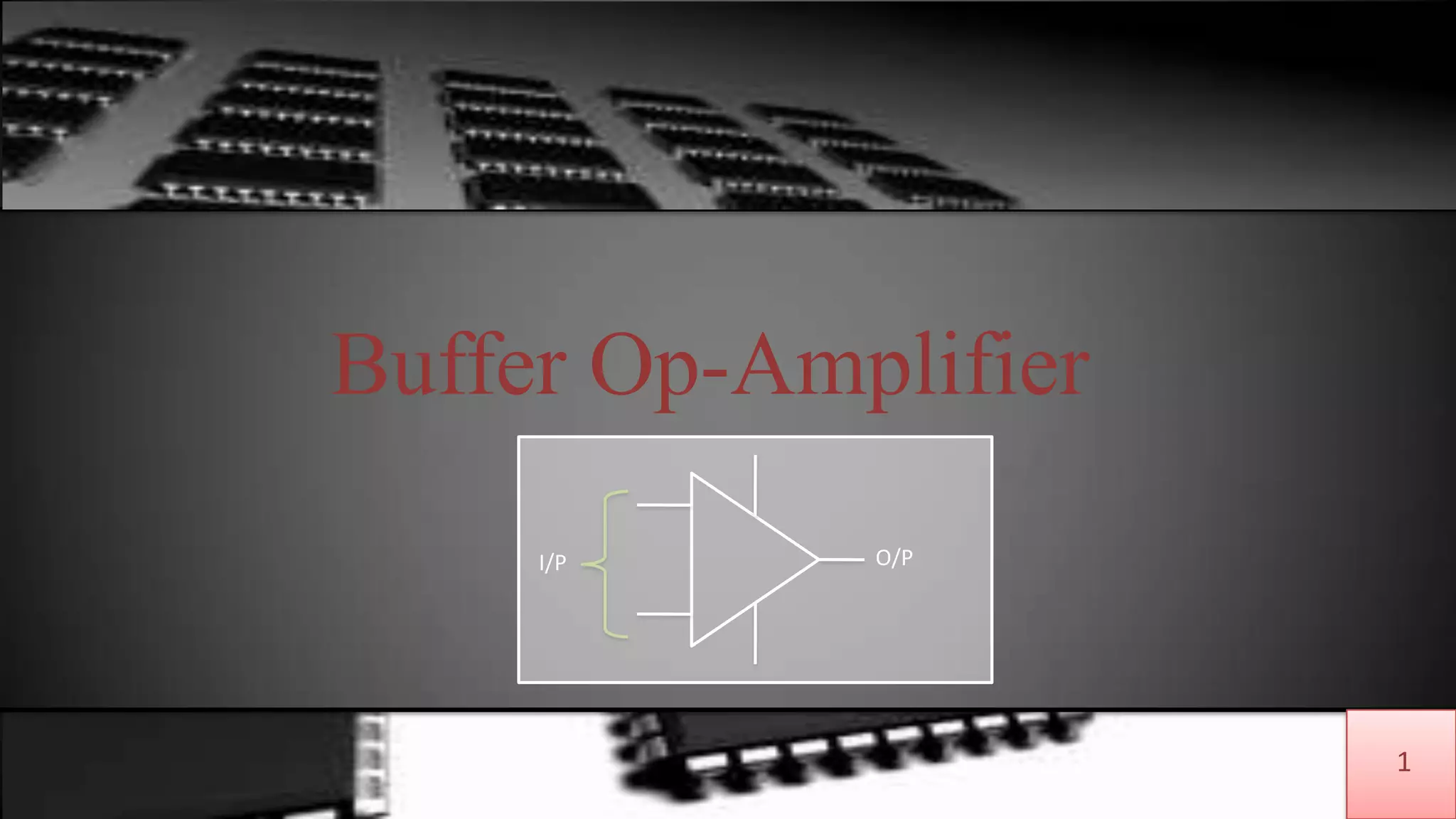
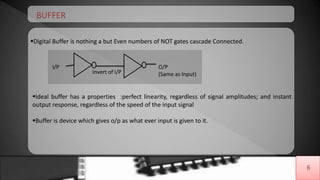
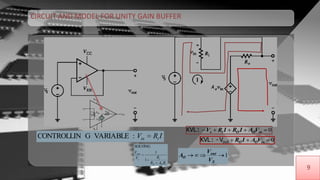
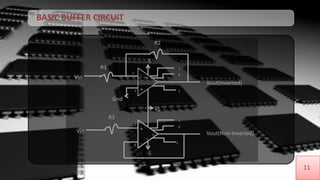
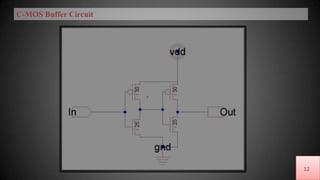
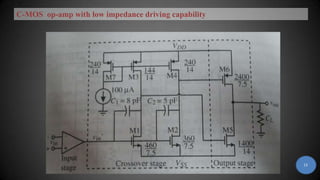
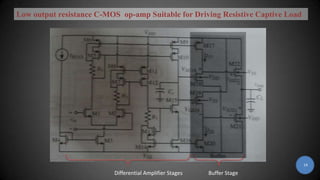
The document discusses buffer amplifiers and operational amplifiers. It defines a buffer as a device that provides an output that is identical to its input. An operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower acts as a buffer amplifier, with a gain of exactly 1. This allows the buffer to provide electrical isolation while maintaining the signal voltage level. Real op-amps can achieve gains very close to 1, making them suitable for use as buffer amplifiers. Applications of buffer amplifiers include driving resistive loads and use in sensor and data acquisition systems.