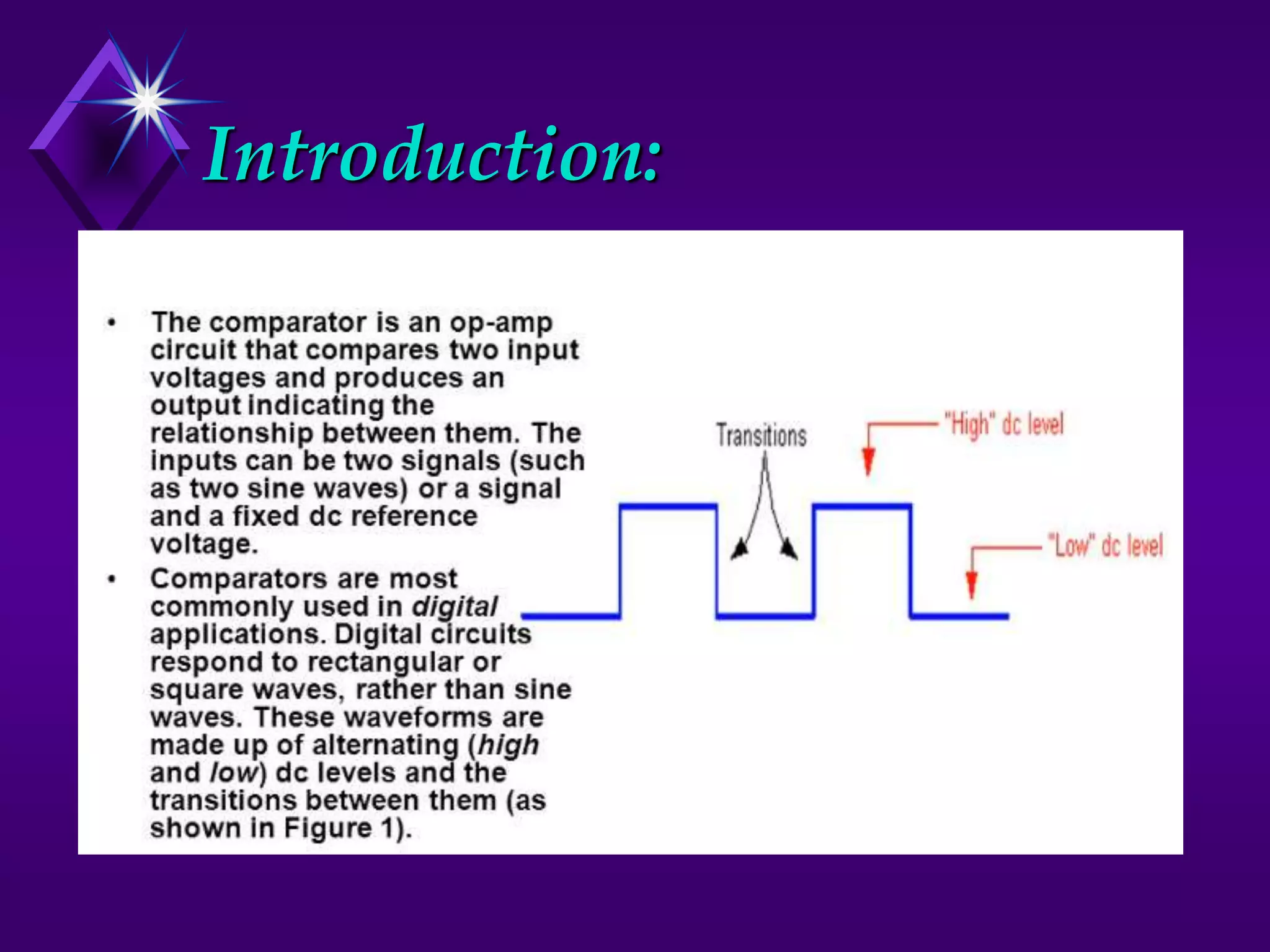
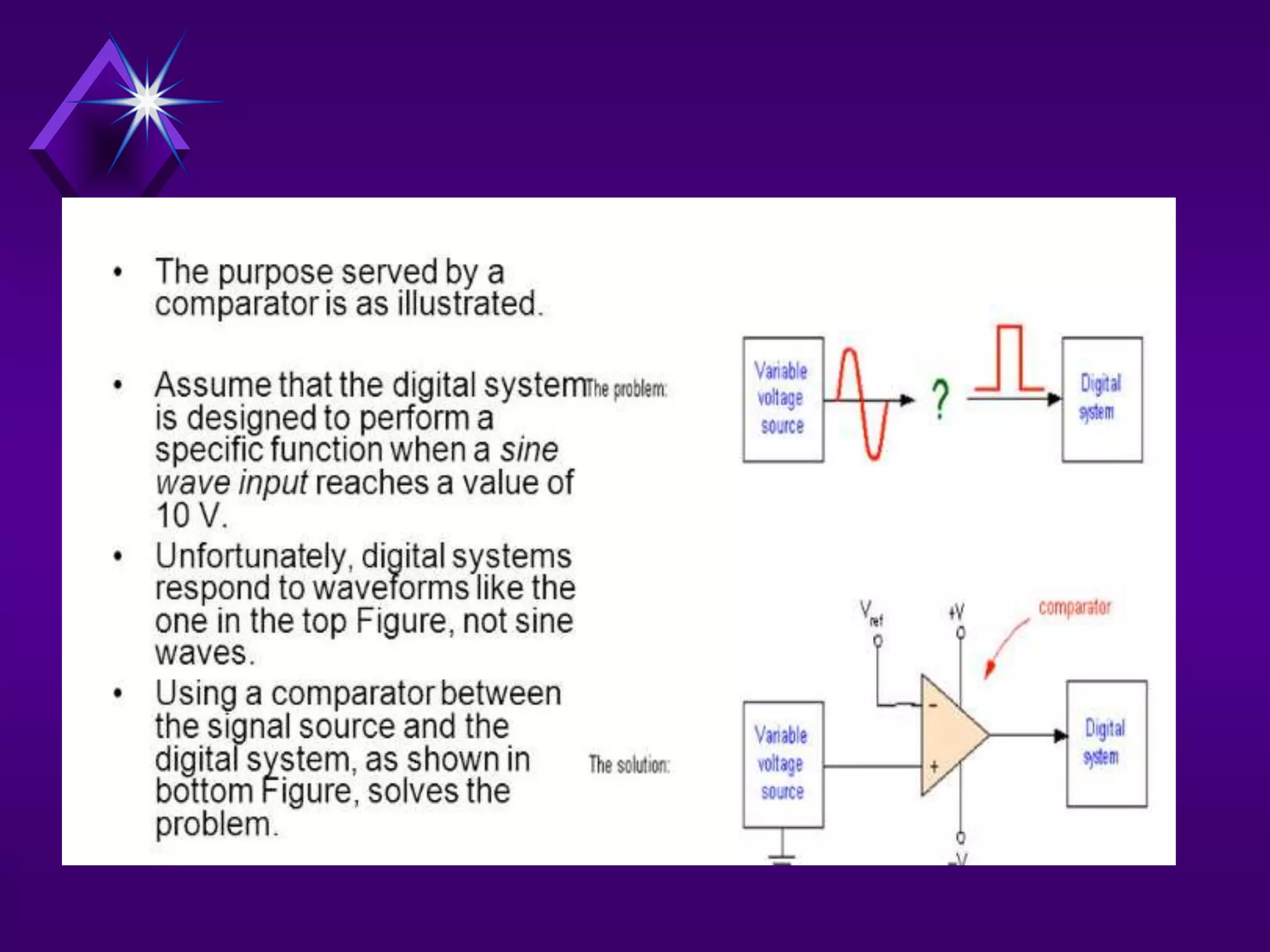
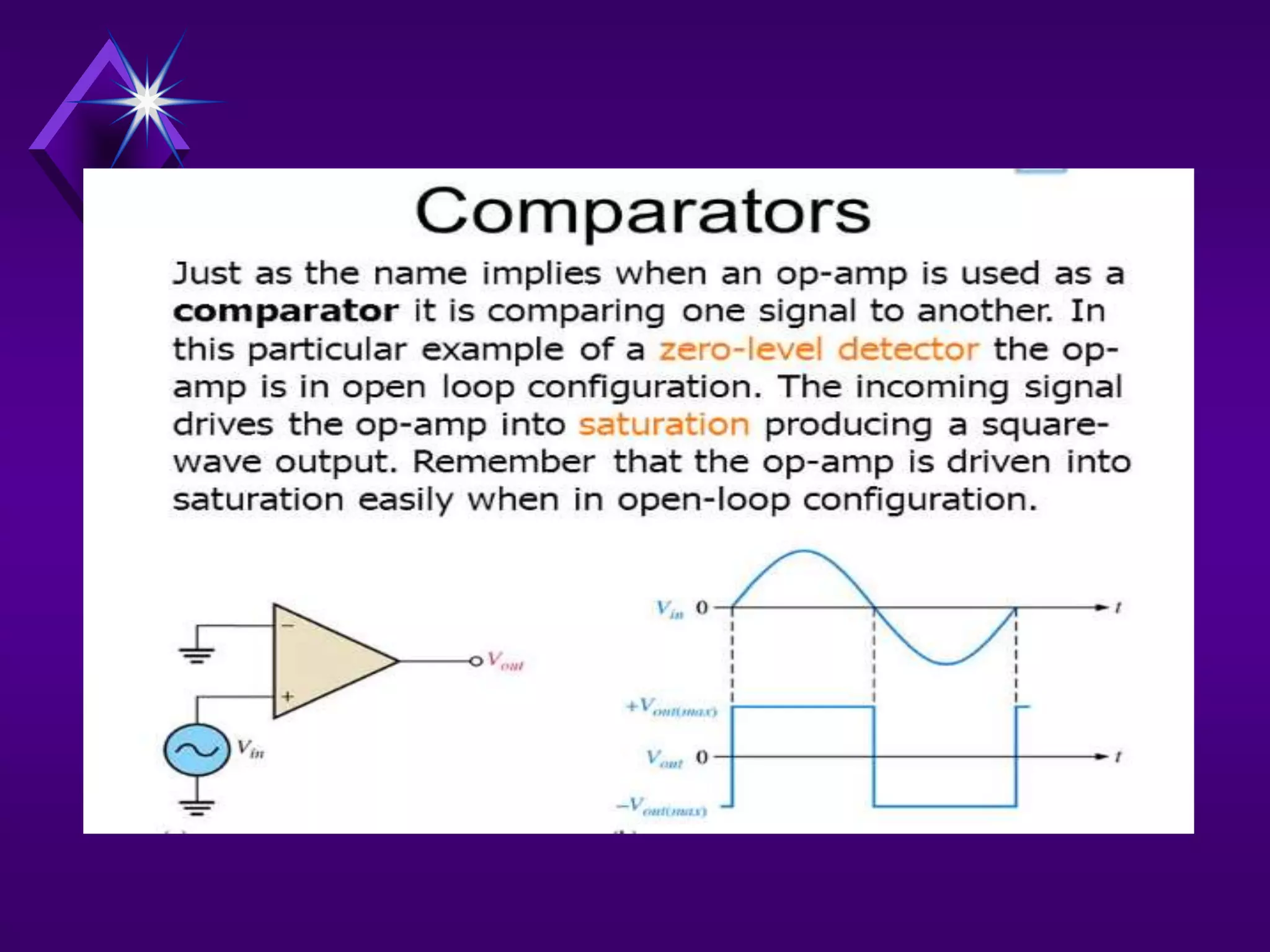
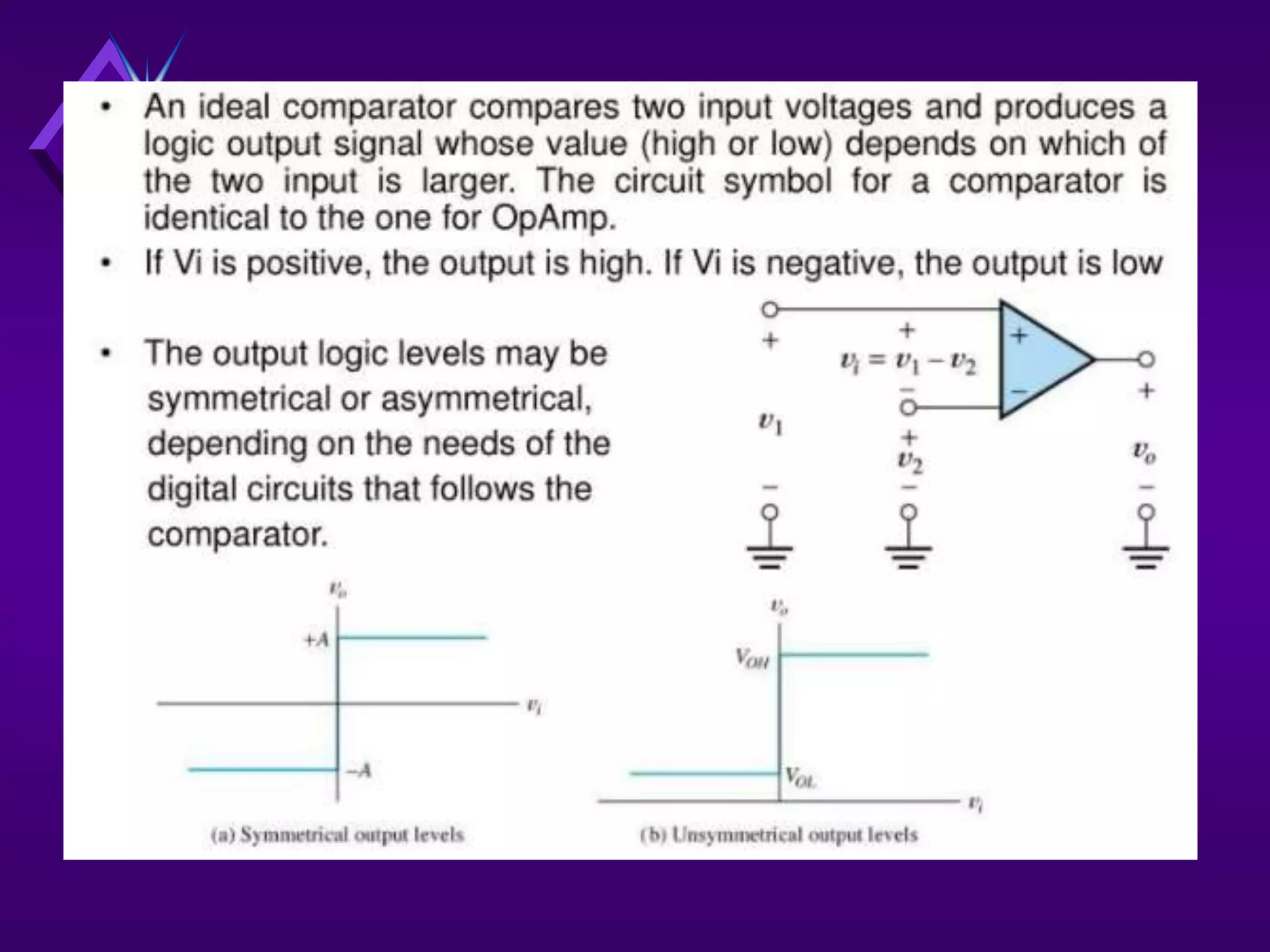
