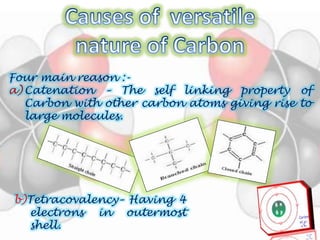
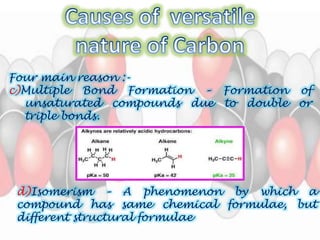
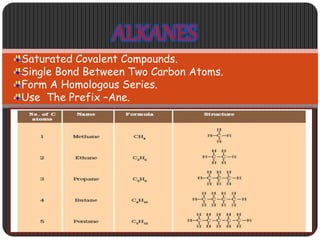
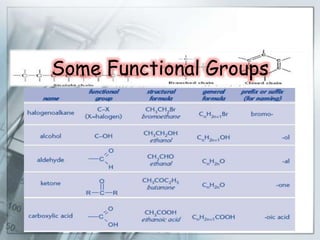
This document is a PowerPoint presentation on carbon and its compounds submitted by a student group. It provides information on carbon including that it is a nonmetallic element with an atomic number of 6 that forms covalent bonds. It discusses the origin of carbon in nature, the reasons for its versatility including catenation and tetracovalency. The presentation also covers different forms of carbon including graphite, diamond and fullerenes as well as saturated and unsaturated compounds. It provides examples of functional groups and homologous series and discusses chemical properties and uses of carbon compounds.