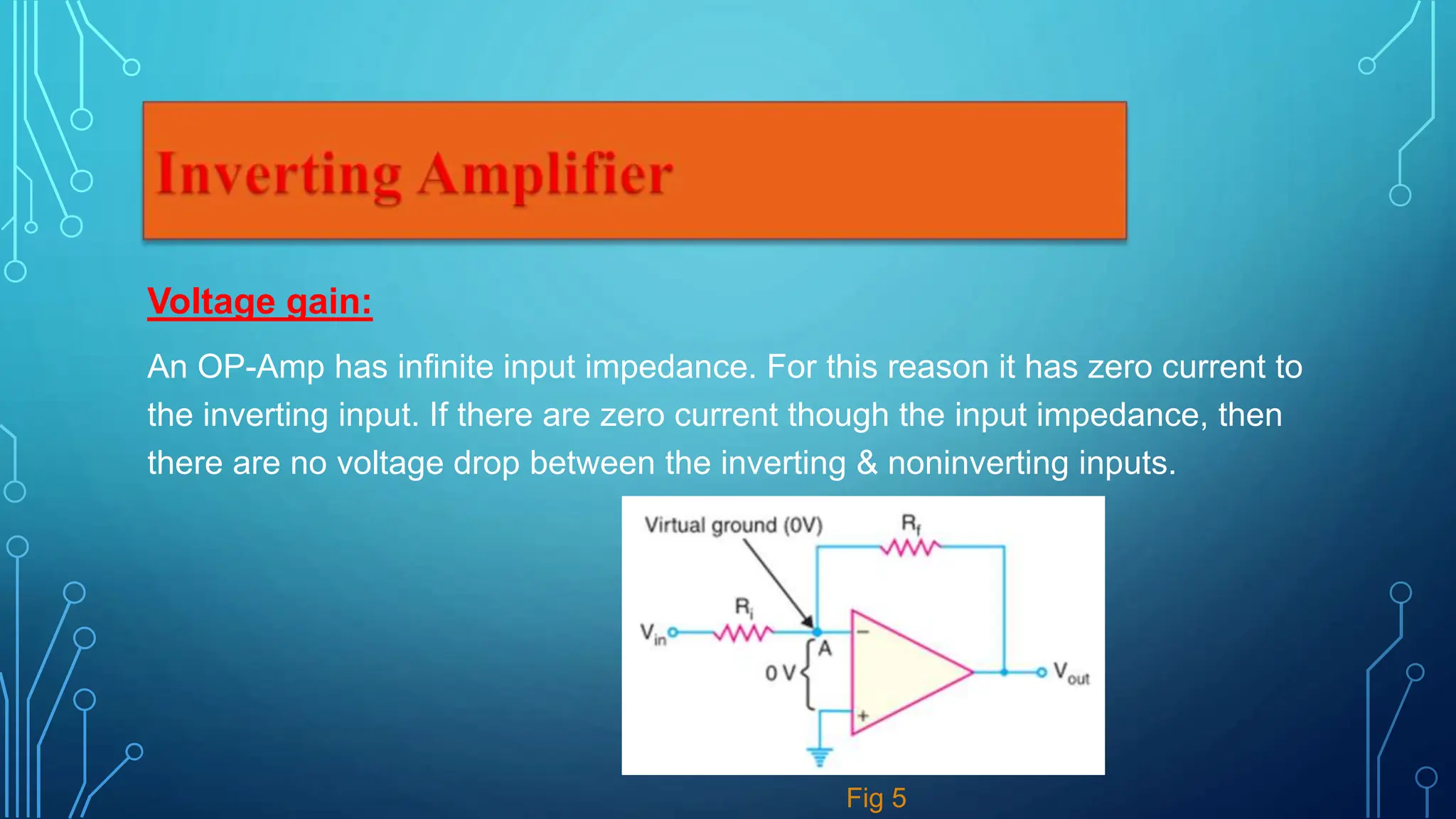
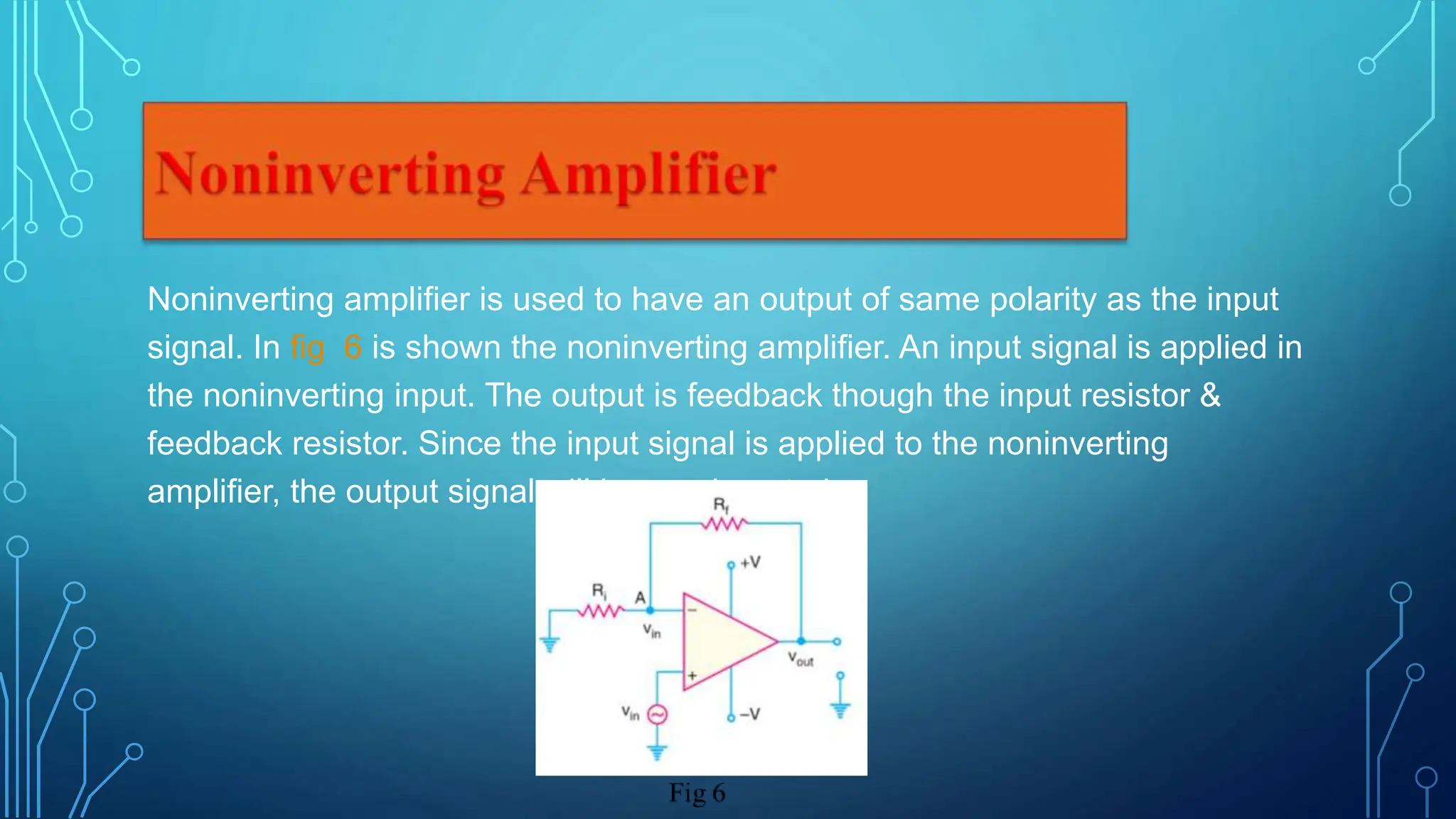
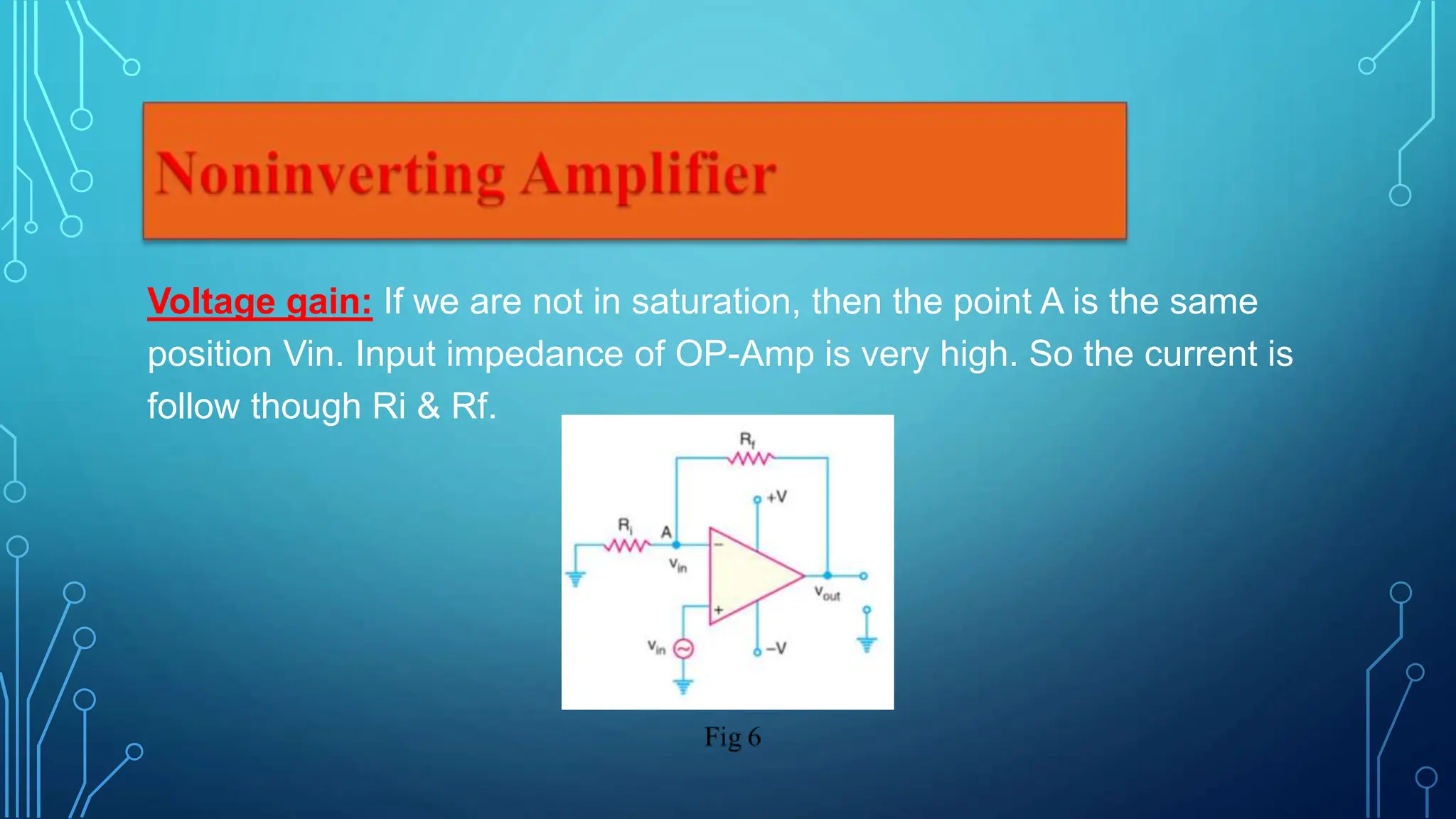
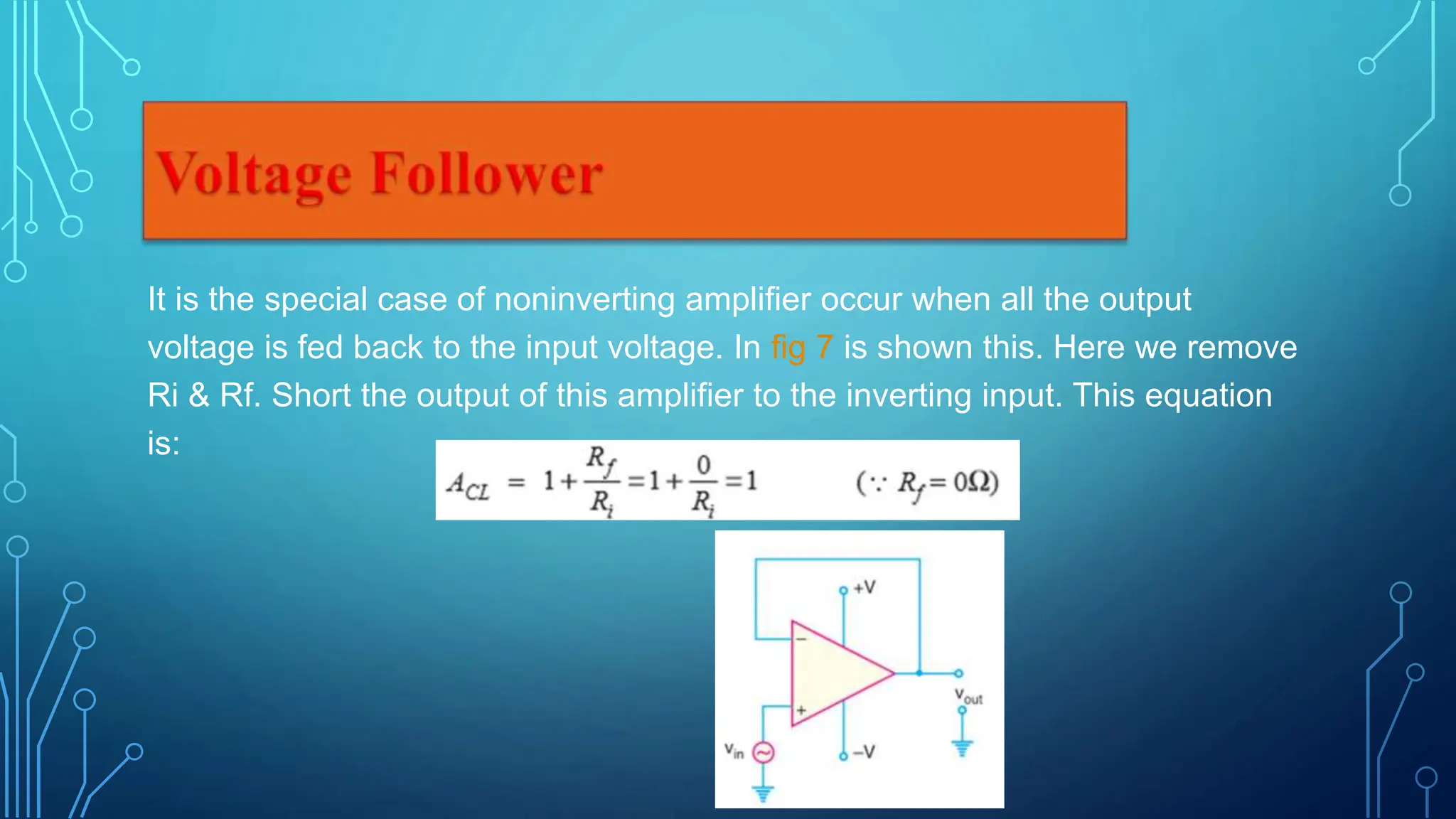
This document presents information about operational amplifiers including their components, properties, and applications. It discusses that an operational amplifier is a multistage amplifier with three stages: a differential amplifier input stage followed by a high gain CE amplifier and output stage. It also outlines some key properties of operational amplifiers like high input impedance, low output impedance, and ability to perform mathematical operations. Finally, it describes common applications of operational amplifiers such as inverting amplifiers, non-inverting amplifiers, and voltage followers.