This document discusses functional strategies and provides examples in key functional areas. It begins by defining functional strategy as how functional areas achieve corporate objectives through maximizing resource productivity. It then lists common functional strategy objectives like profitability, market share, and innovation.
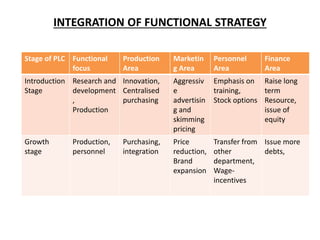
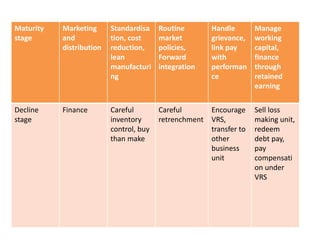
The document goes on to describe different types of functional strategies, including manufacturing, marketing, human resources, research and development, and financial management strategies. For each type, it provides high-level explanations of their focus and processes. Finally, it discusses how functional strategies should be integrated at different stages of the product lifecycle from introduction to maturity to decline.