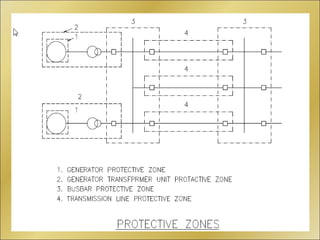
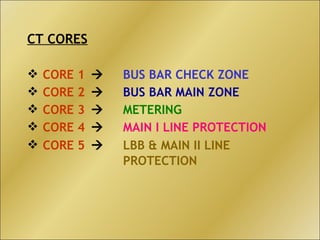
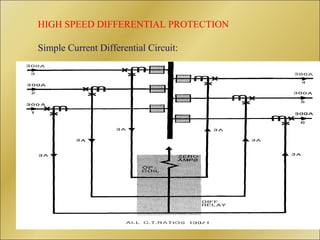
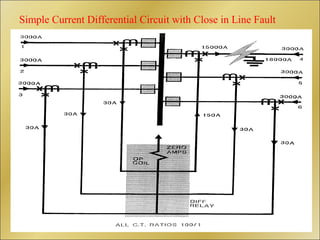
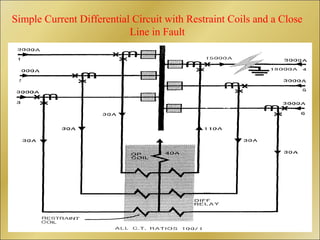
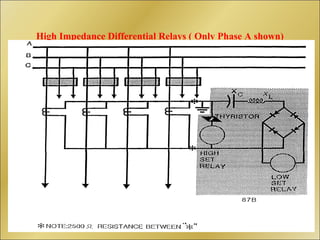
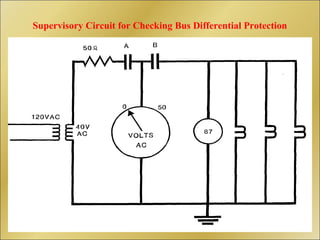
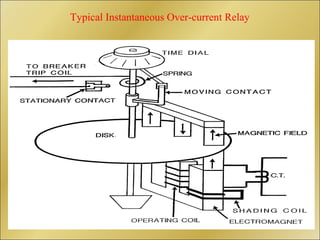
The document discusses bus bar protection in substations, highlighting its importance in safeguarding against faults that can cause widespread disruptions and damage. It outlines the design and operational requirements for effective bus bar protection, including the necessity for high-speed, selective, and reliable systems, particularly in new and existing high voltage substations. Key technical concepts, such as Kirchoff’s current law and the types of bus bar protection, are also covered.