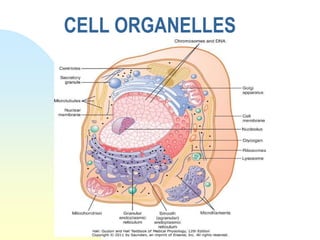
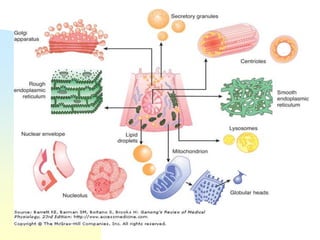
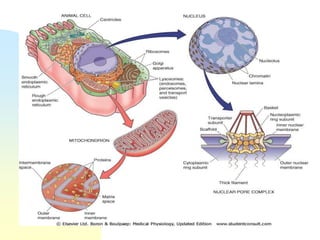
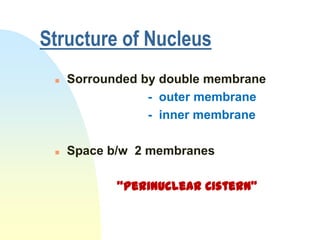
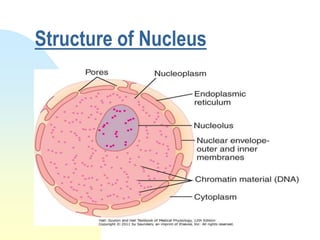
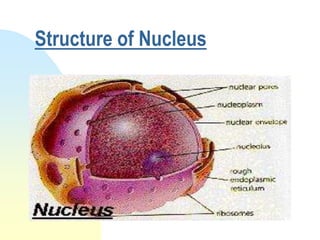
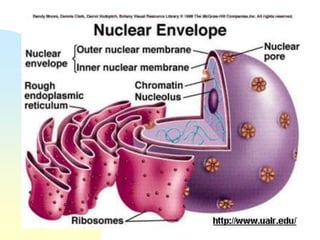
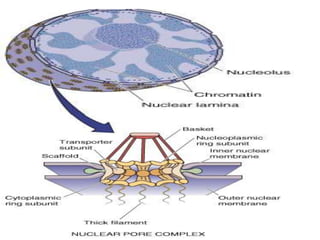
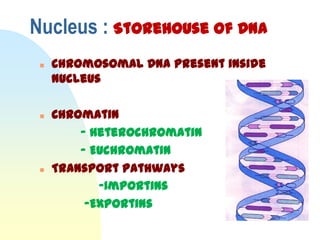
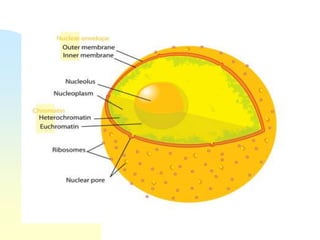
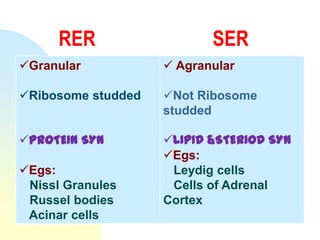
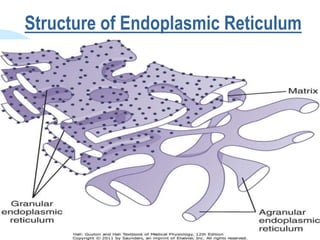
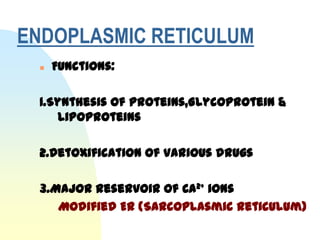
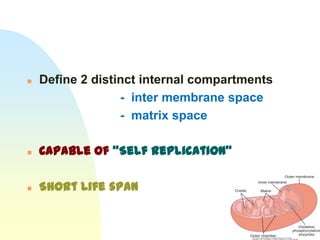
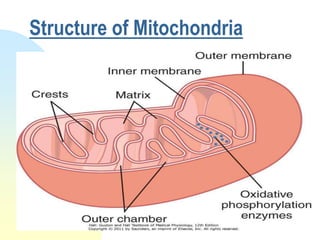
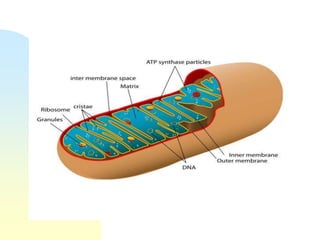
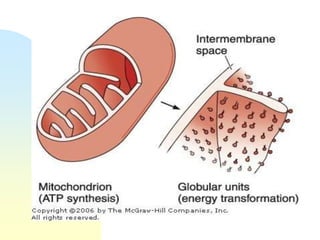
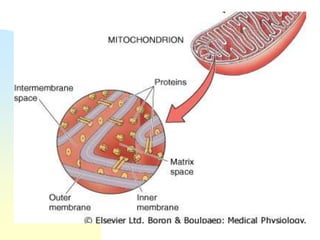
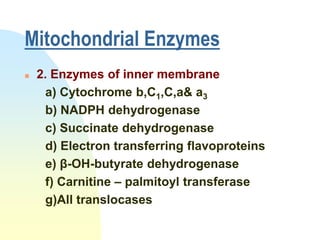
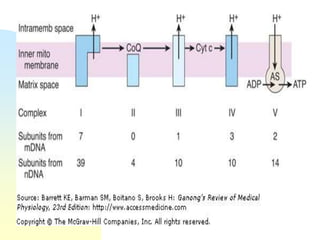
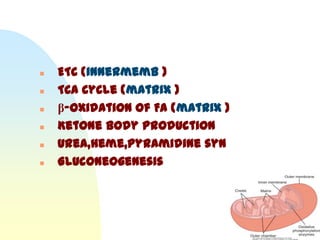
