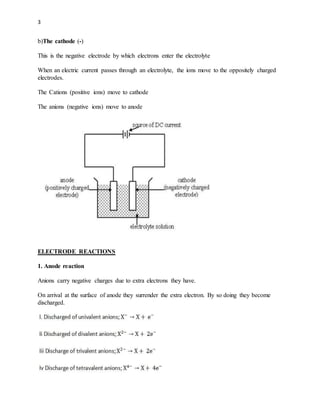
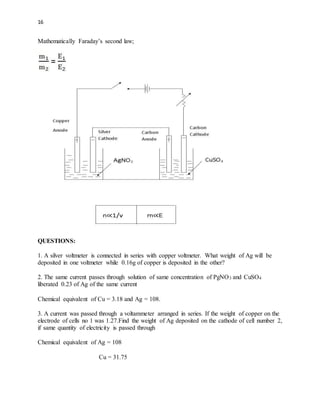
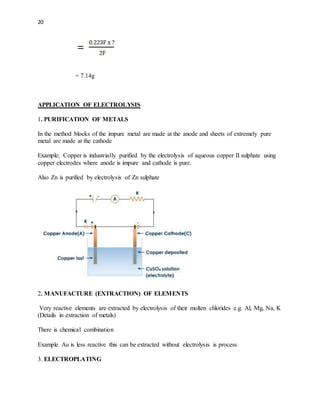
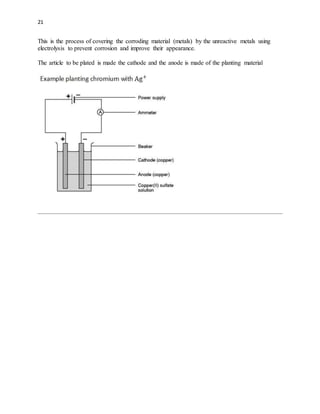
1) Electrolysis is the decomposition of electrolytes by the passage of an electric current through it. During electrolysis, ions move to the oppositely charged electrodes - cations to the cathode and anions to the anode.
2) At the anode, anions lose electrons in an oxidation reaction. At the cathode, cations gain electrons in a reduction reaction.
3) Which ion is discharged depends on factors like their position in the electrochemical series, concentration, and the electrode material. Ions higher in concentration or lower in the series will preferentially discharge.