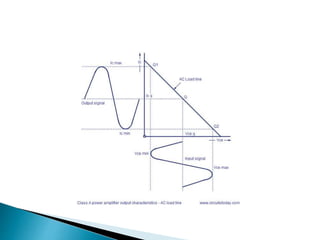
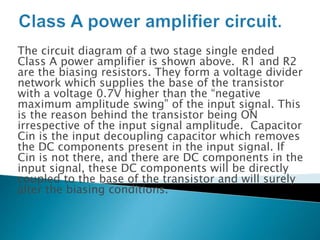
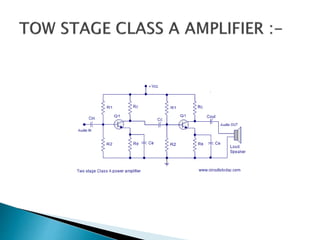
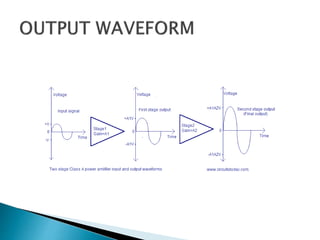
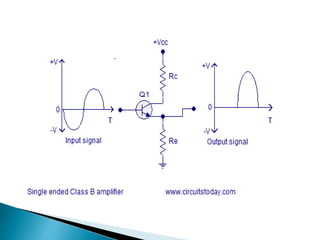
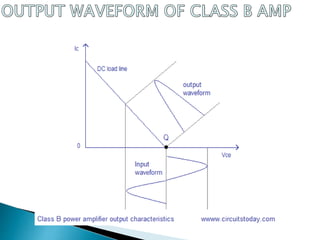
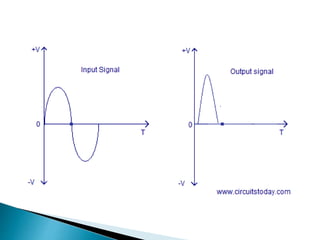
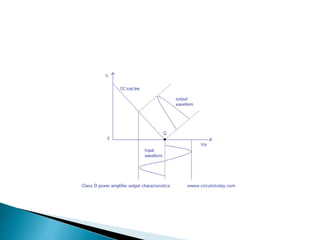
Class A power amplifiers have the transistor ON full time, resulting in high fidelity but poor efficiency. The output current flows for the entire input waveform cycle. Class B amplifiers have the transistor conducting for only half of the input cycle, improving efficiency to a maximum of 78.5% but introducing crossover distortion. Class C amplifiers have the transistor conducting for less than half of the input cycle, further improving efficiency to a maximum of 90% but causing significant distortion unsuitable for audio applications.