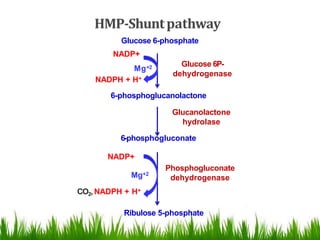
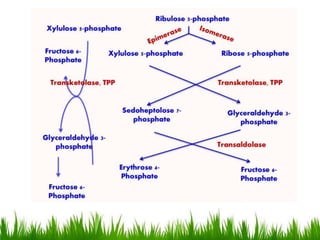
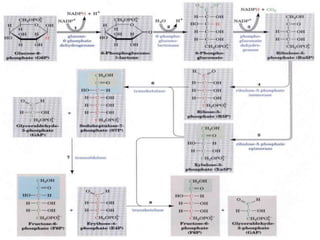
The HMP shunt, also known as the pentose phosphate pathway or phosphogluconate pathway, is an alternative pathway to glycolysis and the TCA cycle for glucose oxidation. It is more anabolic in nature and concerned with biosynthesis of NADPH and pentoses. The pathway occurs in the cytosol of tissues involved in biosynthesis like the liver, adipose tissue, and erythrocytes. It is significant in generating NADPH and pentoses like ribose-5-phosphate. NADPH is important for biosynthesis of fatty acids, steroids, and antioxidant defense while pentoses are precursors for nucleic acid synthesis. Regulation involves inhibition of the first step by NADPH. Genetic deficiencies can