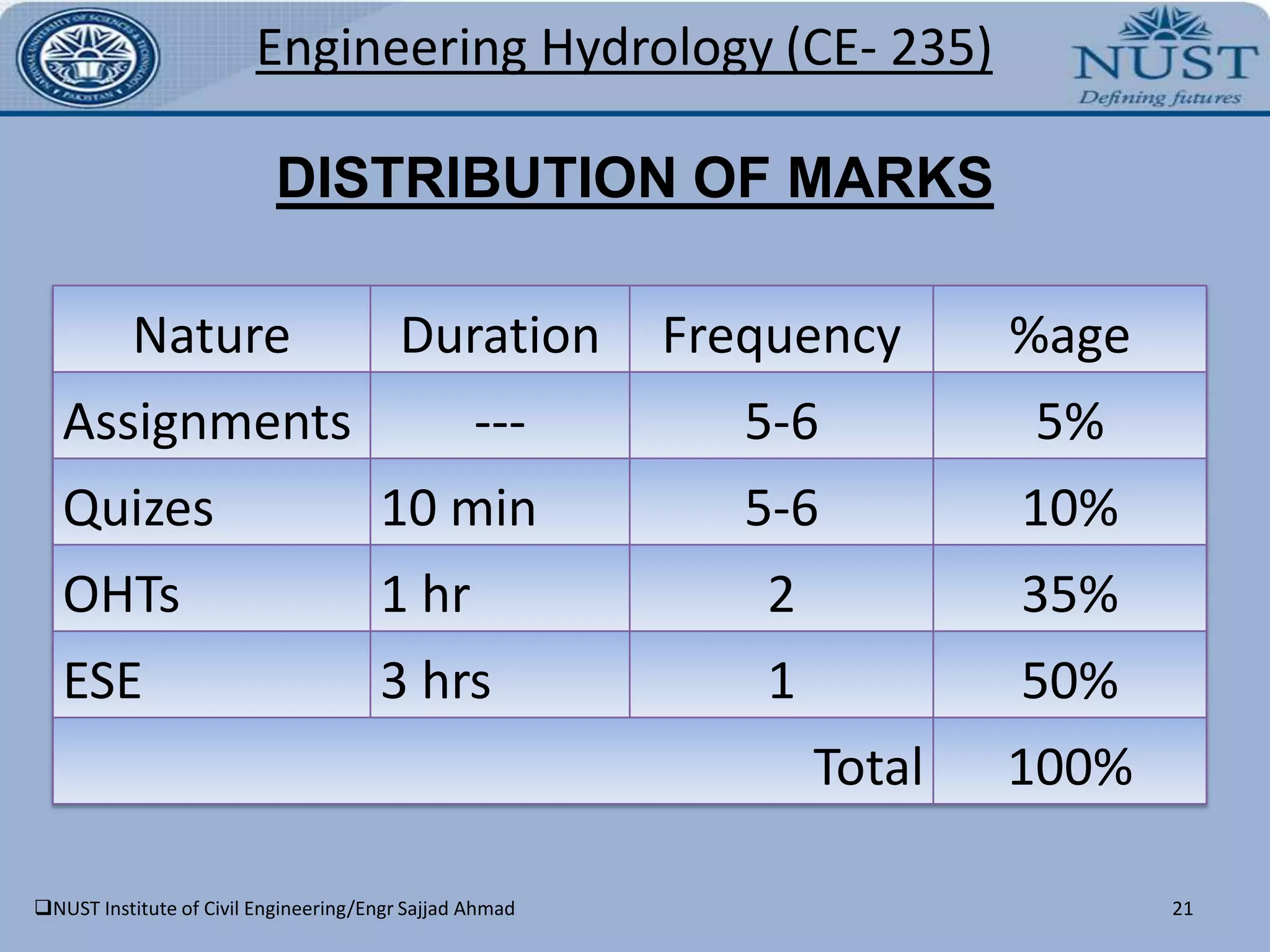
This document outlines the course details for Engineering Hydrology (CE-235) at NUST Institute of Civil Engineering. The course will be taught by Engr. Sajjad Ahmad and covers principles of surface water and groundwater hydrology over 22 lectures. Topics include the hydrologic cycle, precipitation measurement, runoff analysis, streamflow routing, groundwater flow principles, well hydraulics, and tube well construction. Students will be assessed through assignments, quizzes, midterms, and a final exam.