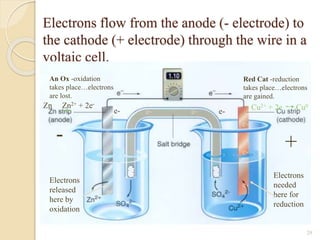
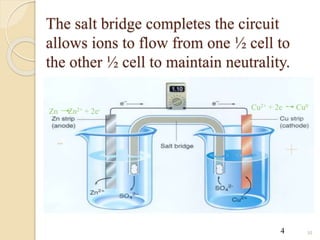
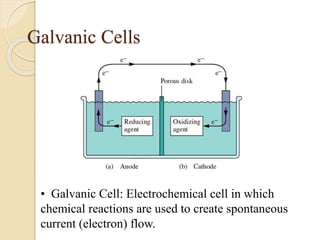
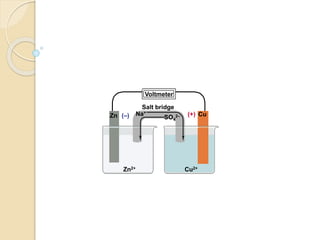
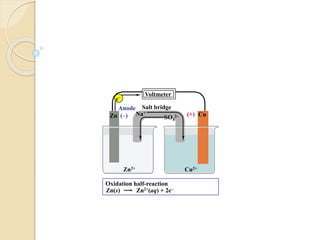
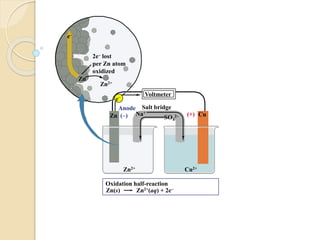
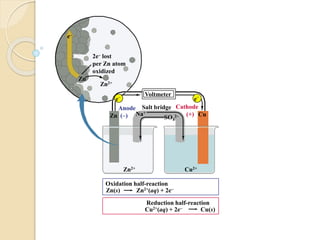
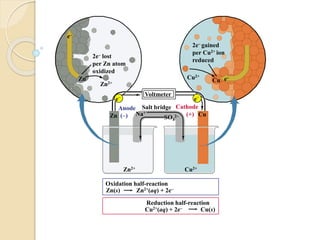
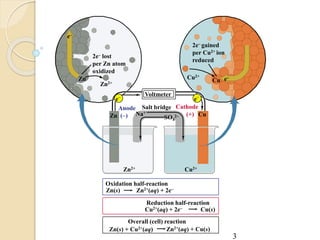
Arrhenius proposed the theory of electrolytic dissociation to explain the properties of electrolytic solutions. The theory states that when an electrolyte dissolves in water, it breaks up into ions - positively charged cations and negatively charged anions. This process is called ionization. Ions are constantly recombining and dissociating, reaching a state of dynamic equilibrium. The extent of ionization depends on an equilibrium constant. Strong electrolytes have a high equilibrium constant and ionize completely, while weak electrolytes have a low constant and only partially ionize.





![ Ions present in solution constantly re-unite to
form neutral molecules and, thus, there is a
state of dynamic equilibrium between the
ionized and non-ionized molecules.
[A+ ][B- ] /[AB] =K
K is known as ionization constant.
The electrolytes having high value of K are
termed strong electrolytes
those having low value of K as weak
electrolytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150318043634-conversion-gate01/85/B-tech-ii-engineering-chemistry-unit-5-A-electrochemistry-6-320.jpg)






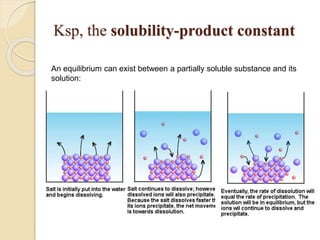
![For example:
BaSO4 (s) Ba2+ (aq) + SO4
2- (aq)
When writing the equilibrium constant
expression for the dissolution of BaSO4, we
remember that the concentration of a solid is
constant.
The equilibrium expression is therefore:
K = [Ba2+][SO4
2-]
K = Ksp, the solubility-product constant.
Ksp = [Ba2+][SO4
2-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150318043634-conversion-gate01/85/B-tech-ii-engineering-chemistry-unit-5-A-electrochemistry-16-320.jpg)
![The Solubility Expression
AaBb(s) aAb+ (aq) + bBa- (aq)
Ksp = [Ab+]a [Ba-]b
Example: PbI2 (s) Pb2+ + 2 I-
Ksp = [Pb2+] [I-]2
The greater the ksp the more soluble the solid
is in H2O.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-150318043634-conversion-gate01/85/B-tech-ii-engineering-chemistry-unit-5-A-electrochemistry-17-320.jpg)