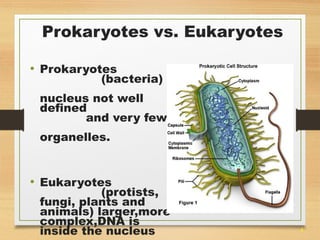
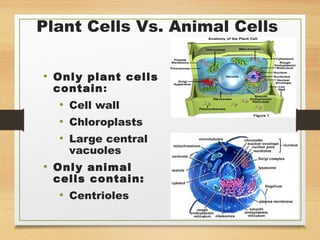
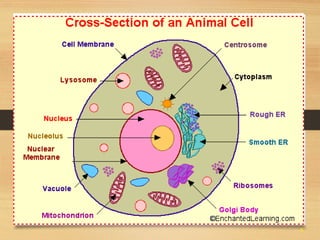
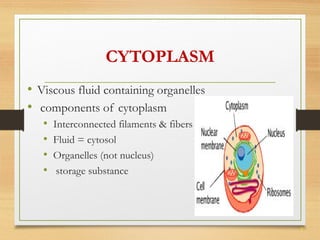
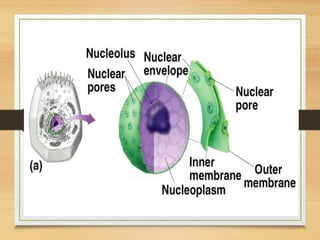
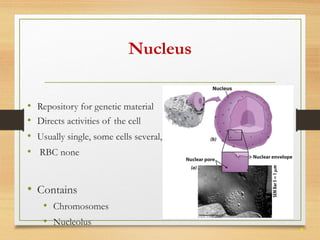
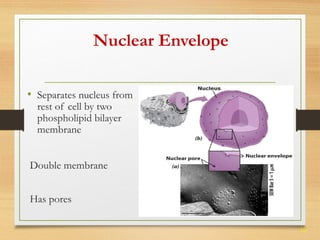
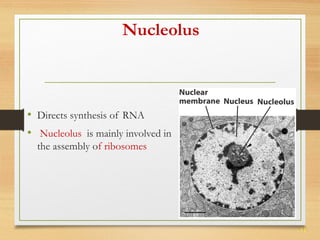
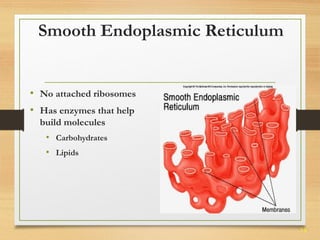
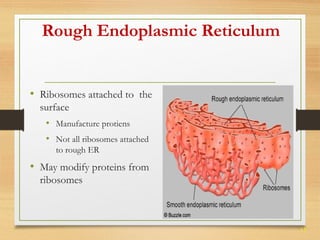
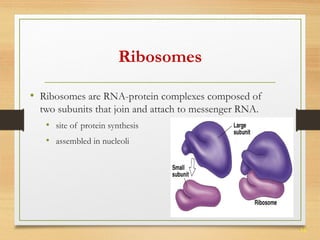
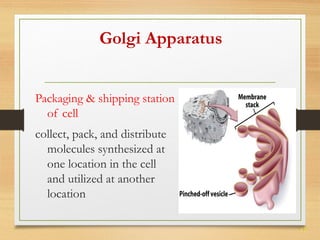
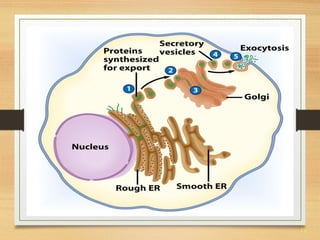
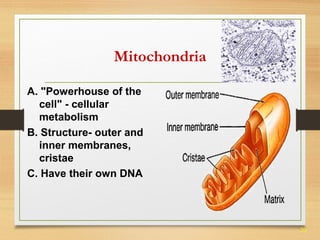
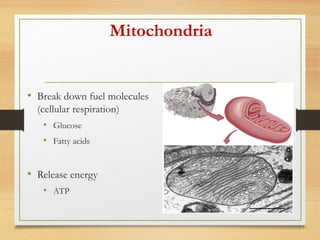
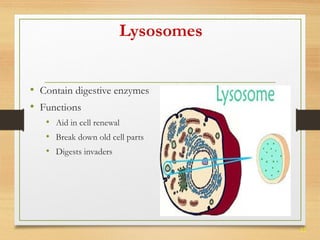
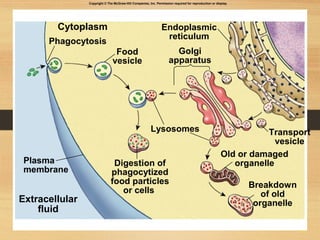
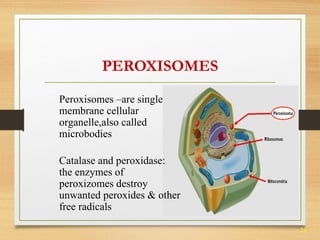
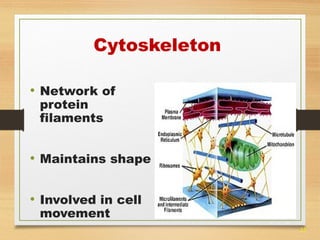
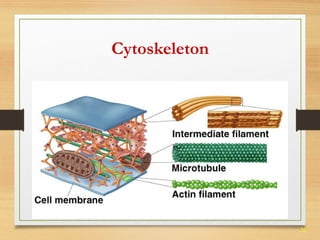
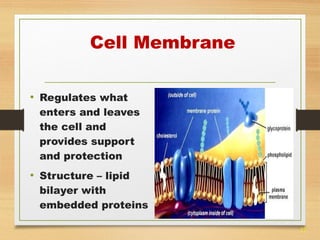
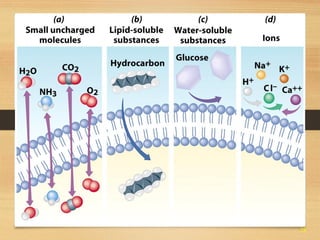
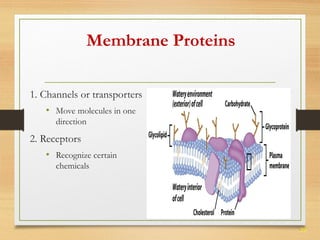
