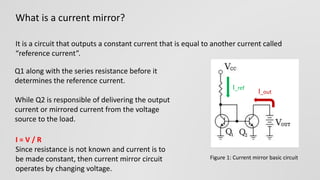
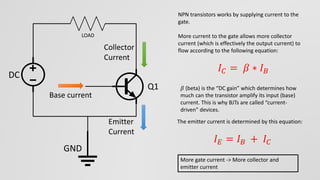
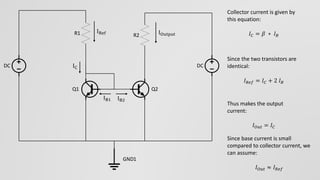
This document discusses current mirror circuits. It explains that a current mirror circuit outputs a constant current (I_out) that is equal to a reference current (I_ref) regardless of load or voltage variations. It works by using two identical transistors - one sets the reference current while the other mirrors it. Applications include requiring constant current, making multiple current sources from one, and stabilizing current against temperature changes.