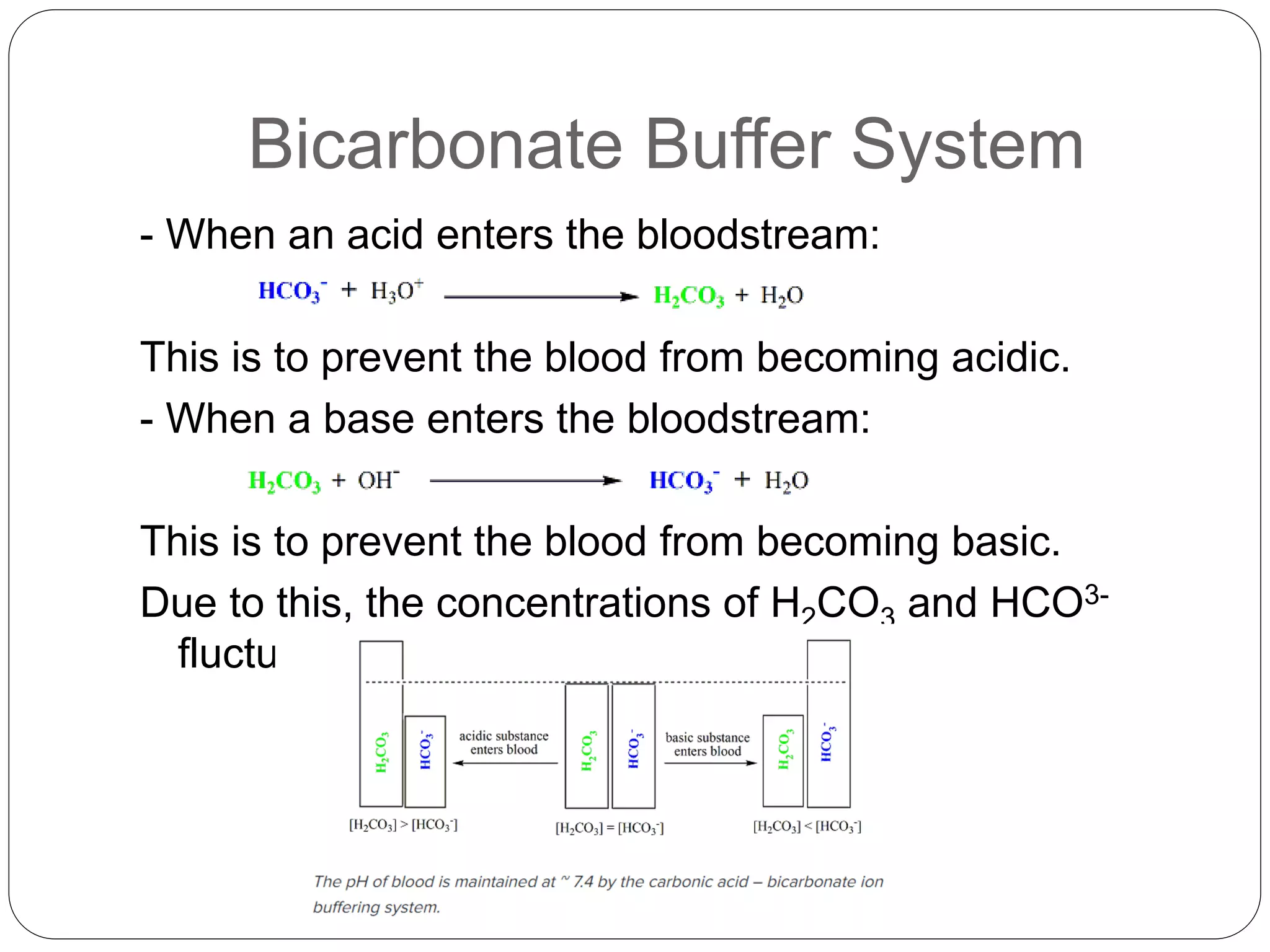
The blood buffer system maintains blood pH between 6.8-7.4 by using bicarbonate, carbonic acid, and other buffers. When acids enter the bloodstream, bicarbonate buffers help prevent acidosis by neutralizing them. Similarly, when bases enter, bicarbonate helps prevent alkalosis. Abnormal pH outside this range can denature enzymes and cells, stopping bodily functions and potentially causing death. Acidosis results from excess acid and alkalosis from excess base, requiring treatment of the underlying cause to restore pH balance.