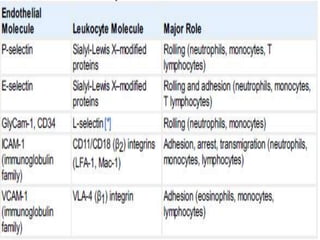
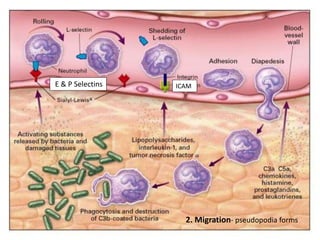
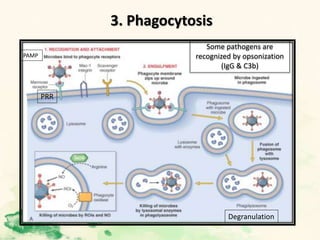
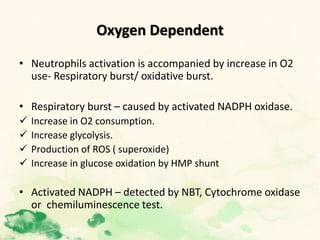
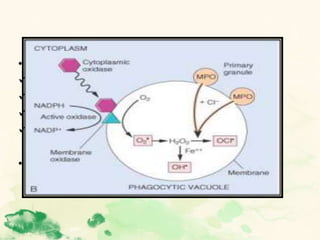
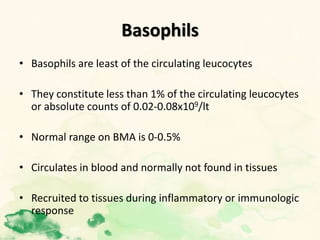
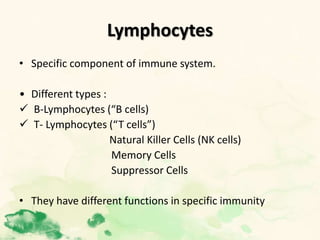
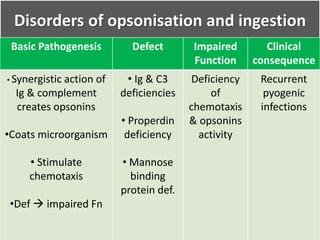
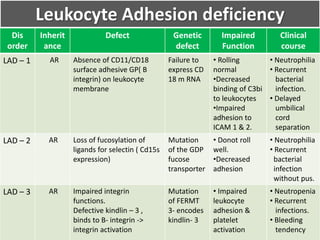
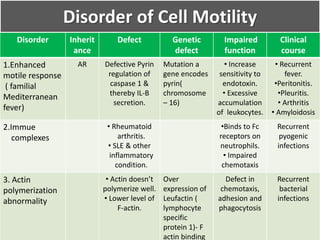
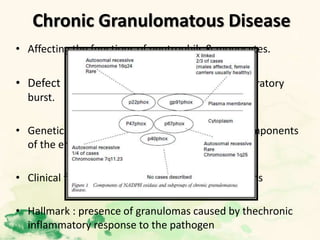
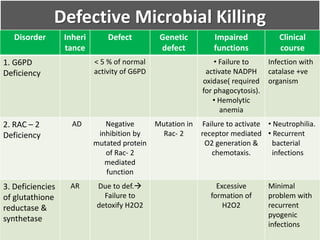
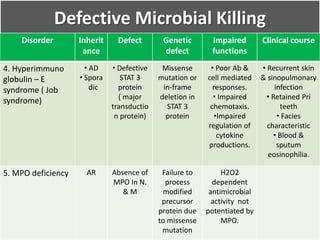
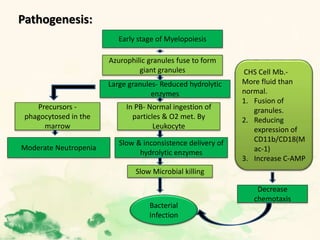
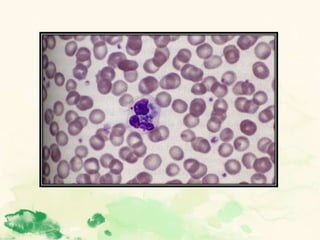
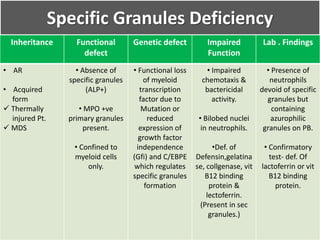
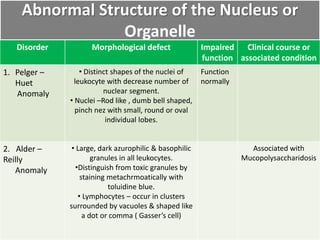
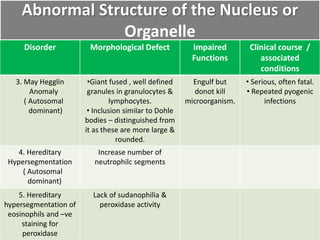
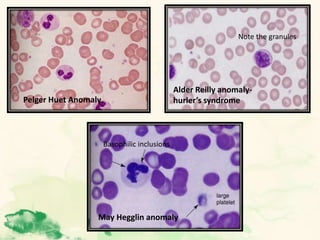
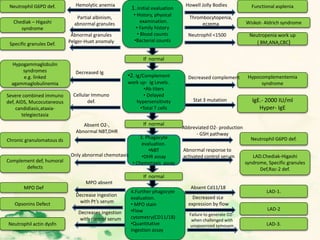
This document summarizes the functions of leukocytes (white blood cells), which develop from stem cells in the bone marrow and include granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils), monocytes, and lymphocytes. Leukocytes protect the host from pathogens through innate and adaptive immune responses. Neutrophils are the most abundant granulocyte and use adhesion, chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and microbial killing to defend against bacteria and fungi. Defects in these leukocyte functions can lead to increased susceptibility to infection. The document then discusses specific disorders that impact leukocyte development and function.