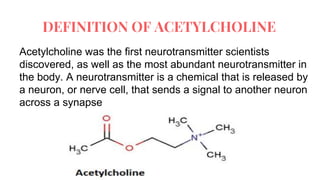
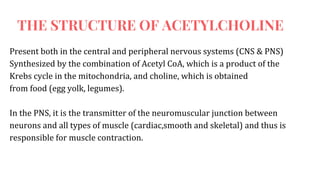
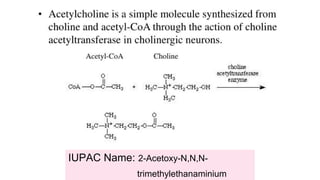
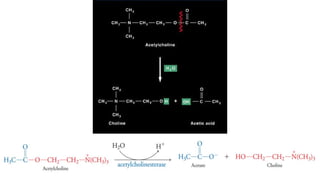
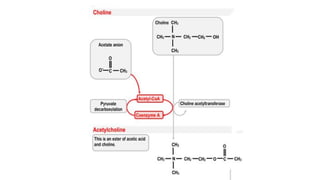
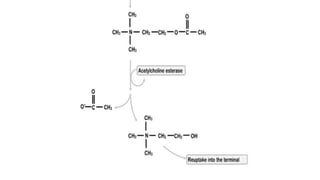
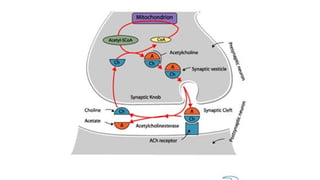
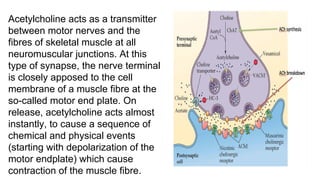
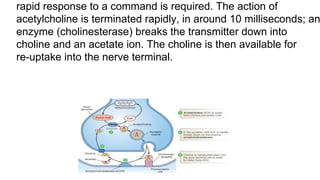
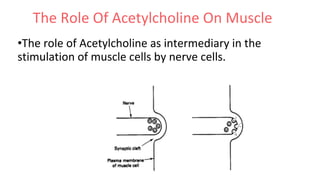
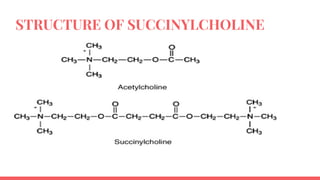
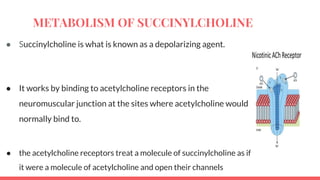
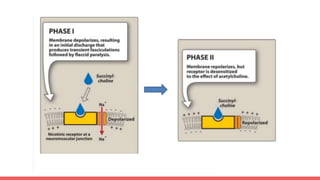
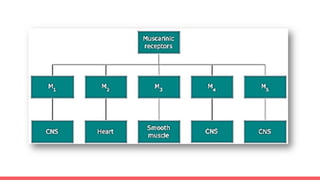
Acetylcholine and succinylcholine are important neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the body and acts as a chemical messenger between neurons and muscles. It is synthesized from choline and acetyl-CoA and works by binding to nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Succinylcholine is a neuromuscular blocking drug that causes paralysis by binding to acetylcholine receptors and depolarizing muscle cells. Both acetylcholine and succinylcholine act at the neuromuscular junction to either stimulate or block muscle contraction. Their effects are location-dependent, with risks including hyperkalemia and malignant hyperthermia.