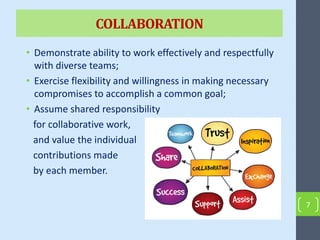
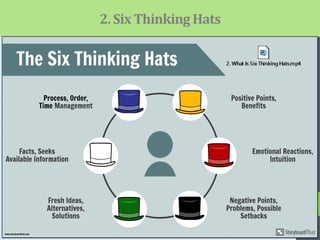
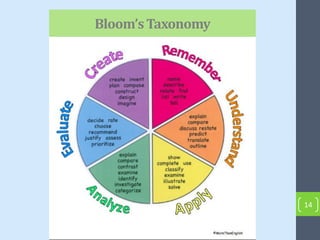
This document outlines strategies for stimulating critical thinking in EFL classes. It discusses developing critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity skills using techniques like reading images, the six thinking hats method, questioning games, gallery walks, the 5 why technique, graphic organizers, identifying facts versus opinions, listing pros and cons, and group projects. The document concludes that using these strategies helps engage students, improve understanding and retention, develop problem-solving abilities, and build skills necessary for future success.