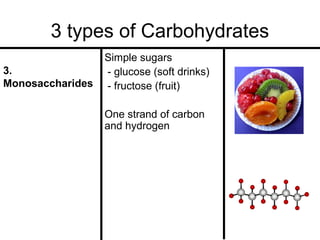
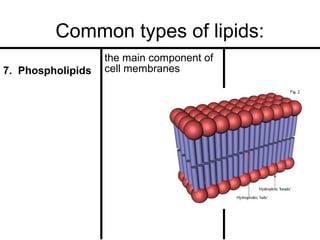
Organic molecules in living organisms are made up of four main types: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates include sugars and starches, proteins include enzymes and antibodies, lipids include fats, and nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. All life on Earth is made of these organic molecules, which contain carbon as a basic building block. Carbon is uniquely able to form four bonds with other atoms, allowing it to link to other carbons and create a diverse array of carbon skeletons essential for life.