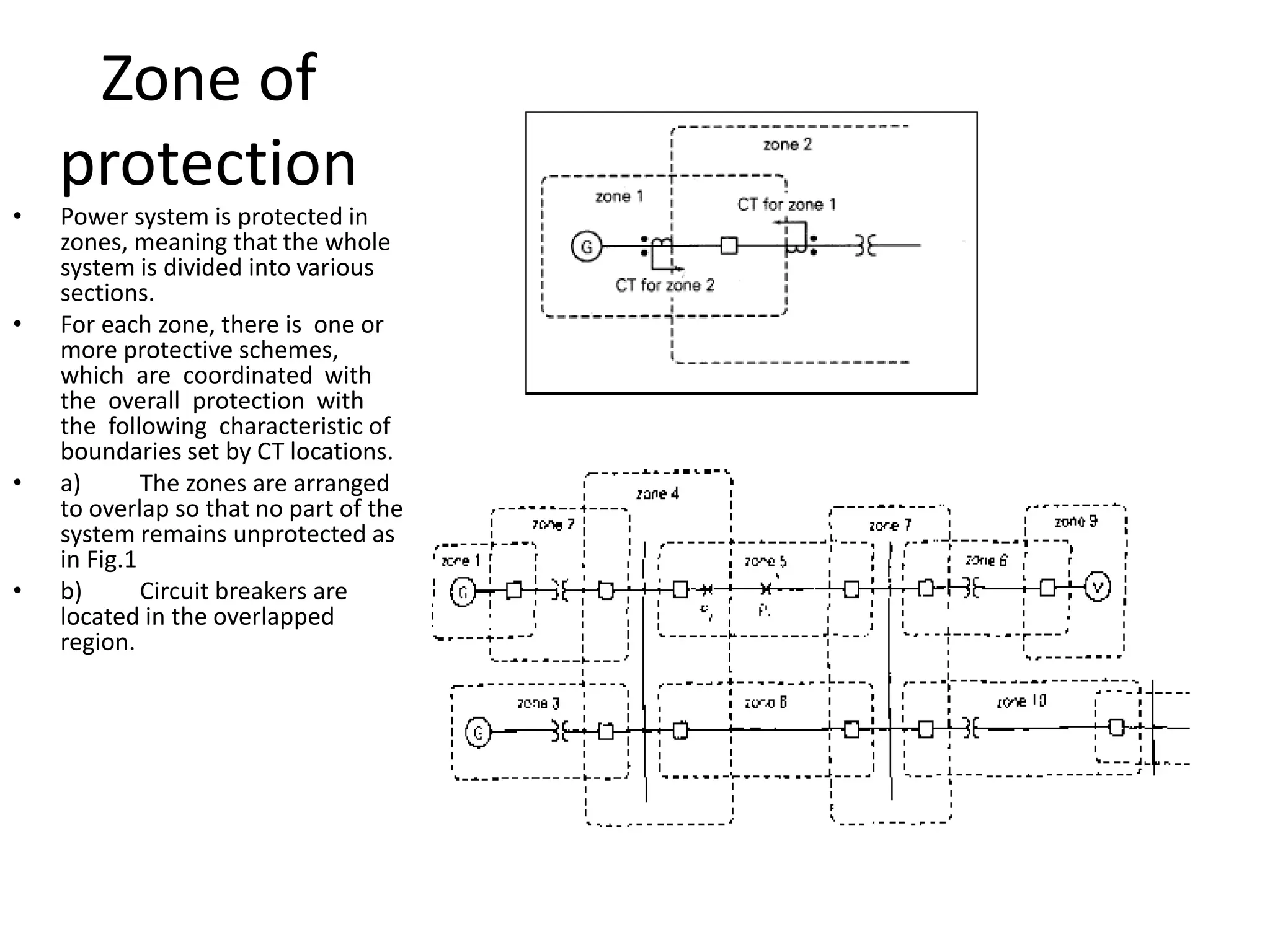
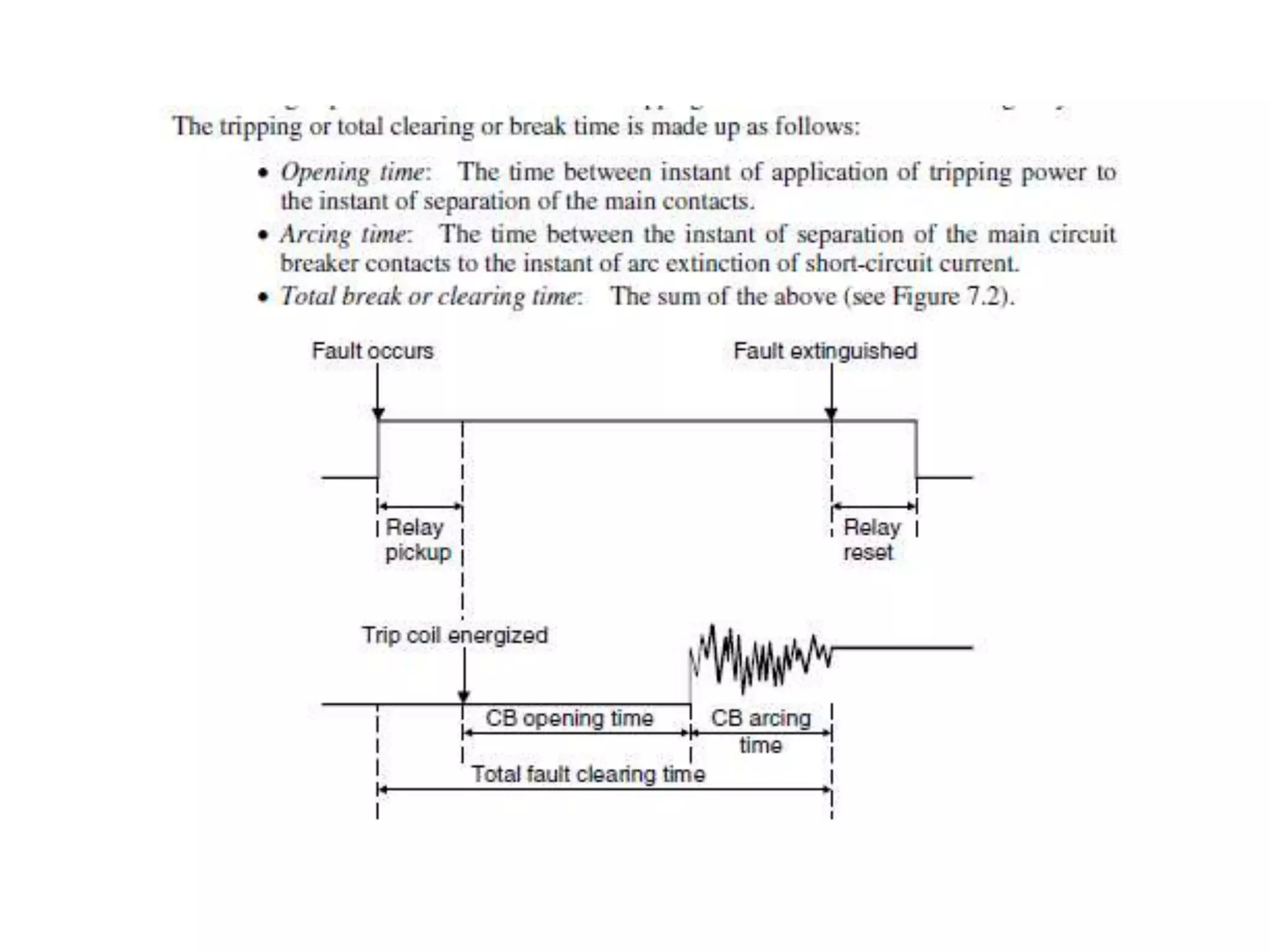
The power system is protected through a zone protection scheme where the system is divided into sections, with each zone having one or more protective relays coordinated with the overall protection system. The zones are arranged to overlap so that no part of the system remains unprotected, and circuit breakers are located in the overlapped regions. Protective relaying schemes must be reliable, selective, and fast acting. Reliability ensures the relay will operate correctly, selectivity allows the relay to distinguish faults inside and outside its zone, and speed minimizes fault duration and equipment damage. Modern high-speed relays have operating times of 1-2 cycles while circuit breakers have interrupting times of 2.5-3 cycles, resulting in total clearing