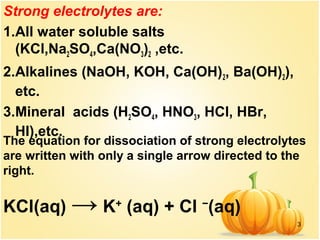
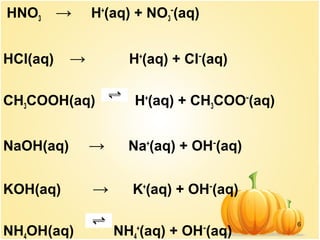
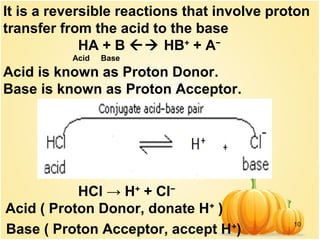
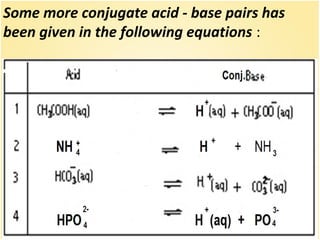
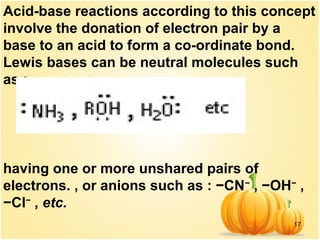
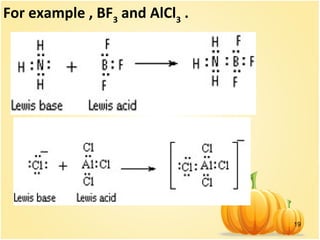
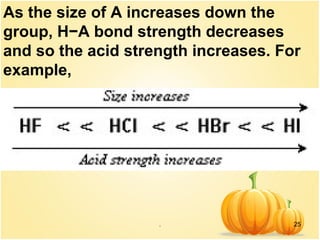
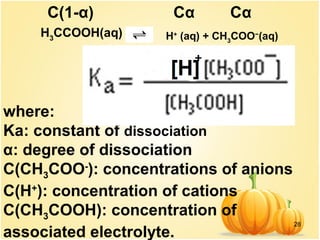
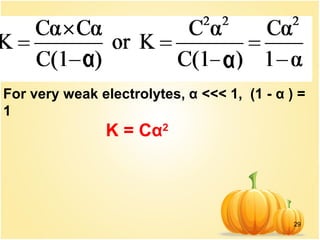
This document discusses various concepts related to ionic equilibrium in solution including strong and weak electrolytes, acid-base theories of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry, and Lewis. It defines strong electrolytes as completely dissociating in water and weak electrolytes as achieving an equilibrium between dissociated and undissociated molecules. Acids are defined as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors under the Bronsted-Lowry theory. The Lewis theory further defines acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as electron pair donors. Dissociation constants and factors affecting acid strength are also covered.





















![32
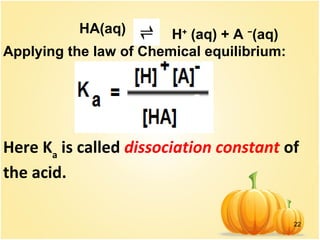
Applying the Law of mass action to the second
equilibrium,
where K is the equilibrium constant and [AB] is the
concentration of the dissolved salt. Cross
multiplying we get
K[AB] = [A+
] [B−
]
Since the solution is saturated , the concentration of
the dissolved salt remains constant at a fixed
temperature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4ionicsolutions-151203094115-lva1-app6892/85/4-ionic-solutions-32-320.jpg)
![. 33
Hence . [A+
] [B−
]= K × Constant = KSp
where KSp
is another
constant. This constant K sp is known as the solubility
product of the electrolyte. It is the maximum value of product
of concentrations of the ions of the electrolyte.
In the case of silver chloride, we have :
AgCl Ag+
+ Cl−
KSp = [Ag+
] [Cl−
]
In general , for any sparingly soluble salt Ax By which
dissociates to set up the equilibrium :
Ax
By x Ay+
y Bx−](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4ionicsolutions-151203094115-lva1-app6892/85/4-ionic-solutions-33-320.jpg)
![34
where Ay+
and Bx−
denote the positive and
negative ions , x and y represent the number
of these ions in the formula of the electrolyte.
The solubility product constant may be
expressed as :
KSp = [Ay+
]x
[Bx−
]y
Thus solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt at a
given temperature may be defined as the product of
the concentrations of its ions in the saturated
solution, with each concentration term raised to the
power equal to the number of times the ion occurs
in the equation representing the dissociation of the
electrolyte.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4ionicsolutions-151203094115-lva1-app6892/85/4-ionic-solutions-34-320.jpg)
![35
KSp = [A+
] [B−
] = S × S = S2
Suppose at a particular temperature its solubility is
S mol L−1
. S moles of salt on ionisation give S moles
of A+
and S moles of B−
ions.
AB A+
(aq) + B−
(aq)
In general , for any sparingly soluble salt A x B y
which dissociates to set up the equilibrium :
Ax By In general , for any sparingly
soluble salt A x B y which dissociates to set up the
equilibrium :
Ax By
x Ay+
y Bx−
[Ay+
] = x S and [Bx−
] = y S](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4ionicsolutions-151203094115-lva1-app6892/85/4-ionic-solutions-35-320.jpg)
![36
KSp =[x S]x
[y S ]y
= xx
yy
S(x+y)
The concept of solubility product principle helps us to predict
whether a salt will precipitate or not.
Precipitation occurs : if calculated ionic product > K sp
No precipitation : if calculated ionic product < KSp
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4ionicsolutions-151203094115-lva1-app6892/85/4-ionic-solutions-36-320.jpg)
