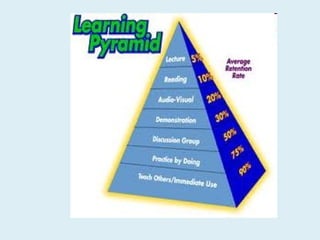
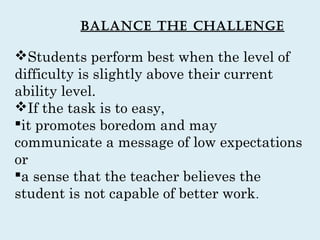
This document discusses strategies for all-inclusive learning. It begins by asking teachers to reflect on students who struggled in school. It then discusses challenges in motivating these at-risk students and implementing new instructional approaches. The rest of the document provides strategies for teachers, including understanding different learning styles, providing feedback, balancing challenges, and establishing a sense of belonging in the classroom. The overall message is that using diverse, supportive teaching strategies can help engage even the most difficult students.