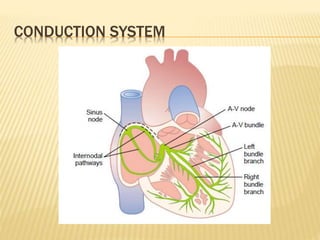
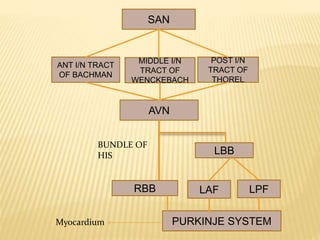
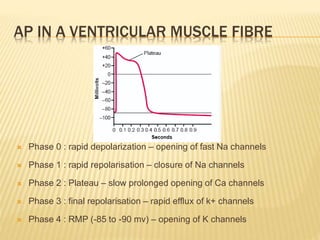
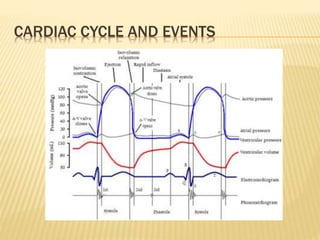
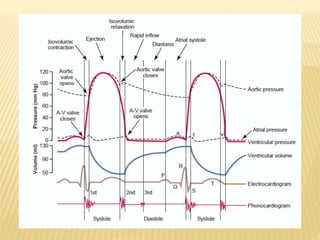
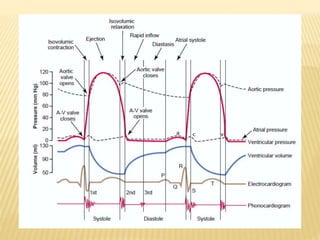
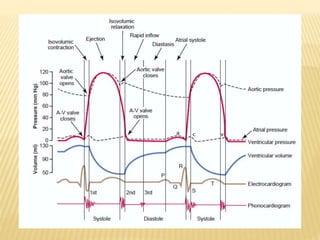
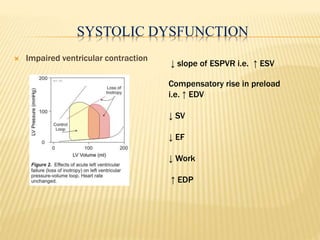
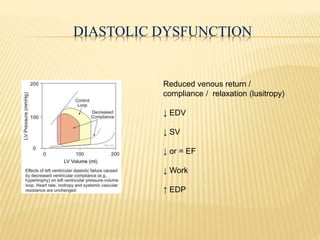
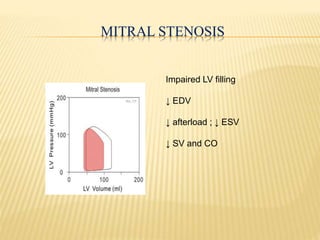
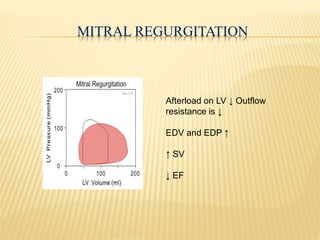
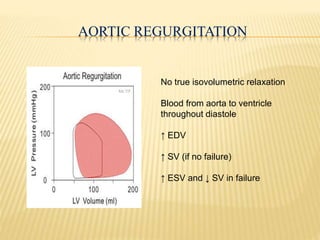
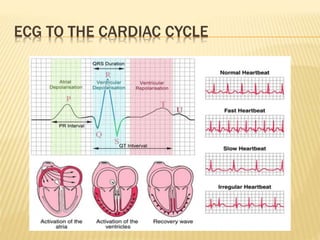
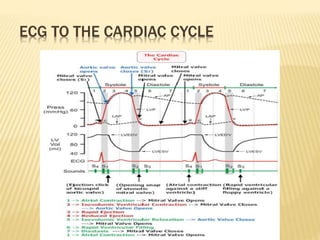
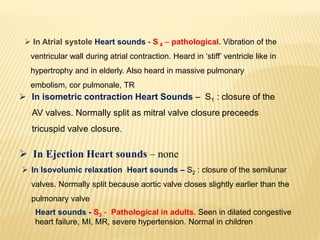
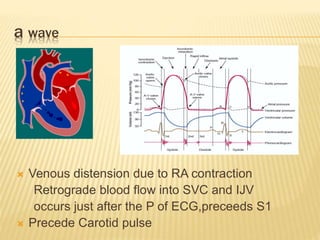
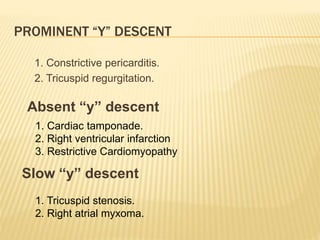
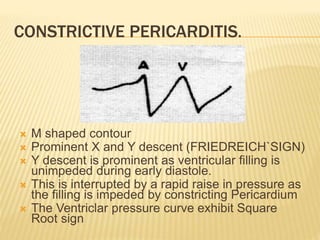
The cardiac cycle describes the sequence of events that occur with each heartbeat. It begins with spontaneous depolarization of the sinoatrial node which generates an electrical impulse that causes the atria to contract. There is a brief delay before the impulse reaches the ventricles allowing the atria to empty blood into the ventricles. The ventricles then contract ejecting blood from the heart.