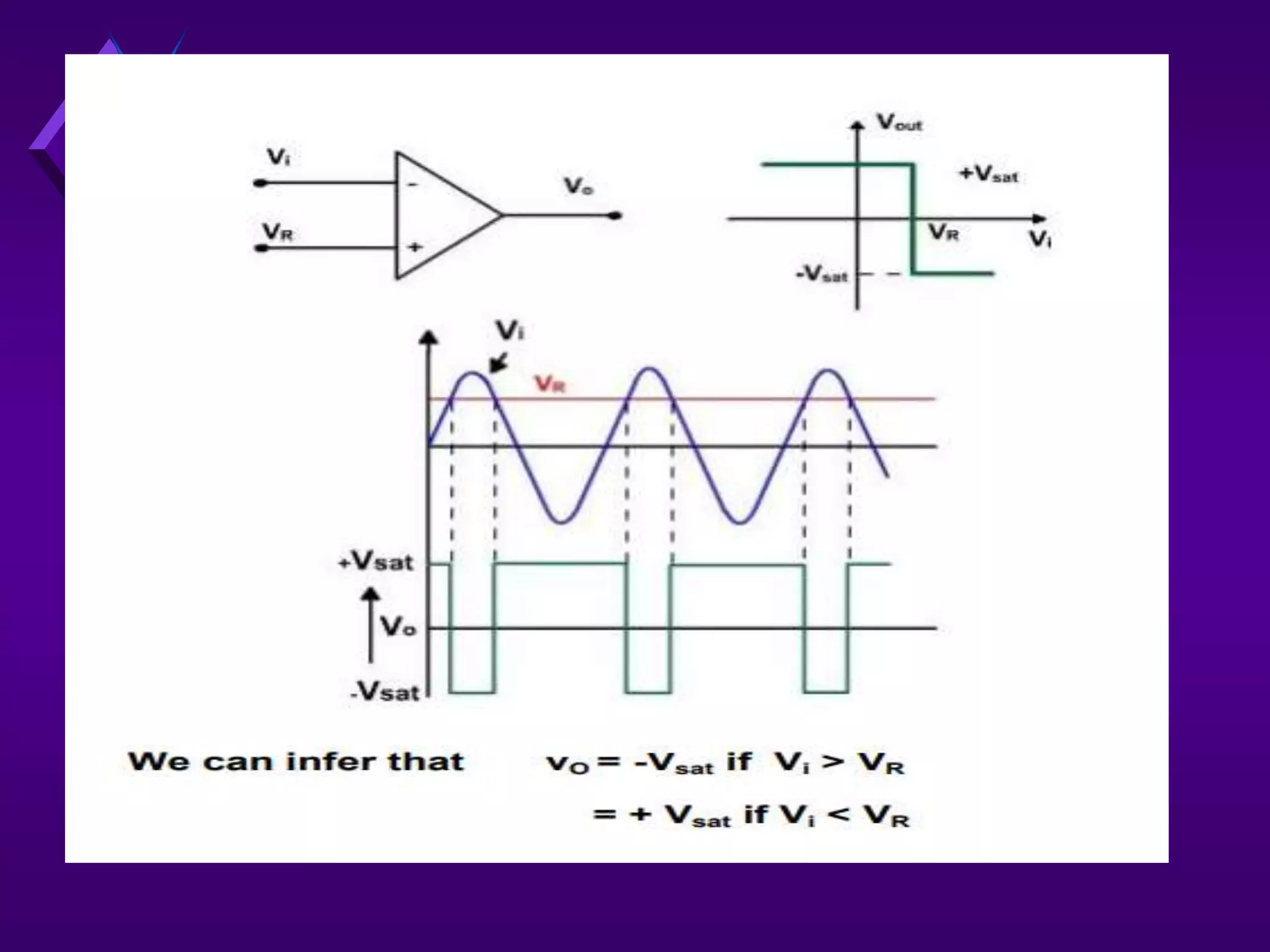
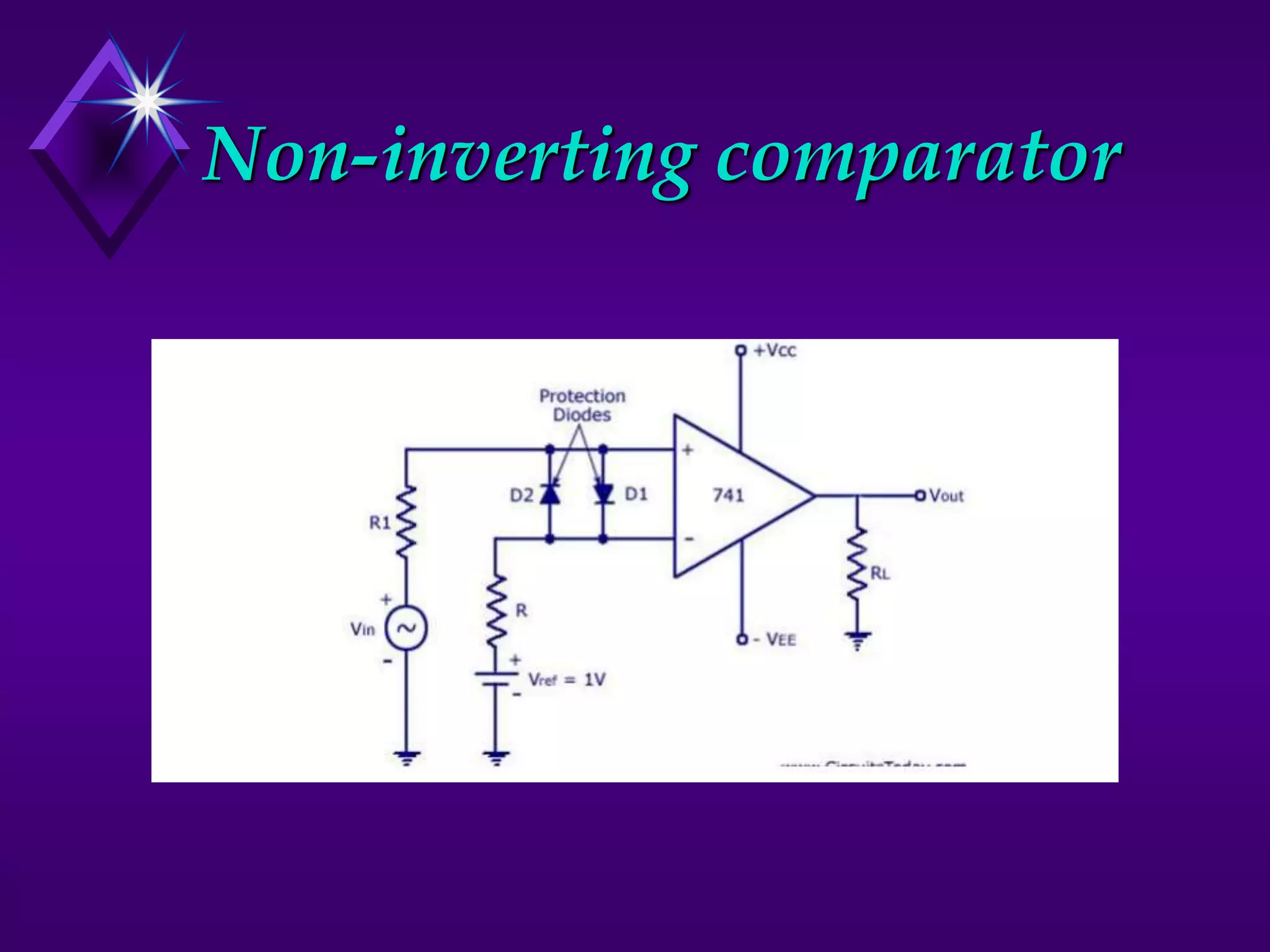
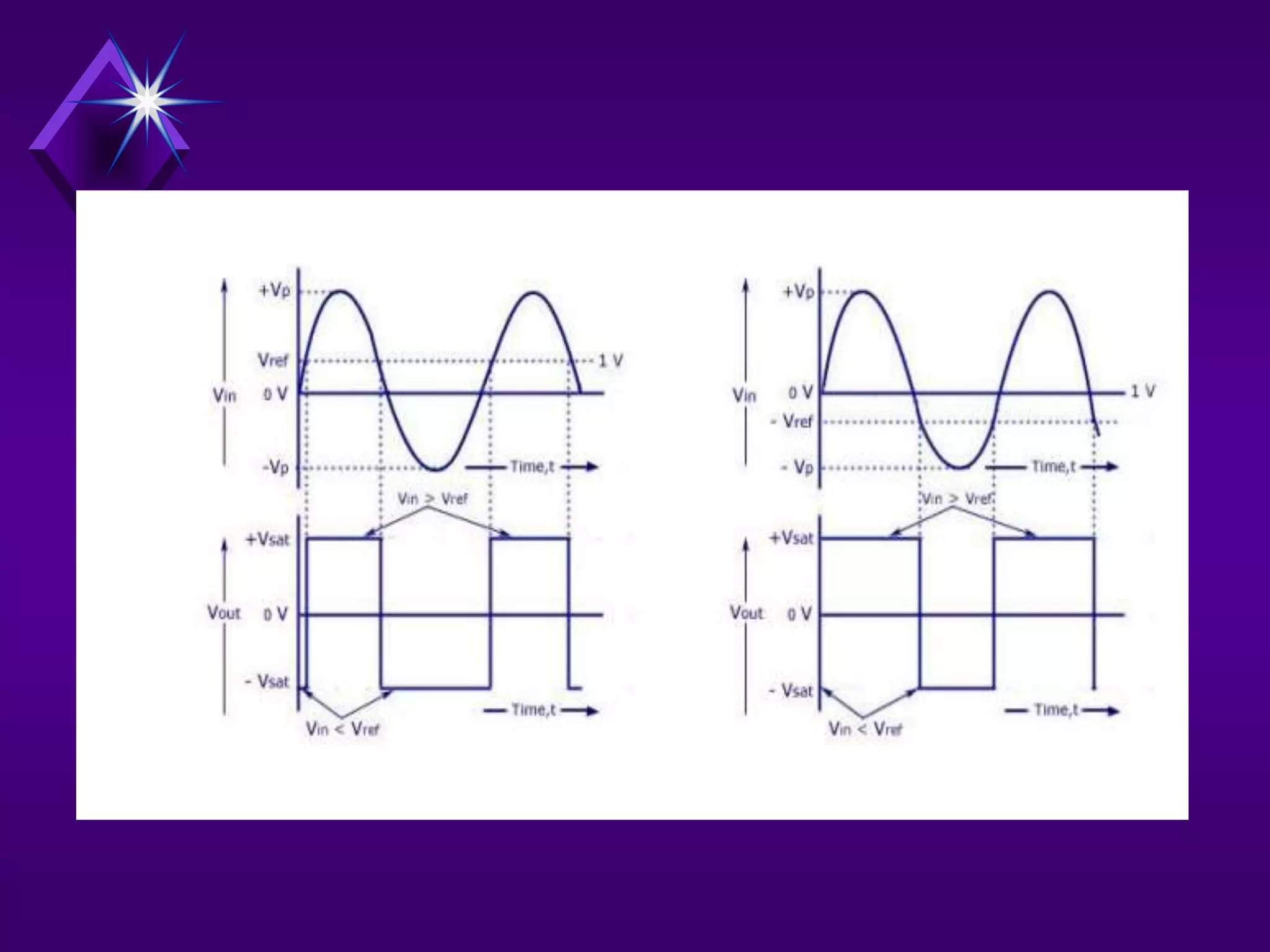
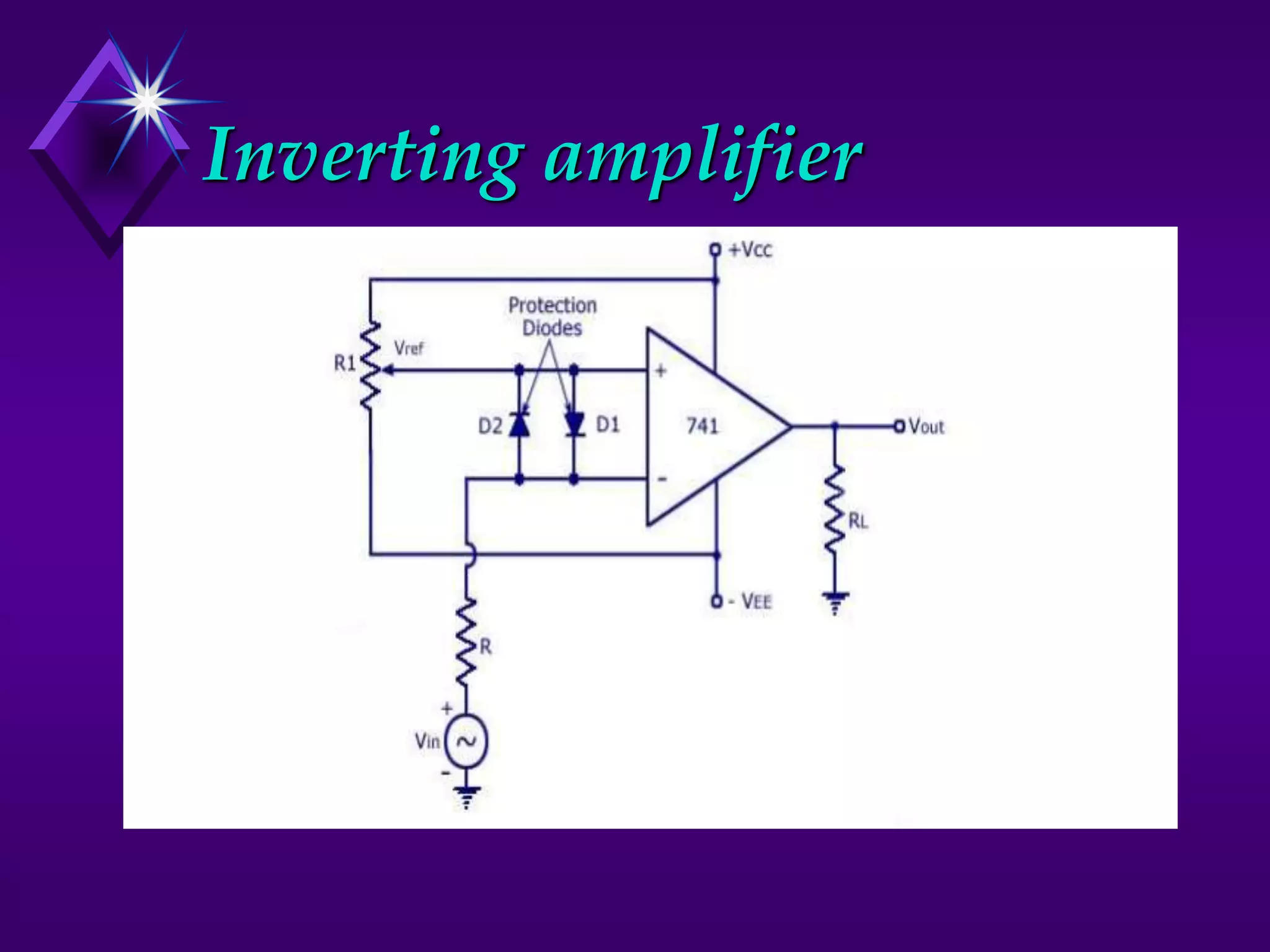
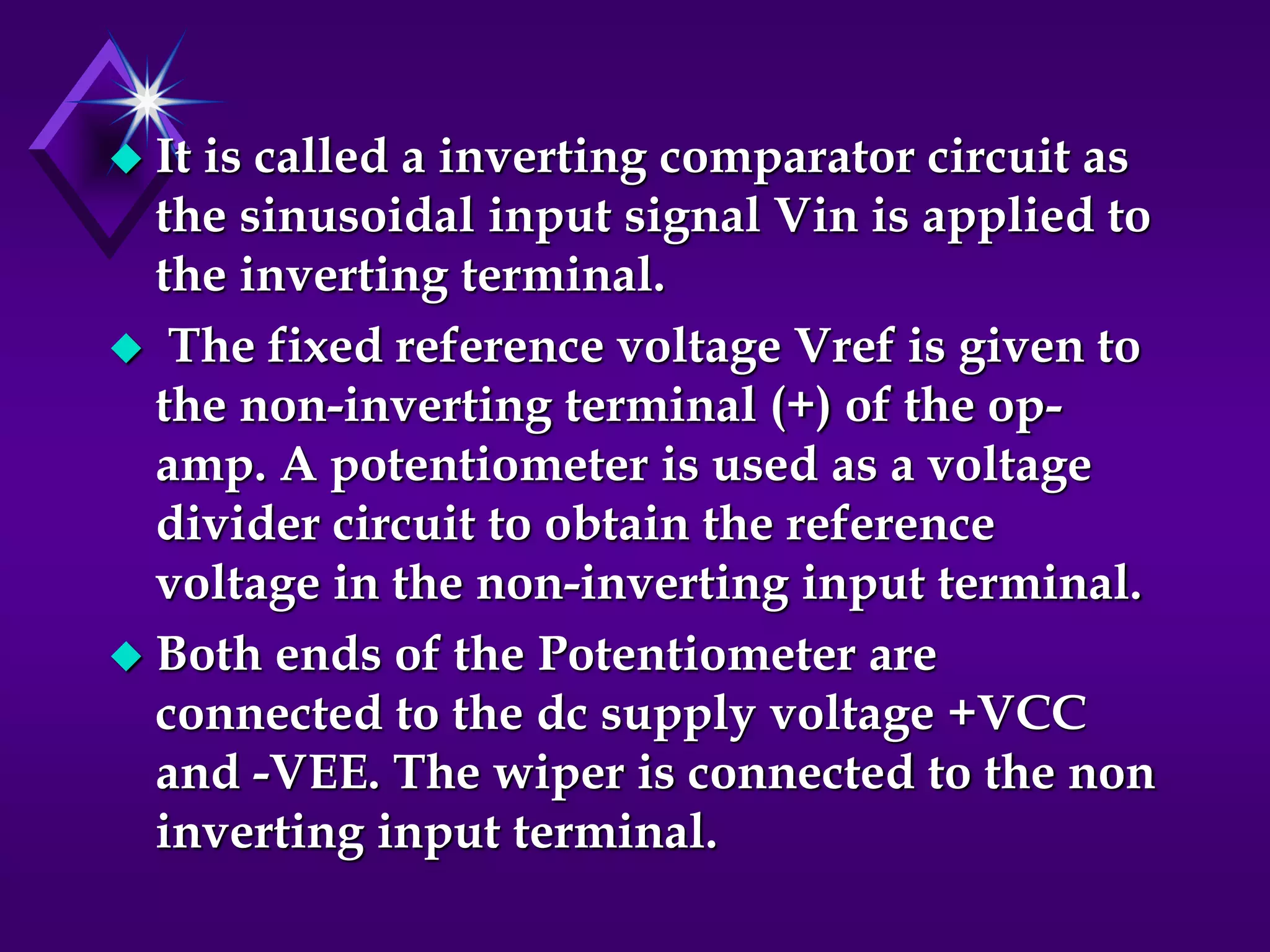
