This document discusses 10 effective methods for infusing critical thinking into online education. It begins by explaining why critical thinking is important as it cultivates student curiosity and encourages engagement, integrity, empathy and responsibility. It then outlines 10 methods which include: providing thoughtful curriculum and critical thinking questions, using Bloom's taxonomy, arousing student curiosity with assignments, stressing the importance of critical thinking, providing in-depth assignments, teaching transferable decision making skills, developing effective online groups, exposing students to cultural conditioning, and implementing and evaluating virtual learning. The goal is to prepare students to be visionary leaders with strong critical thinking skills.









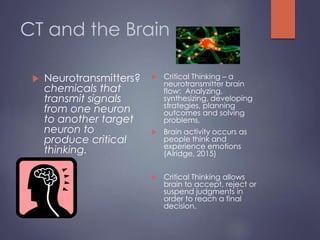

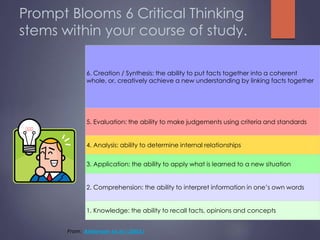
![Bloom’s Taxonomy sample
questions: Stem Questions
1: Knowledge Exhibits previously learned material by recalling
facts, terms, basic concepts and answers.
What is . . . ?
When did ____ happen?
How would you explain . . . ?
Why did . .. ?
How would you describe . .. ?
2: Comprehension Demonstrating understanding of facts and
ideas by organising, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving
descriptions and stating main ideas.
How would you compare . .. ? contrast.. ?
Explain in your own words . . . ?
What facts or ideas show . .. ?
What evidence is there that…?
3: Application Solving problems by applying acquired
knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way.
What examples can you find to . . . ?
How would you show your understanding of. .. ?
What approach would you use to ... ?
What might have happened if. . . ?
4: Analysis Examining and breaking information
into parts by identifying motives or causes; making
inferences and finding evidence to support
generalisations.
What inference can you make from. . . ?
How would you classify . . . ?
How would you categorise . .. ?
Can you identify the difference parts... ?
5: Evaluation Presenting and defending opinions by
making judgments about information, validity of
ideas or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
How would you compare ……?
Which do you think is better….?
Evaluate contribution of ….. to …………….
What was the value or importance of …….. in
…………..?
What would you have recommended if you had been
……?
6: Creation / Synthesis: Compiling information
together in a different way by combining elements in
a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions.
What might have happened if… ?
Can you propose an alternative interpretation to that
of ……. . ?
Is there a marmite solution [1] here?http://www.ucdoer.ie/index.php/How_to_Ask_Questions_that_Prompt_Critical_Thinking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss10effectivectmethods-150218201030-conversion-gate02/85/10-Effective-Methods-Infusing-Critical-Thinking-in-Online-Education-13-320.jpg)




![FYI: Importance of CT by
International Associations
The National Council of Teachers of English (NCTE) Committee on Critical
Thinking "a process which stresses an attitude of suspended judgment,
incorporates logical inquiry and problem solving, and leads to an evaluative
decision or action." Critical thinking refers to a "way of reasoning that
demands adequate support for one's beliefs and an unwillingness to
be persuaded unless the support is forthcoming."
Association of American Colleges and Universities (AACU) survey of business
and non-profit leaders found that 93% believe "a demonstrated capacity to
think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more
important than [a job candidate’s] undergraduate major." More than 75% of
those surveyed say they want more emphasis on critical thinking, complex
problem solving, written and oral communication, and applied knowledge in
real-world settings for all colleges and universities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss10effectivectmethods-150218201030-conversion-gate02/85/10-Effective-Methods-Infusing-Critical-Thinking-in-Online-Education-18-320.jpg)















![Reference Websites:
http://onlinelearninginsights.wordpress.com/2013/10/01/how-to-
promote-critical-thinkin-with-online-discussion-forums/
http://www.saylor.org/courses/phil102/
http://onlinelearninginsights.wordpress.com/2013/10/01/how-to-
promote-critical-thinking-with-online-discussion-forums/
http://austhink.com/critical/
http://www.editlib.org/p/36242/ ]
http://www.editlib.org/noaccess/36242/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ss10effectivectmethods-150218201030-conversion-gate02/85/10-Effective-Methods-Infusing-Critical-Thinking-in-Online-Education-34-320.jpg)