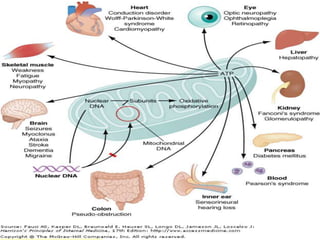
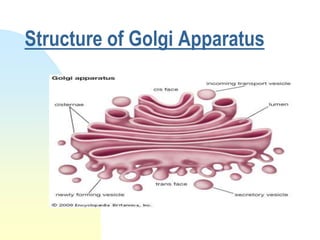
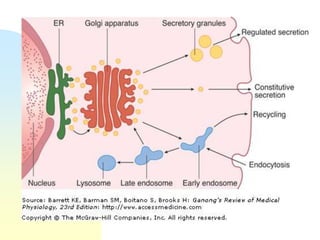
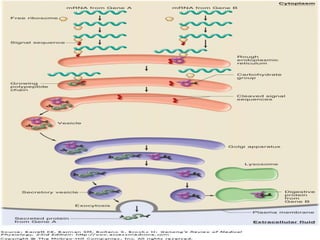
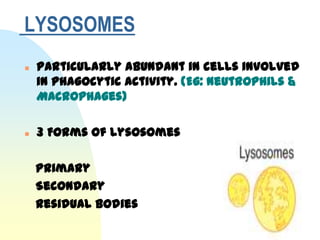
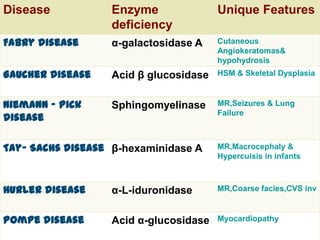
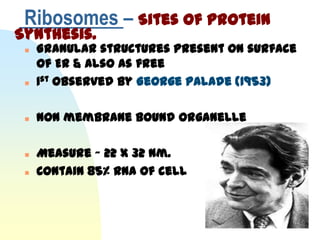
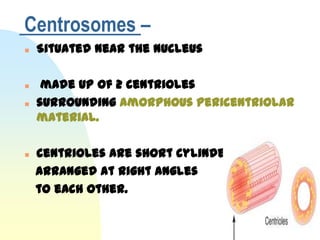
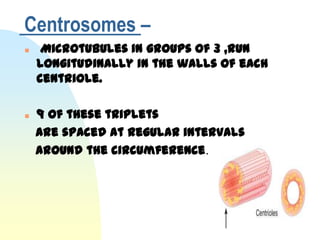
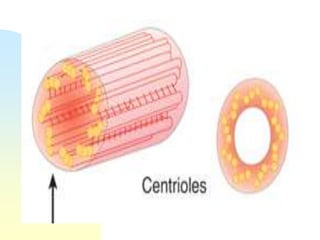
This document summarizes a seminar on cell organelles presented by Dr. Simi M. The seminar covered the major cell organelles including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and ribosomes. It described the structure and functions of each organelle, highlighting their roles in processes like protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, cellular respiration, waste disposal, and more. The history of the discovery of each organelle was also briefly outlined.