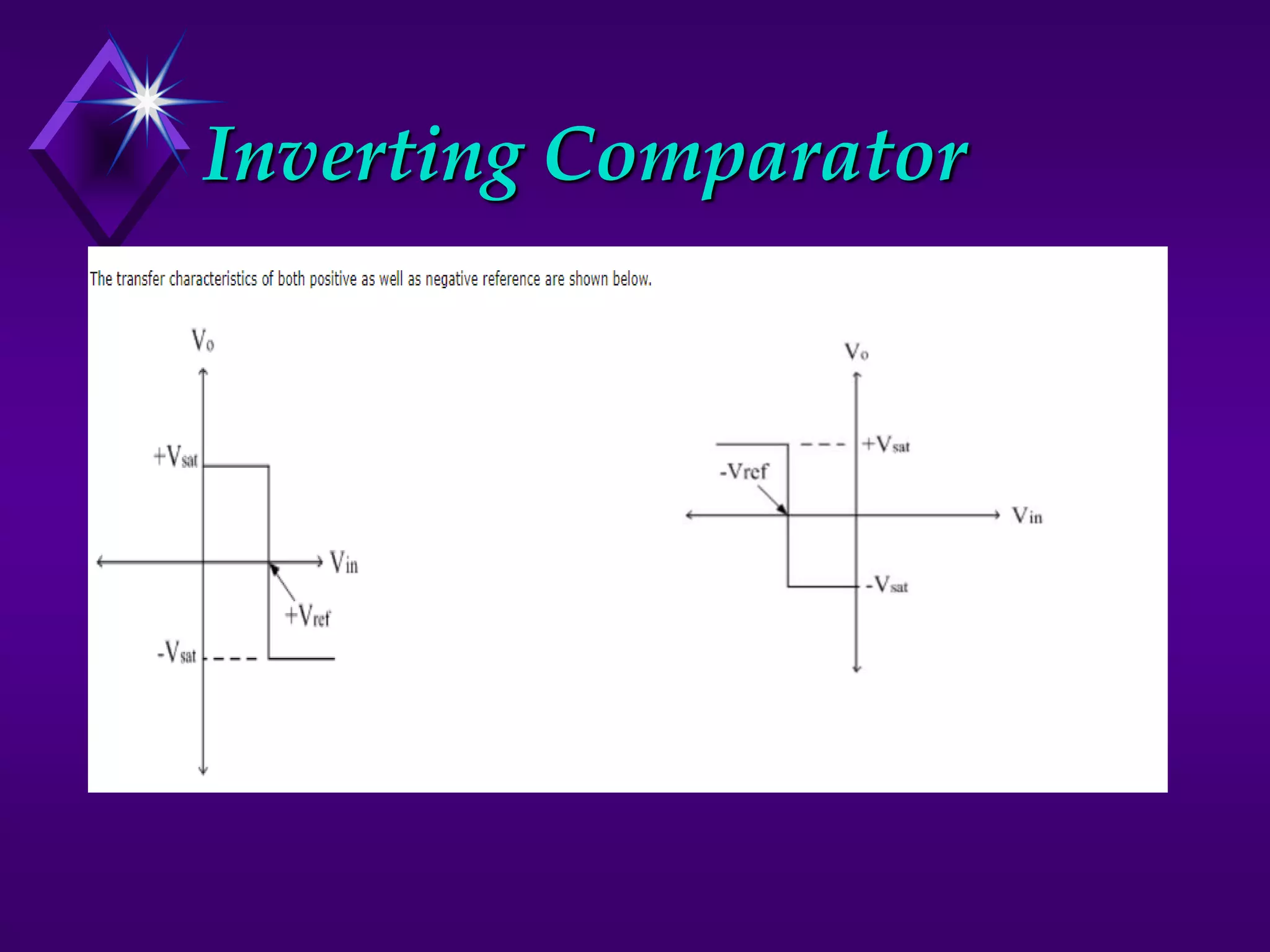
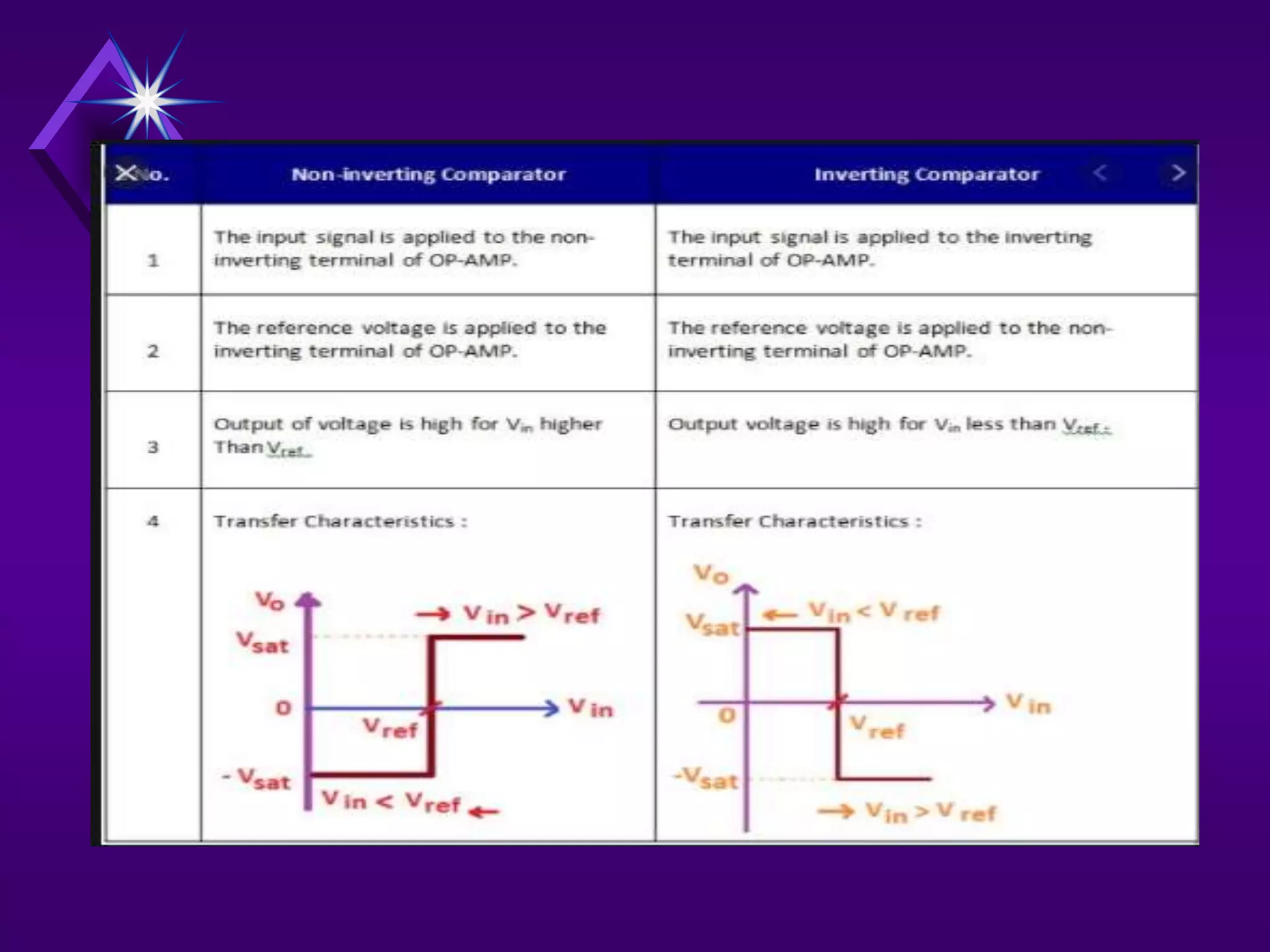
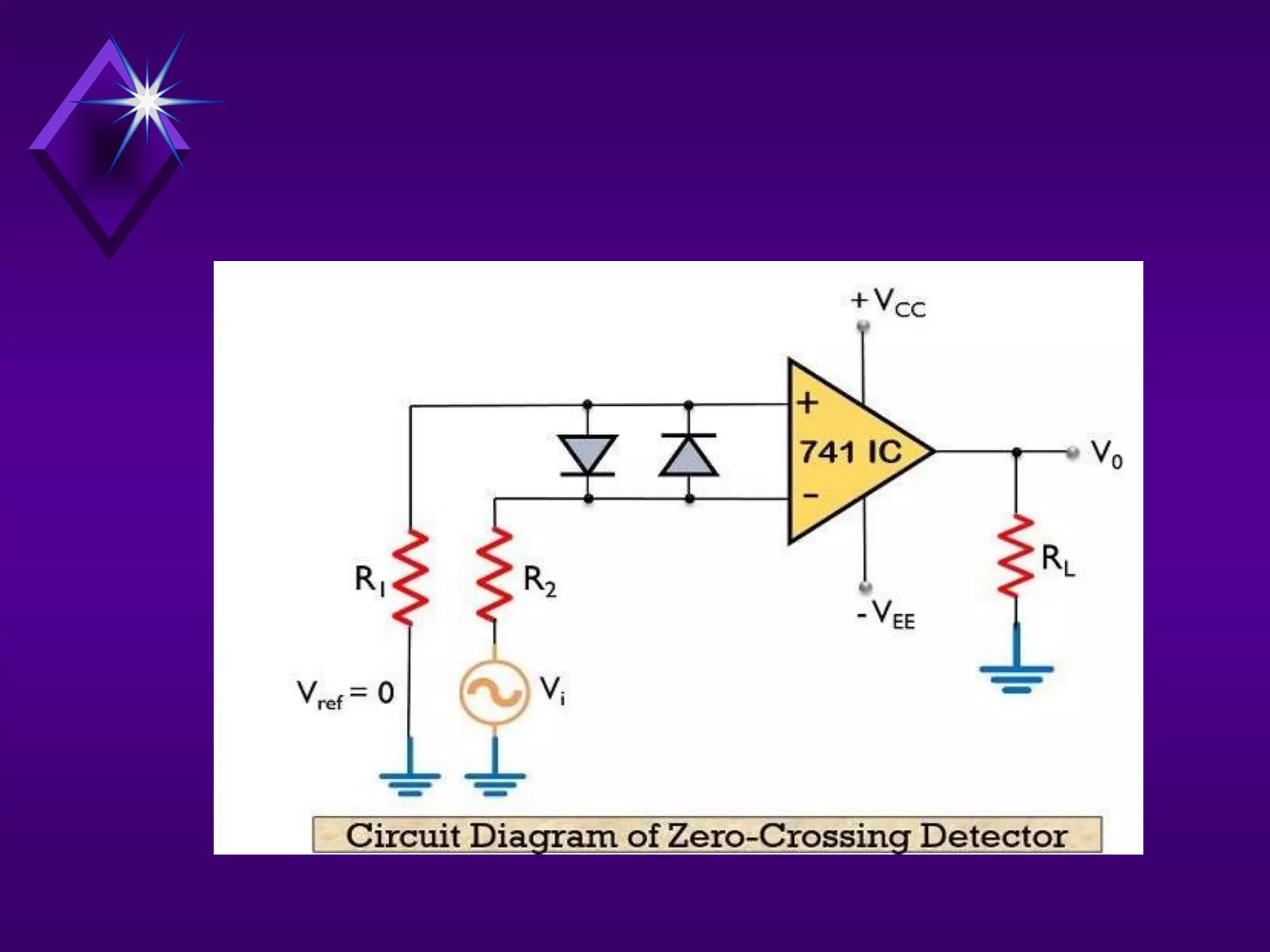
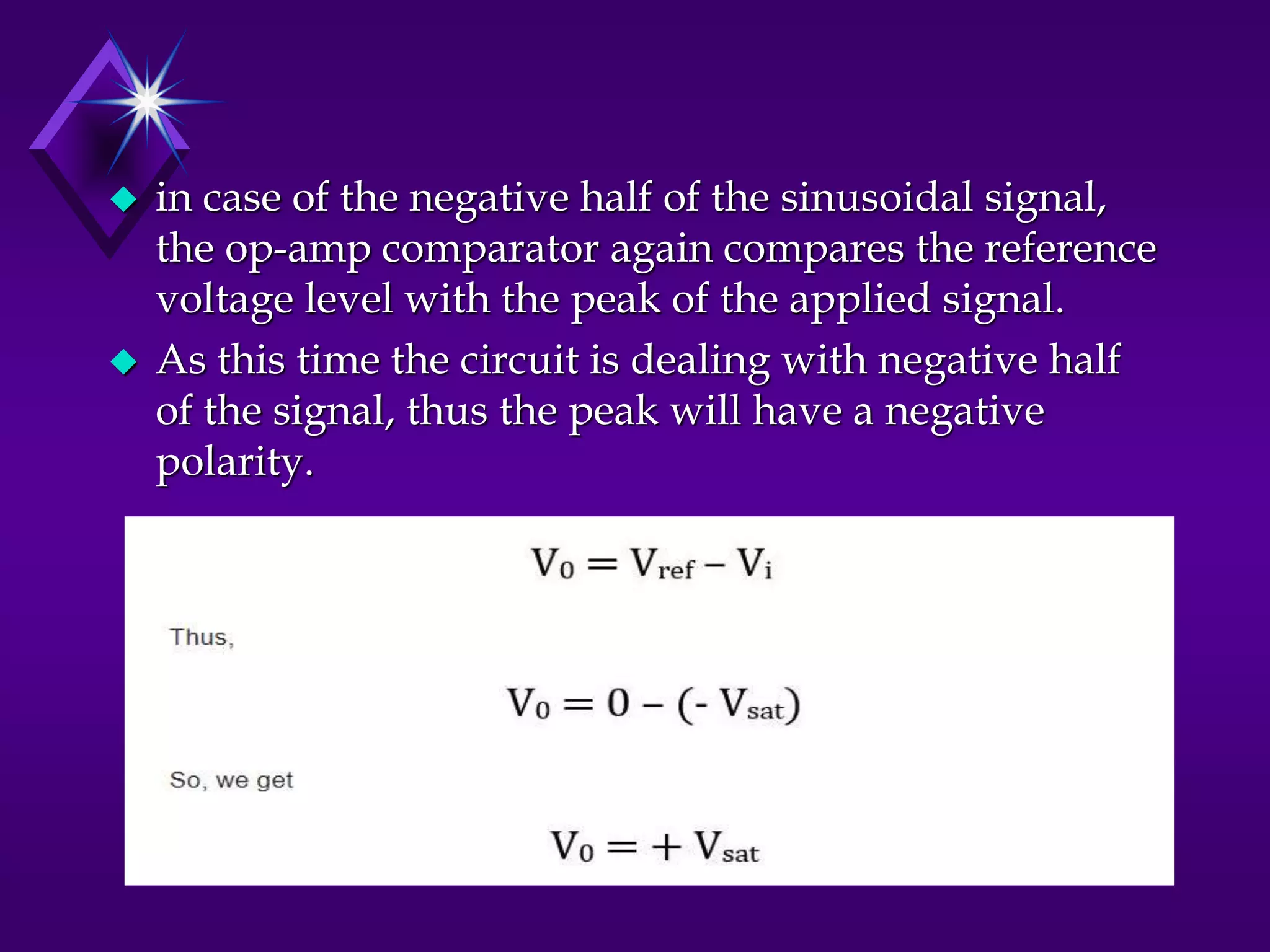
