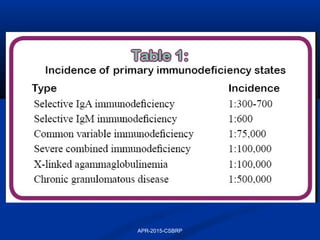
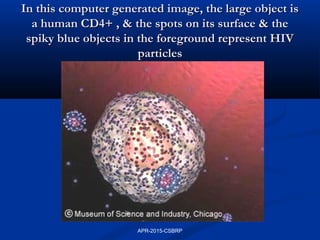
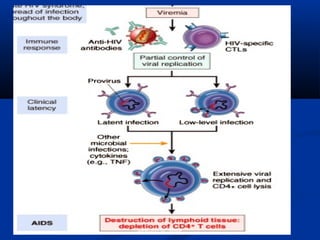
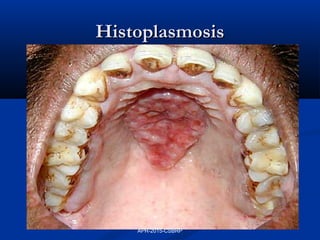
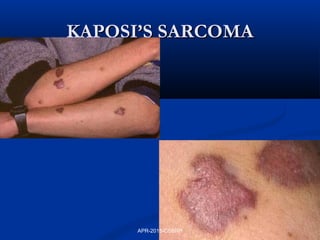
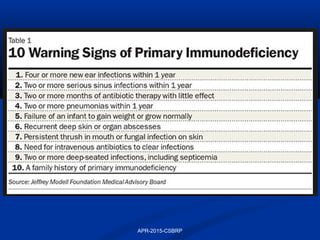
This document discusses immunodeficiency disorders. It describes how deficiencies in antibodies, phagocytes, or complement components can lead to infections by extracellular bacteria. Deficiencies in cell-mediated immunity are associated with recurrent viral, protozoal, and fungal infections. Primary immunodeficiencies are caused by genetic defects, while secondary immunodeficiencies result from infection, toxicity, radiation, or other acquired factors. Specific primary immunodeficiencies that affect B cells, T cells, phagocytes, or the complement system are described. The document also discusses acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) caused by HIV, outlining the virus structure, pathogenesis, clinical features, and diagnosis.