This document provides information about urine analysis including:
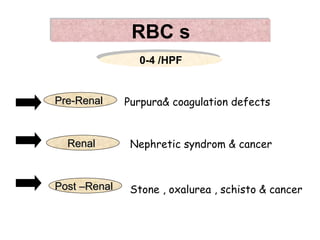
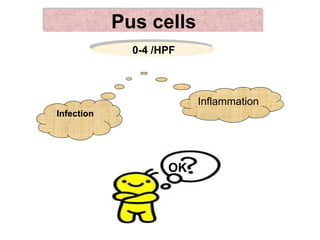
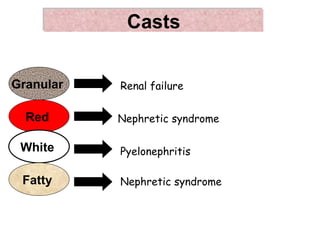
1. It lists 12 components that are analyzed in a urine test including volume, color, reaction, specific gravity, albumin, red blood cells, pus cells, casts, pigments, crystals, glucose, and keton bodies.
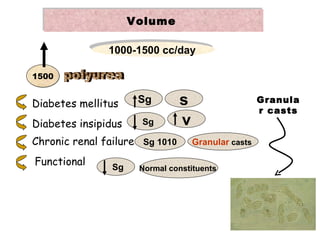
2. It describes normal ranges and possible indications for abnormal findings for each component such as specific gravity being high in diabetes insipidus and low in renal failure.
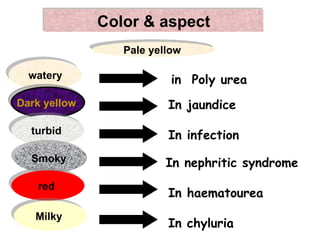
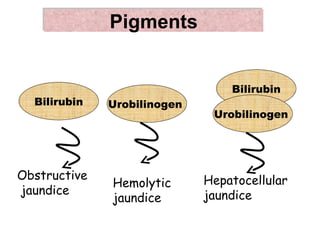
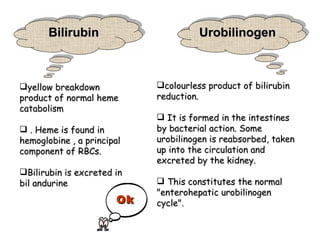
3. It explains what certain findings may indicate such as bilirubin in urine signifying obstructive jaundice or urobilinogen signifying hepatocellular jaundice.