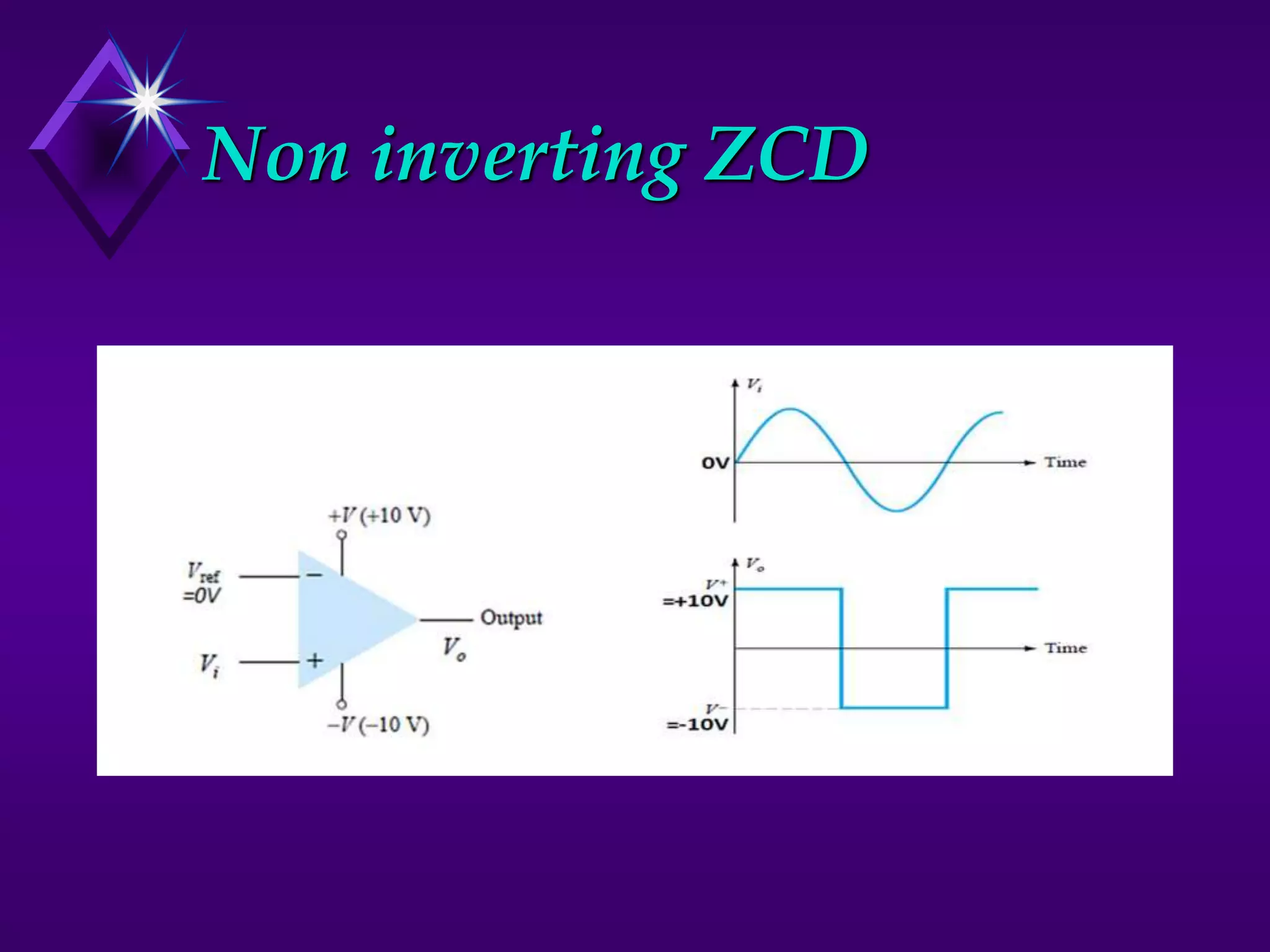
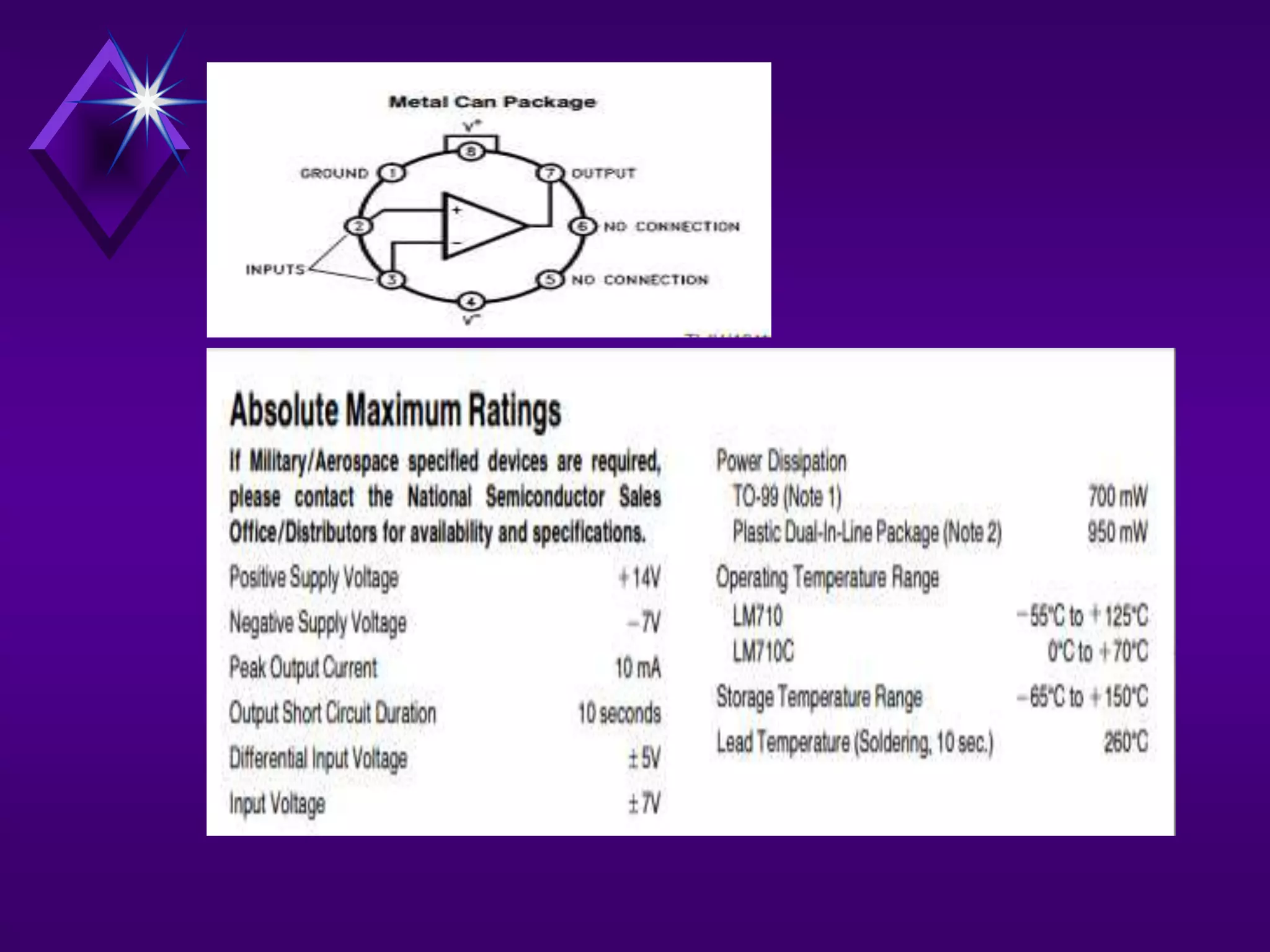
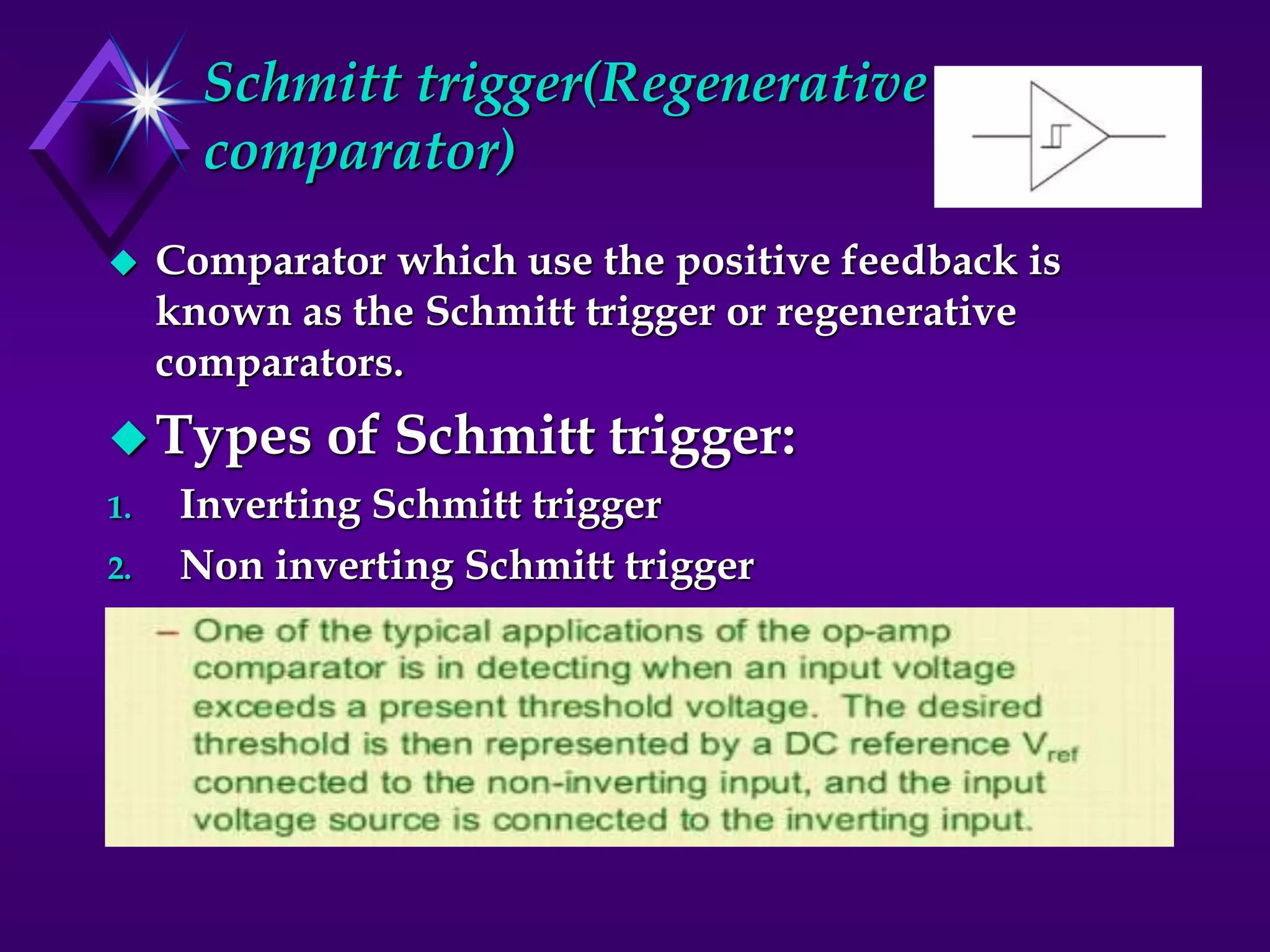
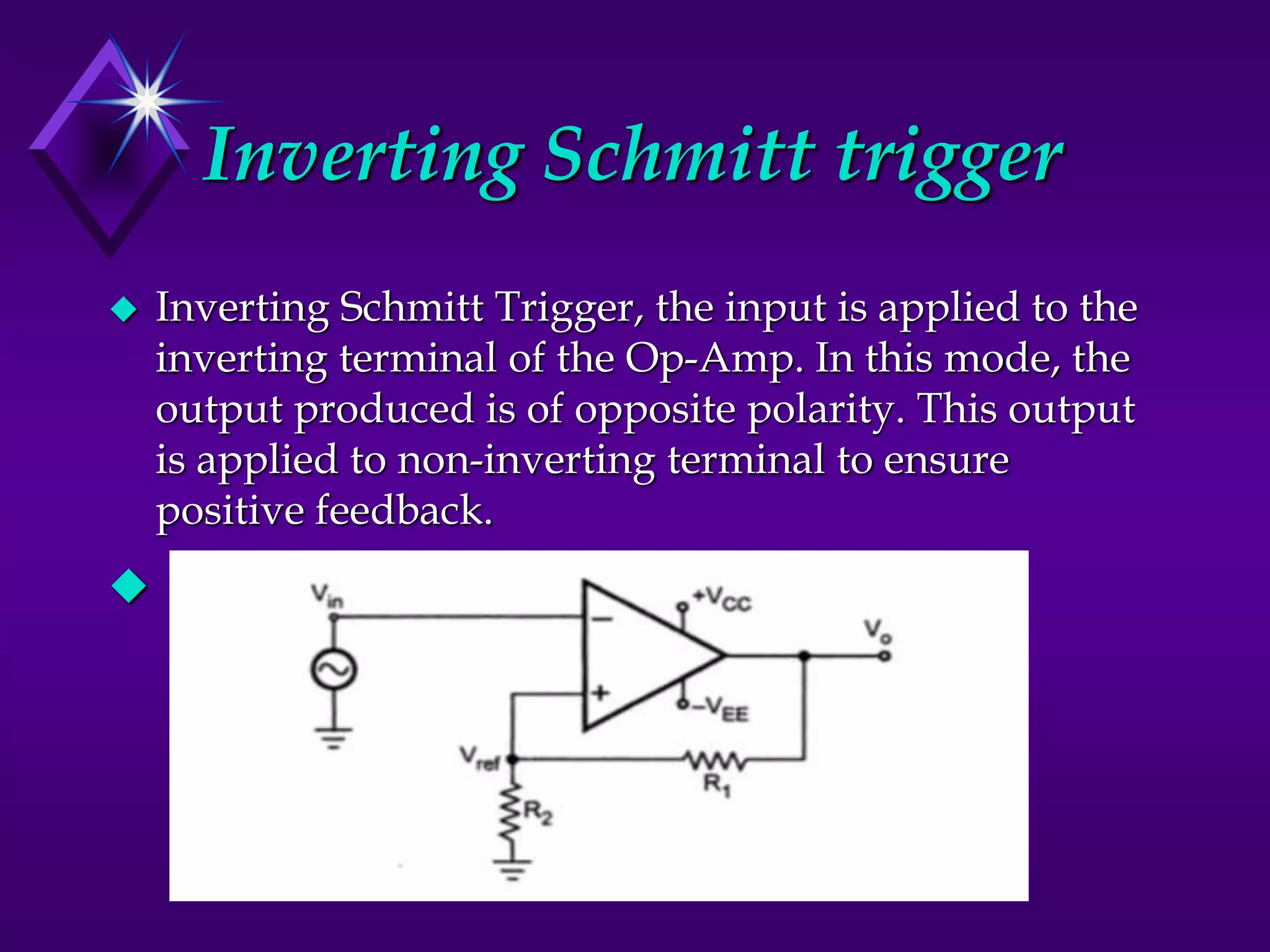
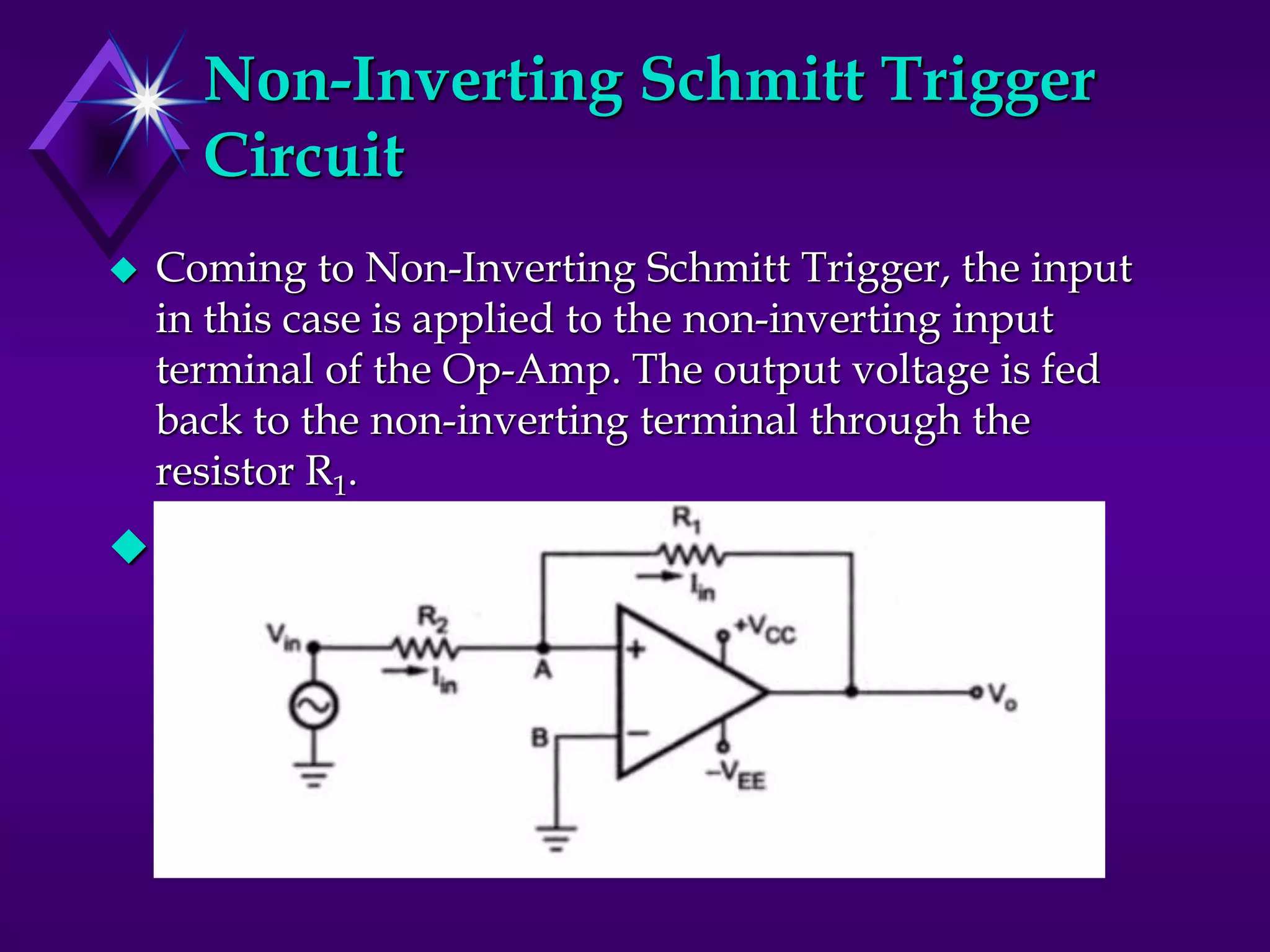
