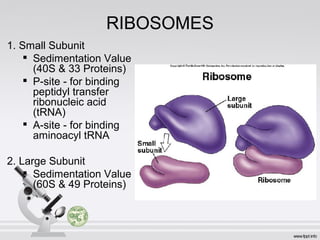
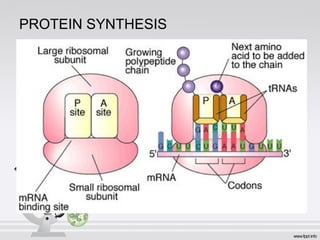
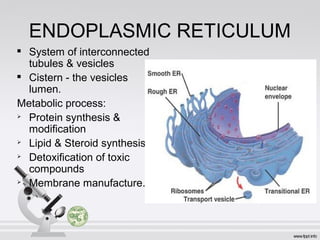
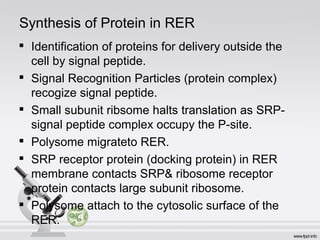
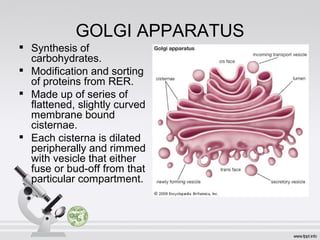
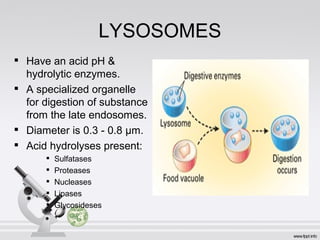
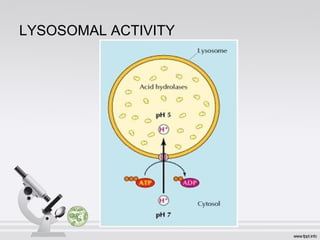
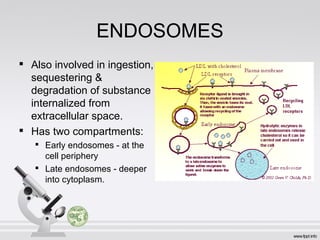
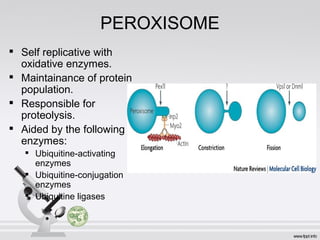
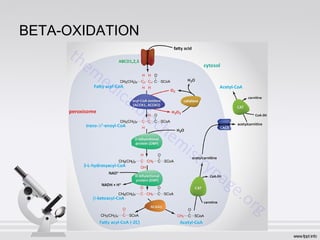
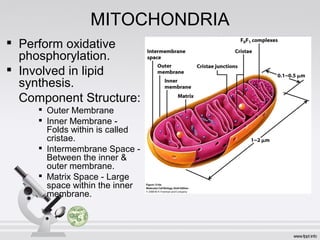
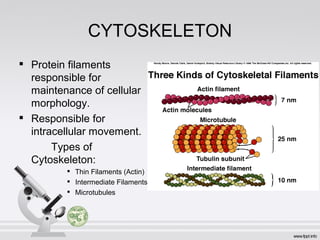
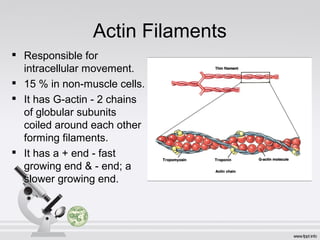
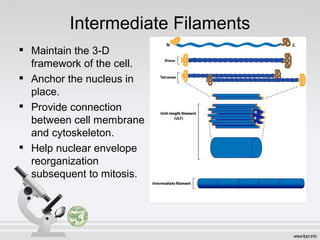
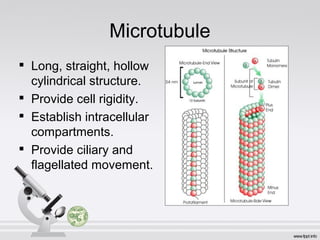
This document summarizes various cell structures and their functions. It discusses ribosomes, which synthesize proteins, and polyribosomes, the components of which include DNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA. It describes the endoplasmic reticulum, where proteins are synthesized and modified, and the Golgi apparatus, where proteins and carbohydrates are further processed and sorted. Lysosomes aid digestion, while peroxisomes contain oxidative enzymes and aid in protein degradation. Mitochondria perform oxidative phosphorylation and lipid synthesis. The cytoskeleton, comprising actin filaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, maintains cell shape and enables intracellular movement.