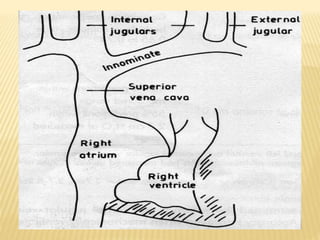
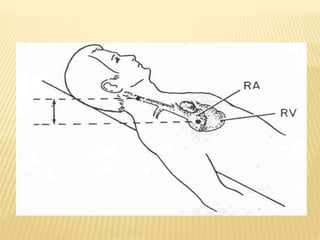
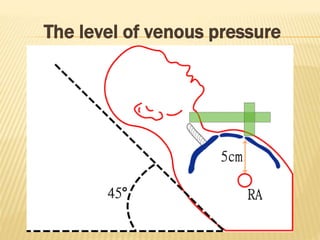
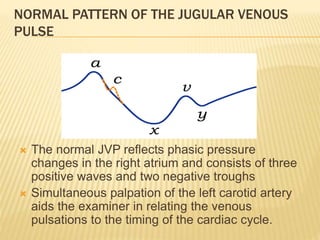
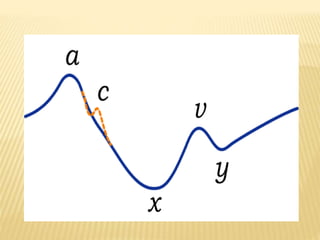
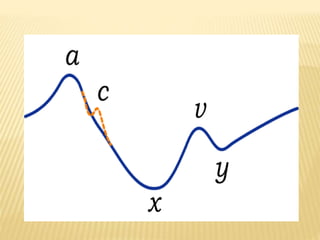
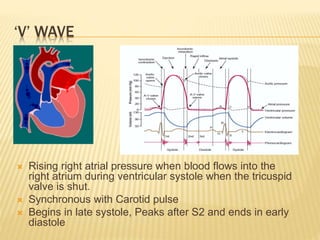
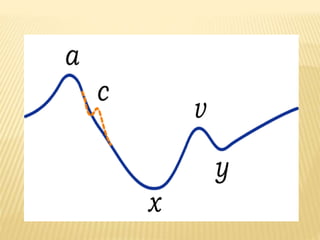
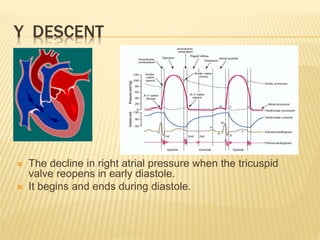
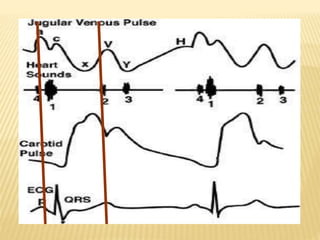
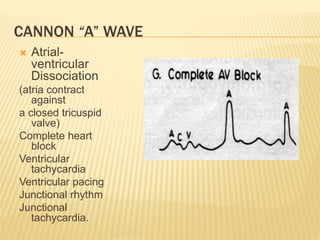
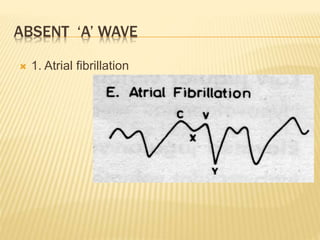
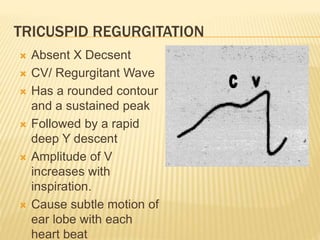
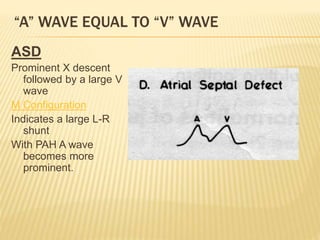
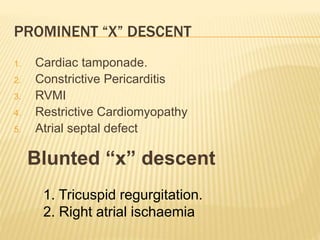
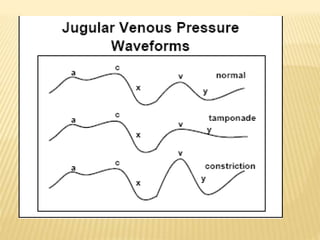
The jugular venous pulse reflects right atrial pressure changes during the cardiac cycle. It normally displays 3 positive waves and 2 negative troughs that can be related to timing of heart sounds on auscultation. Abnormal jugular venous waveforms provide clues about underlying cardiac abnormalities such as increased right heart pressures or valvular