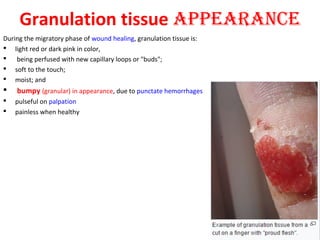
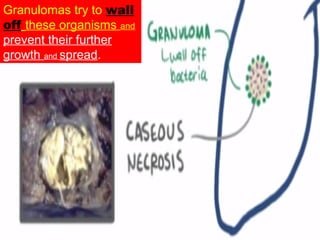
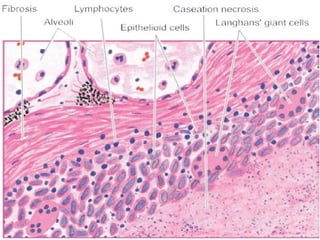
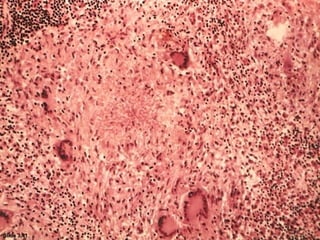
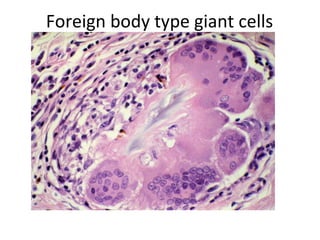
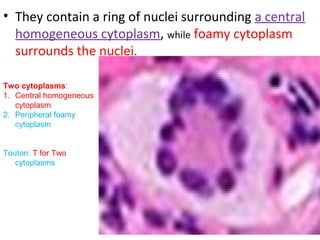
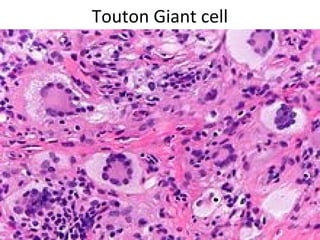
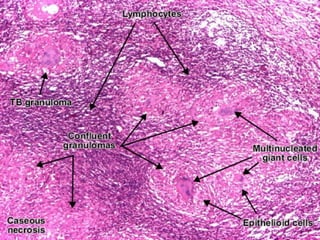
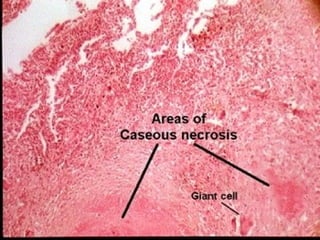
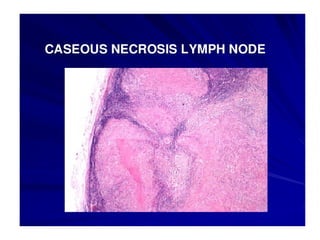
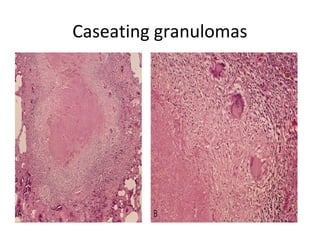
Granuloma is defined as a localized collection of modified macrophages called epithelioid cells surrounded by lymphocytes. It forms as an immune response to foreign substances that cannot be easily eliminated by the body. A granuloma contains epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells formed by the fusion of macrophages, and a rim of lymphocytes, and may develop central caseous necrosis. Tuberculosis causes immune granulomas known as tubercles, which typically feature caseating necrosis. Granulomas aim to wall off pathogens and prevent their spread in the body.