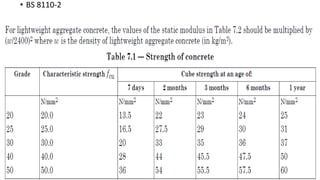
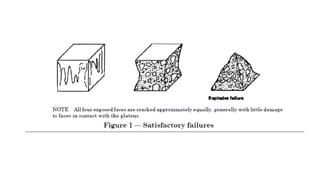
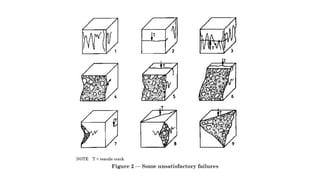
The document provides procedures for testing the compressive strength of hardened concrete cubes according to British standards. Key steps include:
- Curing concrete cubes in a water tank at 20°C for at least 24 hours before testing.
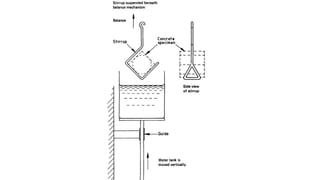
- Determining the density of cubes through water displacement and calculating density based on the cube's mass and volume.
- Crushing cubes in a compression testing machine at a rate of 2-4 kg/cm2/second and calculating compressive strength as the crushing load divided by the cube's surface area.
- Calculating the standard deviation of compressive strengths to ensure it is less than 15% for valid results.











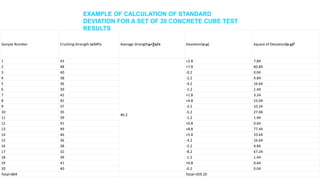
![• Average Strength, μ = 804/20 = 40.2 MPa
• Standard deviation = √[359.2/ (n-1)] = √(359.2/19) =
4.34 MPa
• Where, n = Total number of samples
• Coefficient of Variation = (Standard deviation/Average
strength)*100
• = (4.34/40.2)*100
• = 10.80%<15% ok](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cubetestforcompressivestrengthofconcrete-180903141757/85/Cube-test-for-compressive-strength-of-concrete-14-320.jpg)