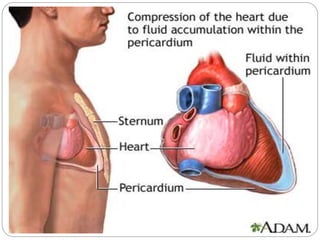
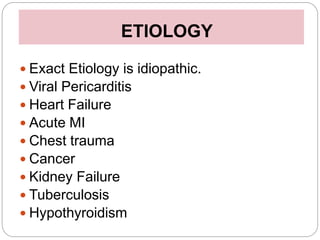
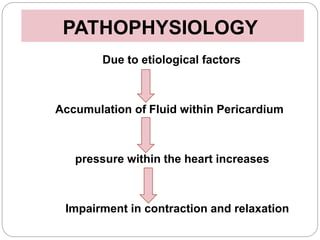
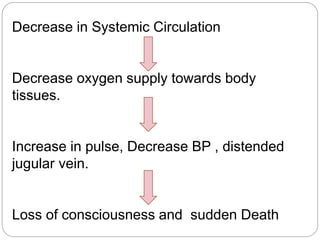
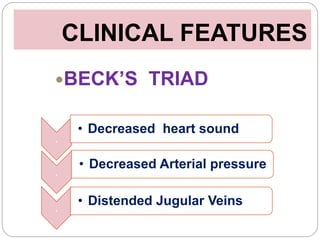
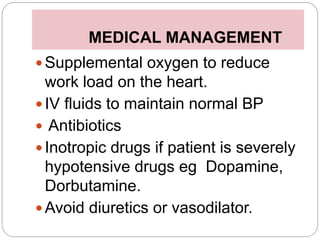
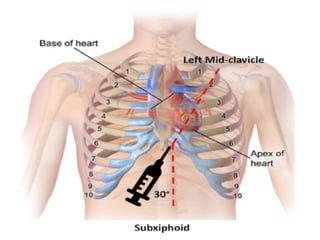
This document discusses cardiac tamponade, which occurs when fluid builds up in the pericardial sac surrounding the heart, putting pressure on the heart and impairing its function. It describes the normal functions of the pericardium, causes of tamponade including infection, heart failure and cancer. Symptoms include Beck's triad of decreased heart sounds, blood pressure and distended neck veins. Diagnosis involves physical exam, ECG, echocardiogram and sometimes CT scan or MRI. Treatment is drainage of excess fluid via pericardiocentesis or surgery. Nursing care focuses on breathing issues, low cardiac output, rest and educating the patient.