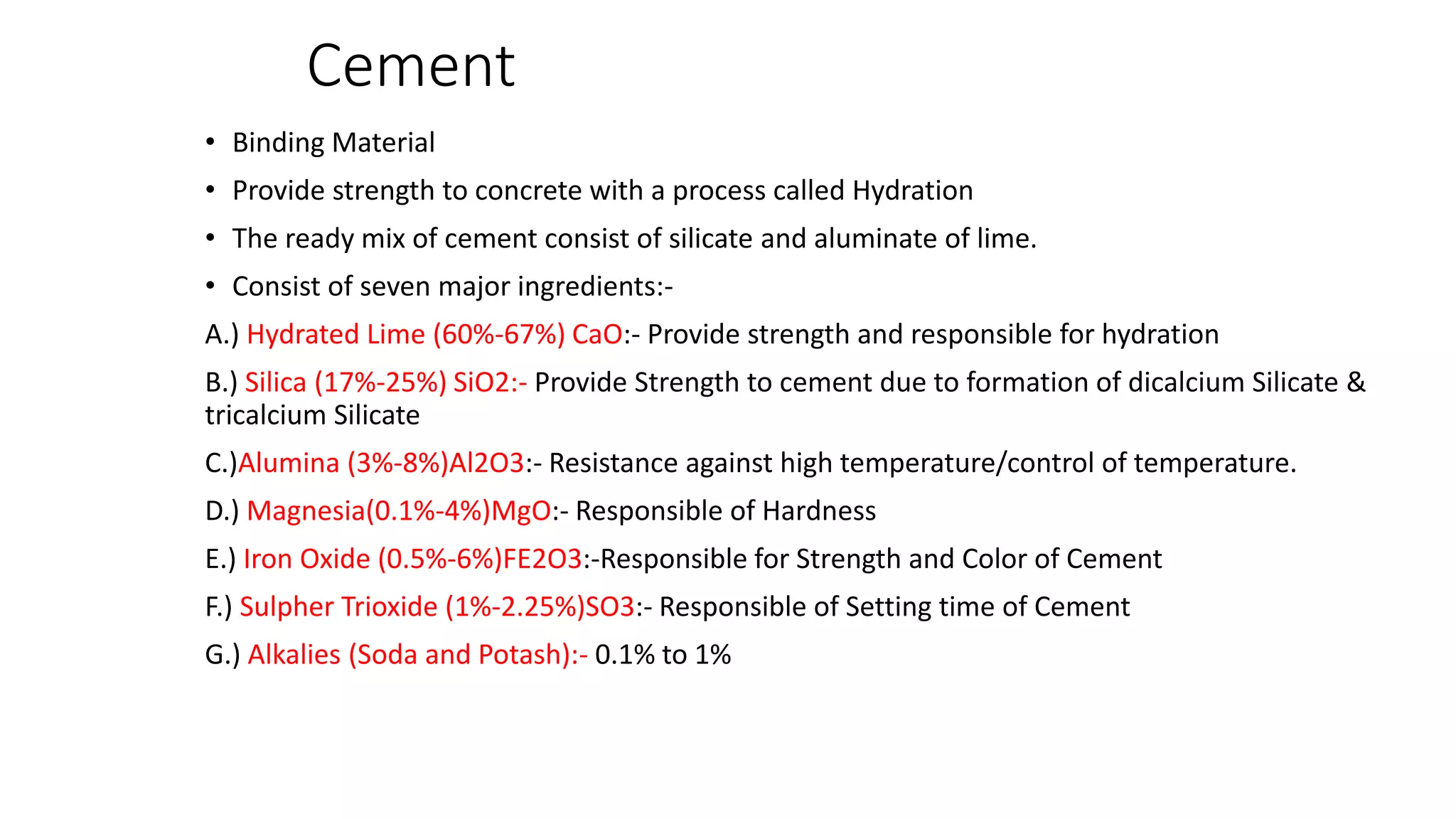
Cement is a binding material that provides strength to concrete through a process called hydration. It consists of calcium, silica, alumina, and other ingredients. The main ingredients are hydrated lime, silica, alumina, iron oxide, and sulfates. There are different types of cement classified based on composition and used for various applications like general construction, structures exposed to sulfate ions, rapid construction projects, and structures requiring high sulfate resistance. Cement is tested for fineness, consistency, setting time, soundness, compression and tensile strength. Ordinary Portland cement gains 112.7 kg/m^2 compression strength at 3 days and 176 kg/m^2 at 7 days, while rapid hardening cement