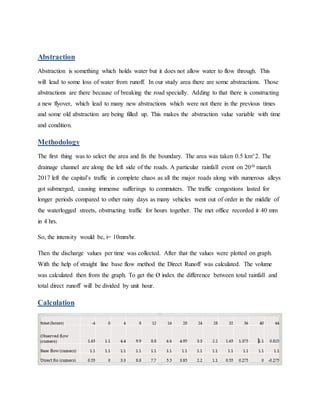
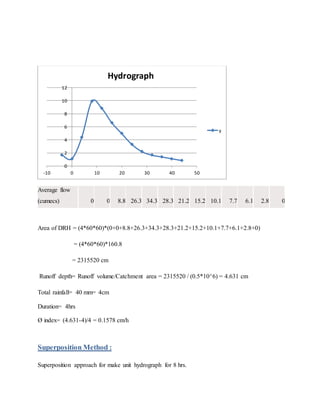
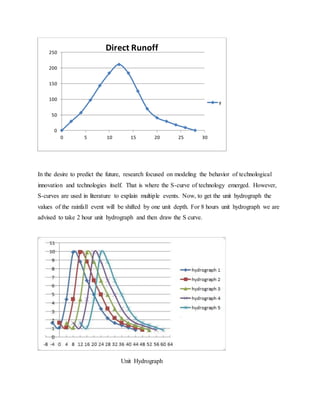
This project analyzed hydrological conditions in the Kuril area of Dhaka, Bangladesh to help drainage engineers design better storm drains. Students measured precipitation, abstraction, direct runoff and discharge rates during a heavy rainfall event. They calculated the runoff depth, total rainfall, duration and unit hydrograph to understand flow patterns. The analysis found the area has high surface runoff due to impervious surfaces and a drainage outlet near Kuril Canal. The project provided practical experience in basic hydrological concepts to help design drainage structures.