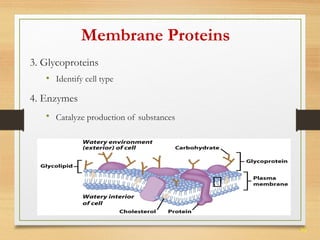
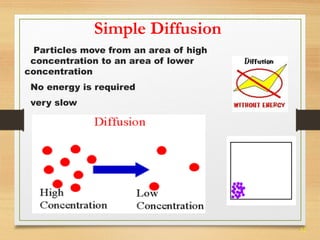
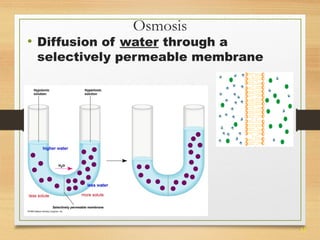
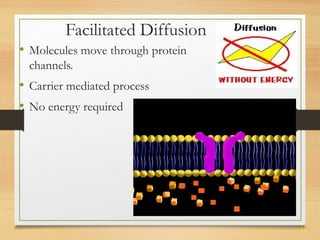
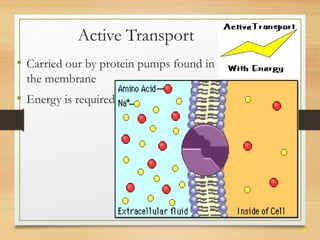
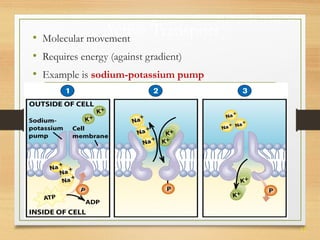
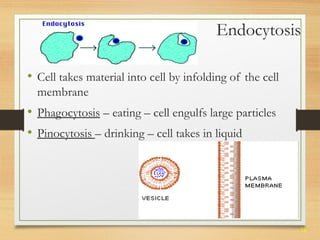
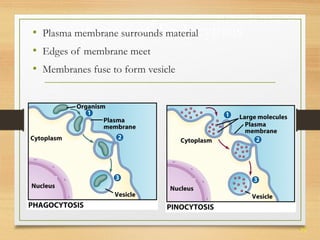
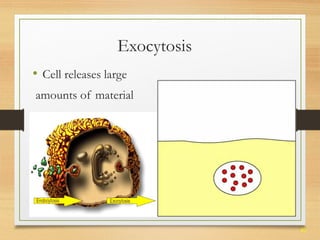
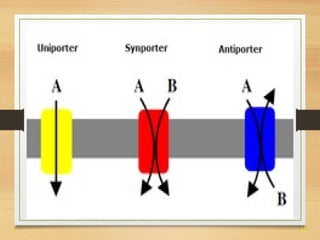
This document provides an overview of cell structure and function. It describes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as plant and animal cells. The major organelles of the cell are defined, including their structures and functions. Specifically, it outlines the roles of the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, cytoskeleton, and cell membrane in cellular processes like transport and protein synthesis. Molecular transport mechanisms like diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis are also summarized.