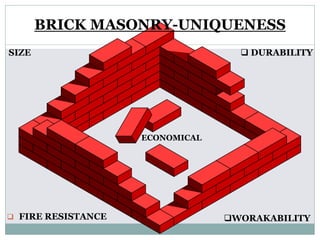
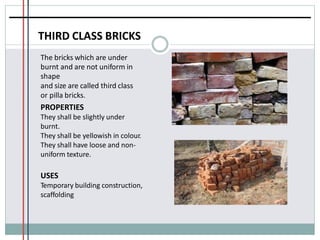
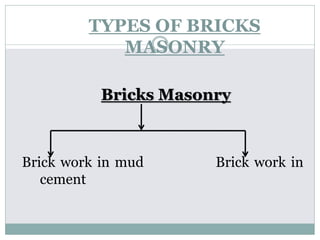
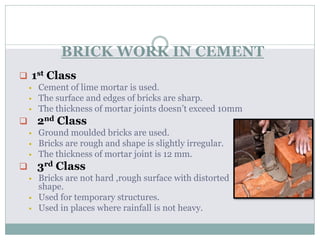
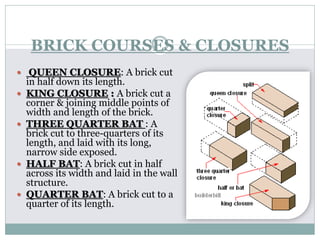
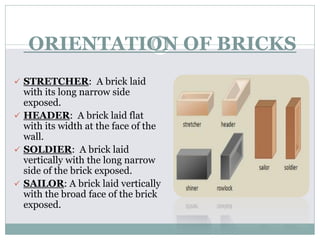
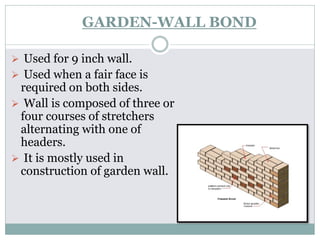
The document outlines the characteristics and types of bricks used in masonry, including sundried and burnt bricks, along with their classifications and uses. It details the advantages of brick masonry, such as fire resistance and durability, and discusses various brick bonding techniques and quality standards. Additionally, it addresses potential defects in brick masonry and the necessary tests to ensure the quality and strength of bricks.