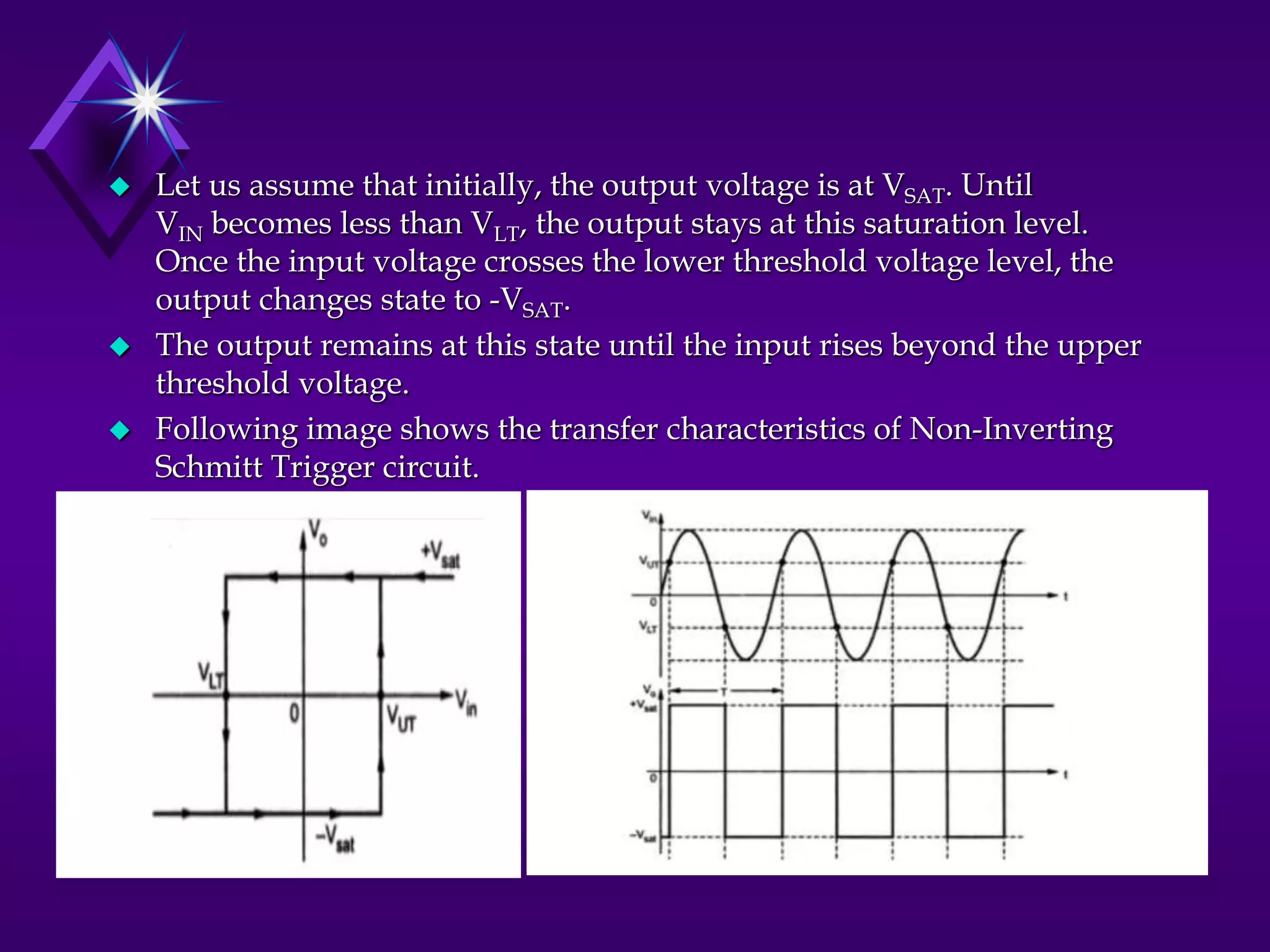
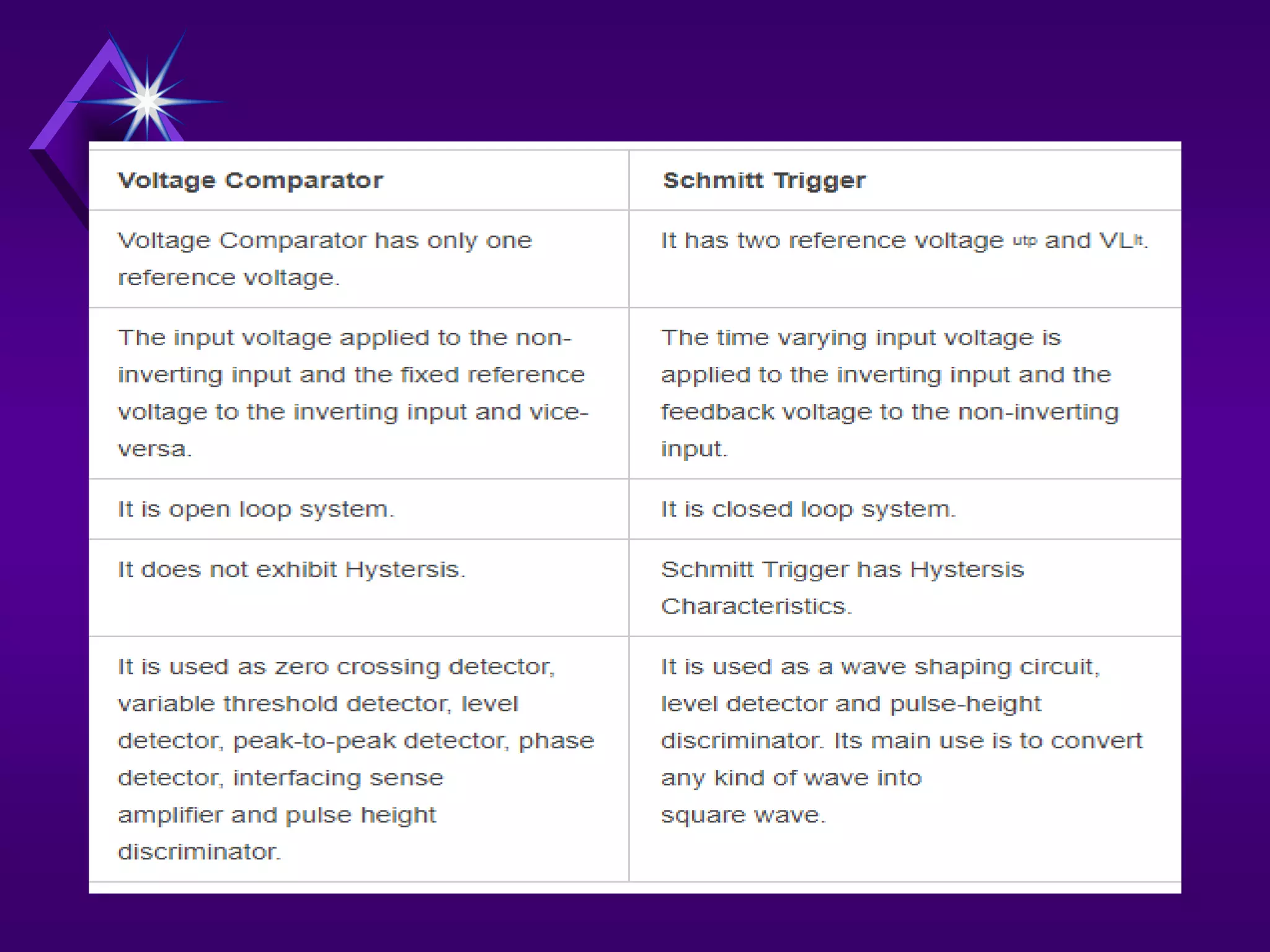
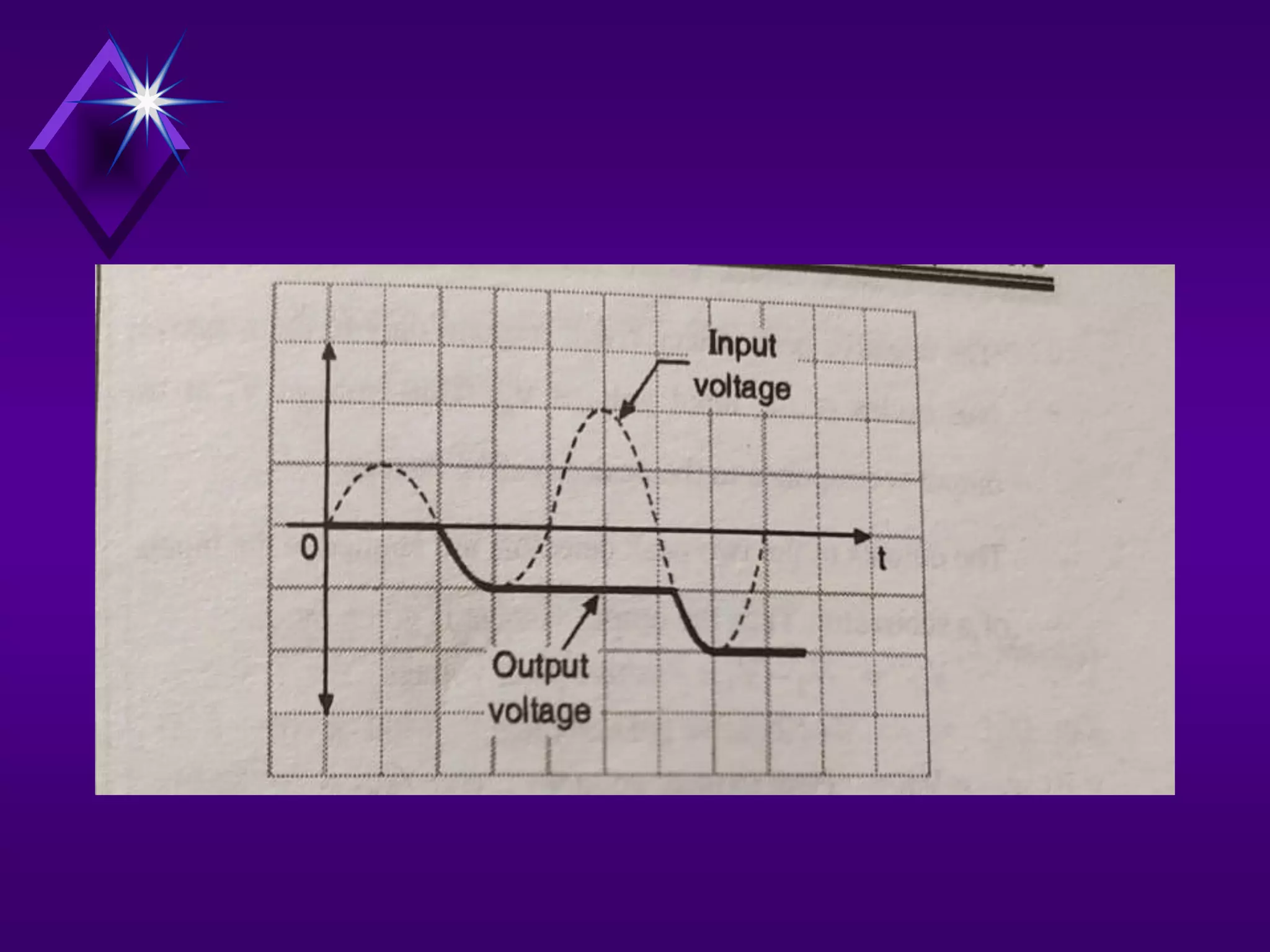
The document discusses different types of comparators and their applications. It begins by explaining how a comparator works by comparing an input signal voltage to a reference voltage. It then describes two types of comparators - non-inverting and inverting - based on which input terminal receives the signal. Several applications of comparators are listed including zero crossing detectors, window comparators, and Schmitt triggers. The document goes on to explain these applications in more detail and discusses other comparator topics such as hysteresis and integrated circuit comparators.